机器翻译及其相关技术
机器翻译是指将⼀段⽂本从⼀种语⾔⾃动翻译到另⼀种语⾔。机器翻译用到了循环神经网络,但因为⼀段⽂本序列在不同语⾔中的⻓度不 ⼀定相同,比如输入是"I am chinese"机器翻译后输出是“我是中国人”,此时的输入是需要3个神经元而输出需要5个,长度是不同的,因此又不能用传统的循环神经网络。
导入包
import os
import sys
sys.path.append('/home/kesci/input/d2l9528/')
import collections
import d2l
import zipfile
from d2l.data.base import Vocab
import time
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils import data
from torch import optim
数据集处理
进行数据清洗,将其转化为神经网络的输入minbatch
with open('/home/kesci/input/fraeng6506/fra.txt', 'r') as f:
raw_text = f.read()
print(raw_text[0:1000])
此数据集是法语和英语的翻译,结果如下图所示,每一行是一个句子。
句子先是一个英语,标点符号,空格,法语,标点符号,还有其他的不需要的。
Go. Va ! CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #2877272 (CM) & #1158250 (Wittydev)
Hi. Salut ! CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #538123 (CM) & #509819 (Aiji)
Hi. Salut. CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #538123 (CM) & #4320462 (gillux)
Run! Cours ! CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #906328 (papabear) & #906331 (sacredceltic)
Run! Courez ! CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #906328 (papabear) & #906332 (sacredceltic)
Who? Qui ? CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #2083030 (CK) & #4366796 (gillux)
Wow! Ça alors ! CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #52027 (Zifre) & #374631 (zmoo)
Fire! Au feu ! CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #1829639 (Spamster) & #4627939 (sacredceltic)
Help! À l'aide ! CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #435084 (lukaszpp) & #128430 (sysko)
Jump. Saute. CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #631038 (Shishir) & #2416938 (Phoenix)
Stop! Ça suffit ! CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tato
首先要去掉乱码,大小写
def preprocess_raw(text):
text = text.replace('\u202f', ' ').replace('\xa0', ' ')
out = ''
for i, char in enumerate(text.lower()):
if char in (',', '!', '.') and i > 0 and text[i-1] != ' ':
out += ' '
out += char
return out
text = preprocess_raw(raw_text)
print(text[0:1000])
结果如下:
和上面的结果相比,全部转换了小写字母且单词和标点符号之间加了空格。
go . va ! cc-by 2 .0 (france) attribution: tatoeba .org #2877272 (cm) & #1158250 (wittydev)
hi . salut ! cc-by 2 .0 (france) attribution: tatoeba .org #538123 (cm) & #509819 (aiji)
hi . salut . cc-by 2 .0 (france) attribution: tatoeba .org #538123 (cm) & #4320462 (gillux)
run ! cours ! cc-by 2 .0 (france) attribution: tatoeba .org #906328 (papabear) & #906331 (sacredceltic)
run ! courez ! cc-by 2 .0 (france) attribution: tatoeba .org #906328 (papabear) & #906332 (sacredceltic)
who? qui ? cc-by 2 .0 (france) attribution: tatoeba .org #2083030 (ck) & #4366796 (gillux)
wow ! ça alors ! cc-by 2 .0 (france) attribution: tatoeba .org #52027 (zifre) & #374631 (zmoo)
fire ! au feu ! cc-by 2 .0 (france) attribution: tatoeba .org #1829639 (spamster) & #4627939 (sacredceltic)
help ! à l'aide ! cc-by 2 .0 (france) attribution: tatoeba .org #435084 (lukaszpp) & #128430 (sysko)
jump . saute . cc-by 2 .0 (france) attribution: tatoeba .org #631038 (shishir) & #2416938 (phoenix)
stop ! ça suffit ! cc-b
字符在计算机里是以编码的形式存在,我们通常所用的空格是 \x20 ,是在标准ASCII可见字符 0x20~0x7e 范围内。 而 \xa0 属于 latin1 (ISO/IEC_8859-1)中的扩展字符集字符,代表不间断空白符nbsp(non-breaking space),超出gbk编码范围,是需要去除的特殊字符。再数据预处理的过程中,我们首先需要对数据进行清洗。对数据进行清洗完成后需要进行分词。
分词
分词是将字符串分为单词组成的列表。
num_examples = 50000
source, target = [], []#sorce代表的英语的列表,target代表法语的列表
for i, line in enumerate(text.split('\n')):#每一行作为划分
if i > num_examples:
break
parts = line.split('\t')
if len(parts) >= 2:
source.append(parts[0].split(' '))#空格把每个单词分开
target.append(parts[1].split(' '))
source[0:3], target[0:3]
输出的结果为,我们已经得到了英语单词构成的一个列表,法语单词构成的一个列表
([['go', '.'], ['hi', '.'], ['hi', '.']],#英语的列表
[['va', '!'], ['salut', '!'], ['salut', '.']])#法语的列表
建立词典
下面我们为英语和法语建立词典。即单词组成的列表---单词id组成的列表
第一步是取出所有单词,即把所有单词连接成一个单词列表(不去重,不做其他任何处理)。
def build_vocab(tokens):
tokens = [token for line in tokens for token in line]
return d2l.data.base.Vocab(tokens, min_freq=3, use_special_tokens=True)#Vocab类
src_vocab = build_vocab(source)#英语中单词列表的个数
len(src_vocab)
class Vocab(object):#Rhis class is saved in d2l
def __init__(self, tokens, min_freq=0, use_special_tokens=False):
#sort by frequency and token
counter = collections.Counter(tokens)
token_freqs = sorted(counter.items(), key = lambda x:x[0])
token_freqs.sort(key = lambda x:x[1], reserved = True)
if use_special_tokens:
#padding, begin of sentence, end of sentence, unknown
self.pad, self.bos, self.eos, self.unk = (0,1,2,3)
tokens = ['', '', '', '']
else:
self.unk = 0
tokens = ['']
tokens += [token for token, freq in token_freqs if freq >= min_freq]
self.idx_to_token = []
self.token_to_idx = dict()
for token in tokens:
self.idx_to_token.append(token)
self.token_to_idx[token]=len(self.idx_to_token)-1
def __len__(self):#单词表的长度(单词的个数)
return len(self.idx_to_token)
def __getitem__(self, tokens):#输入一个单词列表,输出其对应的id
if not isinstance(tokens, (list, tuple)):
return self.token_to_idx.get(tokens, self.unk)
else:
return [self.__getitem__(token) for token in tokens]
3789
载入数据集
def pad(line, max_len, padding_token):#保证输入的时候句子的长度是一样的,
if len(line) > max_len:#如果一段话比maxlen长就将后面的删除
return line[:max_len]
return line + [padding_token] * (max_len - len(line))
pad(src_vocab[source[0]], 10, src_vocab.pad)#不足的进行补足
[38, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
def build_array(lines, vocab, max_len, is_source):
lines = [vocab[line] for line in lines]
if not is_source:#如果是target句子
lines = [[vocab.bos] + line + [vocab.eos] for line in lines]#判断开始和结束
array = torch.tensor([pad(line, max_len, vocab.pad) for line in lines])
valid_len = (array != vocab.pad).sum(1) #第一个维度,保存其原本的长度不是padding后的长度
return array, valid_len
def load_data_nmt(batch_size, max_len): # This function is saved in d2l.
src_vocab, tgt_vocab = build_vocab(source), build_vocab(target)#生成词典
src_array, src_valid_len = build_array(source, src_vocab, max_len, True)#英语
tgt_array, tgt_valid_len = build_array(target, tgt_vocab, max_len, False)#法语
train_data = data.TensorDataset(src_array, src_valid_len, tgt_array, tgt_valid_len)
train_iter = data.DataLoader(train_data, batch_size, shuffle=True)
return src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter
src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter = load_data_nmt(batch_size=2, max_len=8)#数据生成器
for X, X_valid_len, Y, Y_valid_len, in train_iter:
print('X =', X.type(torch.int32), '\nValid lengths for X =', X_valid_len,
'\nY =', Y.type(torch.int32), '\nValid lengths for Y =', Y_valid_len)
break
X = tensor([[ 5, 24, 3, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 12, 1388, 7, 3, 4, 0, 0, 0]], dtype=torch.int32)
Valid lengths for X = tensor([4, 5])
Y = tensor([[ 1, 23, 46, 3, 3, 4, 2, 0],
[ 1, 15, 137, 27, 4736, 4, 2, 0]], dtype=torch.int32)
Valid lengths for Y = tensor([7, 7])
Encoder-Decoder
encoder:输入到隐藏状态
decoder:隐藏状态到输出
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Encoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def forward(self, X, *args):
raise NotImplementedError
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Decoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def init_state(self, enc_outputs, *args):
raise NotImplementedError
def forward(self, X, state):
raise NotImplementedError
Sequence to Sequence模型
训练:
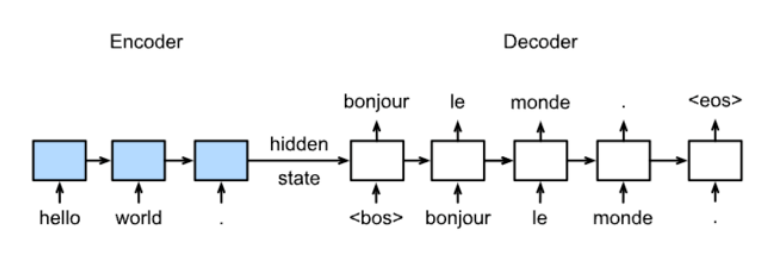
测试:

具体结构
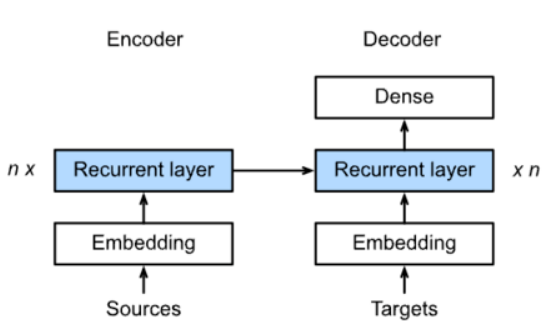
class Seq2SeqEncoder(d2l.Encoder):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers,
dropout=0, **kwargs):
super(Seq2SeqEncoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_hiddens=num_hiddens
self.num_layers=num_layers
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embed_size,num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout=dropout)
def begin_state(self, batch_size, device):
return [torch.zeros(size=(self.num_layers, batch_size, self.num_hiddens), device=device),
torch.zeros(size=(self.num_layers, batch_size, self.num_hiddens), device=device)]
def forward(self, X, *args):
X = self.embedding(X) # X shape: (batch_size, seq_len, embed_size)
X = X.transpose(0, 1) # RNN needs first axes to be time
# state = self.begin_state(X.shape[1], device=X.device)
out, state = self.rnn(X)
# The shape of out is (seq_len, batch_size, num_hiddens).
# state contains the hidden state and the memory cell
# of the last time step, the shape is (num_layers, batch_size, num_hiddens)
return out, state
encoder = Seq2SeqEncoder(vocab_size=10, embed_size=8,num_hiddens=16, num_layers=2)
X = torch.zeros((4, 7),dtype=torch.long)
output, state = encoder(X)
output.shape, len(state), state[0].shape, state[1].shape
class Seq2SeqDecoder(d2l.Decoder):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers,
dropout=0, **kwargs):
super(Seq2SeqDecoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embed_size,num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout=dropout)
self.dense = nn.Linear(num_hiddens,vocab_size)
def init_state(self, enc_outputs, *args):
return enc_outputs[1]
def forward(self, X, state):
X = self.embedding(X).transpose(0, 1)
out, state = self.rnn(X, state)
# Make the batch to be the first dimension to simplify loss computation.
out = self.dense(out).transpose(0, 1)
return out, state
decoder = Seq2SeqDecoder(vocab_size=10, embed_size=8,num_hiddens=16, num_layers=2)
state = decoder.init_state(encoder(X))
out, state = decoder(X, state)
out.shape, len(state), state[0].shape, state[1].shape
损失函数
def SequenceMask(X, X_len,value=0):
maxlen = X.size(1)
mask = torch.arange(maxlen)[None, :].to(X_len.device) < X_len[:, None]
X[~mask]=value
return X
X = torch.tensor([[1,2,3], [4,5,6]])
SequenceMask(X,torch.tensor([1,2]))
X = torch.ones((2,3, 4))
SequenceMask(X, torch.tensor([1,2]),value=-1)
class MaskedSoftmaxCELoss(nn.CrossEntropyLoss):
# pred shape: (batch_size, seq_len, vocab_size)
# label shape: (batch_size, seq_len)
# valid_length shape: (batch_size, )
def forward(self, pred, label, valid_length):
# the sample weights shape should be (batch_size, seq_len)
weights = torch.ones_like(label)
weights = SequenceMask(weights, valid_length).float()
self.reduction='none'
output=super(MaskedSoftmaxCELoss, self).forward(pred.transpose(1,2), label)
return (output*weights).mean(dim=1)
loss = MaskedSoftmaxCELoss()
loss(torch.ones((3, 4, 10)), torch.ones((3,4),dtype=torch.long), torch.tensor([4,3,0]))
训练:
def train_ch7(model, data_iter, lr, num_epochs, device): # Saved in d2l
model.to(device)
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss = MaskedSoftmaxCELoss()
tic = time.time()
for epoch in range(1, num_epochs+1):
l_sum, num_tokens_sum = 0.0, 0.0
for batch in data_iter:
optimizer.zero_grad()
X, X_vlen, Y, Y_vlen = [x.to(device) for x in batch]
Y_input, Y_label, Y_vlen = Y[:,:-1], Y[:,1:], Y_vlen-1
Y_hat, _ = model(X, Y_input, X_vlen, Y_vlen)
l = loss(Y_hat, Y_label, Y_vlen).sum()
l.backward()
with torch.no_grad():
d2l.grad_clipping_nn(model, 5, device)
num_tokens = Y_vlen.sum().item()
optimizer.step()
l_sum += l.sum().item()
num_tokens_sum += num_tokens
if epoch % 50 == 0:
print("epoch {0:4d},loss {1:.3f}, time {2:.1f} sec".format(
epoch, (l_sum/num_tokens_sum), time.time()-tic))
tic = time.time()
embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout = 32, 32, 2, 0.0
batch_size, num_examples, max_len = 64, 1e3, 10
lr, num_epochs, ctx = 0.005, 300, d2l.try_gpu()
src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter = d2l.load_data_nmt(batch_size, max_len,num_examples)
encoder = Seq2SeqEncoder(len(src_vocab), embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout)
decoder = Seq2SeqDecoder(len(tgt_vocab), embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout)
model = d2l.EncoderDecoder(encoder, decoder)
train_ch7(model, train_iter, lr, num_epochs, ctx)
测试:
def translate_ch7(model, src_sentence, src_vocab, tgt_vocab, max_len, device):
src_tokens = src_vocab[src_sentence.lower().split(' ')]
src_len = len(src_tokens)
if src_len ' + translate_ch7(
model, sentence, src_vocab, tgt_vocab, max_len, ctx))
参考:
https://www.kesci.com/org/boyuai/workspace/project
作者:Dxy17