复旦大学计算机学院研究生复试机试题
(不保证代码完全正确,自己敲的可能存在不完善的地方,请各位大佬发现后指出,谢谢!)
未完待续
1、
题目:
输入日期格式:YYYYMMDD,求与 20190205 相隔的天数。
输入:
20190208
输出:
3
解析:
运用Java的日期类来解决。
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.text.*;
public class test19_01 {
public static Date parseDate(String date) throws ParseException{
if(date.isEmpty()){ // 将字符串转化为日期格式
return null;
}
return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd").parse(date);
}
public static int differentDaysByString(String date1,String date2) throws ParseException
{
// 计算相差天数
int days = (int) ((parseDate(date2).getTime() - parseDate(date1).getTime()) / (1000*3600*24));
return days;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String s1 = "20190205";
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String s2 = scanner.next();
System.out.println(differentDaysByString(s1, s2));
}
}
2、
题目:
给定一个数字序列 A1,A2…An,求 i,j(1<=i<=j<=n),使得 Ai+…+Aj 最大,输出这个最大和。
输入:
6
-2 11 -4 13 -5 -2
输出:
20
解析:
dp问题,求最长连续子序列。(尝试复习用java写了,c++也一样)
import java.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.swing.plaf.basic.BasicInternalFrameTitlePane.MaximizeAction;
public class test19_02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int[] A = new int[n+1];
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
A[i]=scanner.nextInt(); // 读取数组
}
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
int ans=A[1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
dp[i]=Math.max(A[i], dp[i-1]+A[i]); // 分两种情况,取第i个元素和不取
ans = Math.max(dp[i], ans);
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
3、题目:求 N 个结点能够组成的二叉树的个数。
输入:
3
输出:
5
解析:
这就是卡特兰数。之前在做408的时候,问n个元素入栈,有几种出栈情况。转化为以先序次序入栈,中序次序出栈,又因为先+中可唯一确定一棵二叉树。因此,出入栈情况就是对应的二叉树个数。注意要用大整数,因为要乘法。(不过不清楚n要不要用大整数)
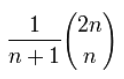
import java.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test19_03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 公式 (2n*2(n-1)*....*n)/(n*(n-1)*...*1)/(n+1) 就是卡特兰数
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=scanner.nextInt();
BigInteger n1 = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
n1=n1.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(n-i));
}
BigInteger n2 = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
n2 = n2.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(2*n-i));
}
BigInteger ans = n2.divide(n1).divide(BigInteger.valueOf(n+1));
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
2018上机题
1、
题目:
求众数。 众数就是一个序列中出现次数最多的数字。 如果不唯一,则输出小的那个值。 给定第一个代表有几个数字。 1<=n<=10^5 每个数字在 int 范围内。
输入:
8
10 3 8 8 3 2 2 2
输出:
2
解析:
这里要注意的是,可能有负数出现,所以不能直接用计数数组。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int n;
vector temp;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int d;
scanf("%d",&d);
temp.push_back(d); // 不用hash数组是因为可能有负数
}
sort(temp.begin(),temp.end()); // 题目要求从小输出,所以先排序
int MAX=-1,ans=temp[0];
int num=1;
for(int i=1;iMAX)
{
MAX=num;
ans=temp[i];
}
}else{
num=1;
}
}
printf("%d",ans);
return 0;
}
2、
题目:
解方程。 给定一个字符串,代表一个 一元一次 方程。 如果有解求解,输出格式“x=数字” ,如果解的个数无穷,输出 “infinite solutions”。 如果没有解输出“no solution”字符串长度不超过 256 。
输入:
10x-2x-8=4x+7+x
输出:
x=5
解析:
这题可能存在一点问题,因为题目没有说方程是否一定有意义,因此可能出现没有x、没有‘=’这样的情况。而且字符串长度不超过256位,可能会有超过int位数的情况。
总的思路就是,将方程化为AX+B=0的情况。因此方程的解:-B/A
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin,s);
string num="";
int xNum=0; // x前系数
int cNum=0; // 常数
bool you =false; // 表示到达等式右边
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
{
if(isdigit(s[i]))
{
num+=s[i];
if(i==s.length()-1)
{
stringstream ss;
ss<>inum;
if(you)
cNum-=inum;
else
cNum+=inum;
}
}else if(s[i]=='x')
{
if(num.empty() || num=="+"||num=="-")
num+='1';
stringstream ss;
ss <> inum;
if(you)
xNum-=inum;
else
xNum+=inum;
num.clear();
}else if((s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')&&!num.empty()){ // 此时是常数
stringstream ss;
ss<>inum;
if(you)
cNum-=inum;
else
cNum+=inum;
num.clear();
num+=s[i]; // 注意把此时的符号给加上
}else if((s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')&&num.empty())
{
num+=s[i];
}else if(s[i]=='='&&!num.empty()) // 等号前常数
{
stringstream ss;
ss<>inum;
if(you)
cNum-=inum;
else
cNum+=inum;
num.clear();
you=true;
}else if(s[i]=='=')
{
you=true;
}
}
if(xNum==0&&cNum!=0)
{
printf("no solution\n");
}else if(xNum==0&&cNum==0)
{
printf("infinite solutions\n");
}else{
cout<<"x="<<-cNum/xNum<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
3、
题目:
骨牌。 有 2xn 的地板,用 1x2 和 2x1 的骨牌进行铺地板。问共有多少种情况。 结果对 999983 取余 。 1<=n<=10000 。
输入:
6
输出:
13
解析:
找规律。
n=1时,只有1种情况。
n=2时,有2种情况。
n=3时,有3种情况,而且刚好是n=1与n=2的情况总和。
因此dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2]
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int M = 999983;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int dp[maxn];
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
dp[2]=2; //初始化
dp[1]=1;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++)
{
dp[i]=dp[i-2]+dp[i-1];
}
printf("%d",dp[n]%M);
return 0;
}
2017上机题
1、
题目:
给定一个整数序列,求中位数。
解析:
这题好像没有样例。就是先排序,然后找中位数。若n为奇数,就直接取中间的;若n为偶数,则取中间两个数之和的平均。(有点纠结,这个平均要不要保留小数啥的)
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int A[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&A[i]);
}
sort(A,A+n);
if(n%2==0)
{
printf("%.1f",1.0*(A[n/2]+A[n/2-1])/2);
}else{
printf("%d",A[n/2]);
}
return 0;
}
2、
题目:
给定一个 9 位数字的 ISBN,求其校验位。ISBN 格式为 2-02-033598,校验位的计算方法如下:从左到右依次将各位数字乘 10,9,8,……,2,求出其和 S,作模运算得 M=S mod11。若 11-M 在 1 和 9 之间,校验位即为该数字;若 11-M 等于 10,校验位为 X;11-M 等于11,校验位为 0。输出添加校验位的 ISBN,如 2-02-033598-0。
输入:
2-02-033598
输出:
2-02-033598-0
解析:
主要根据题目要求一步一步求出来即可。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin,s);
int sum=0;
int m;
int k=10;
for(int i=0;i=1&&d<=9)
{
cout<<s<<"-"<<d<<endl;
}else if(d==10)
{
cout<<s<<"-"<<"X"<<endl;
}else if(d==11)
{
cout<<s<<"-"<<"0"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
3、
题目:
一个无向图,定点为N个,其中M条边已经给定,现在要从K条备选边中选出若干条,使得整个图连通,且选出的边权值和最小。
解析:
这个就是求最小生成树。这里给出克鲁斯卡尔算法,用贪心+并查集的思想。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1010;
const int INF=1000000000;
int cost=0; // 边权之和
int num=0; // 记录边数
struct edge
{
int u,v;
int cost;
}E[maxn]; // 定义边集
bool cmp(edge a,edge b)
{
return a.cost<b.cost;
}
int father[maxn];
int findFather(int x)
{
int a=x;
while(x!=father[x])
{
x=father[x];
}
while(a!=father[a])
{
int z=a;
a=father[a];
father[z]=x;
}
return x;
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int u,v,c;
scanf("%d %d %d",&E[i].u,&E[i].v,&E[i].cost);
}
sort(E,E+m,cmp); // 边权从小到大排列
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) // 顶点范围0~n-1
{
father[i]=i;
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) // 遍历每条边
{
int faU=findFather(E[i].u);
int faV=findFather(E[i].v);
if(faU!=faV)
{
cost+=E[i].cost;
father[faU]=faV;
num++;
if(num==n-1) break;
}
}
if(num!=n-1) printf("无法找到最小生成树"); //这个是自己加的,题目没要求。。。
else printf("%d",cost);
return 0;
}
2016上机题
1、
题目:
给定两个字符串,求最大公共子串的长度。
输入:
fdfdfd42543
232fdfdfdjlkj
输出:
6
解析:
是经典的dp问题。这里注意子串和子序列的区别。子串:必须是连续的;子序列:可以不连续。
dp[i][j]表示s1中0~i-1和s2中0 ~j-1的最大公共子串长度。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1010;
int main()
{
string s1,s2;
getline(cin,s1);
getline(cin,s2);
int len1=s1.length();
int len2=s2.length();
int dp[len1][len2];
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
int ans=-1;
for(int i=0;i<len1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<len2;j++)
{
if(s1[i]==s2[j])
{
if(i==0||j==0)
{
dp[i][j]=1;
}else{
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
}
ans=max(ans,dp[i][j]);
}
}
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
2、
题目:
给定一个后缀序列,要求求值,只有加减运算。
输入:
23+1+
输出:
6
解析:
根据后缀序列的计算规则:建一个栈,依次读字符串。读到数字就入栈,若读到运算符op,就依次出栈Y、X,并计算XopY,再把结果入栈。直到读完字符串,栈中最后一个元素就是所求的值。若栈中元素多于1个则表达式错误。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1010;
stack s;
int main()
{
string str;
getline(cin,str);
int d;
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++)
{
if(isdigit(str[i])) // 是数字就入栈
{
d=str[i]-'0';
s.push(d);
}else{
int y=s.top();
s.pop();
int x=s.top();
s.pop();
if(str[i]=='+')
{
d=x+y;
}else if(str[i]=='-')
{
d=x-y;
}
s.push(d);
}
}
if(s.size()==1)
cout<<s.top()<<endl;
else
cout<<"表达式有误"<<endl;
return 0;
}
3、
题目:
给定一个字符串,求哈夫曼编码的最短长度。
输入:
aaaaabbbbcccdde
输出:
33
解析:
本题非常巧妙的转化了思路,就很容易求解。求哈夫曼编码的带权路径长度(所有叶子结点的带权路径路径之和),等价于求哈夫曼树中非叶结点的权值之和。因此,先得到每一个字符出现的频次,存入优先队列中,然后累加每次入队的元素值,就是结果。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
2015上机题
1、
题目:
给出长方形的长和宽,每次从长方形里撕去最大的正方形,输出最后能得到多少正方形。
输入:(自编)
3 4
输出:
4
解析:
就是每次找长宽中较短的边,以该边来画正方形,依次下去,直到最后长=宽,注意此时也是一个正方形要计入。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int m,n;
scanf("%d %d",&m,&n);
int ans=0;
while(m!=n)
{
if(m>n)
{
m=m-n;
ans++;
}else{
n=n-m;
ans++;
}
}
ans++; // 长=宽时也有一个正方形
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
2、
题目:
给出 a,b,c(3 个整数),判断 a,b 能否通过±*/得到 c,a,b 可以交换位置,可以输出YES,不行输出 NO。
输入:
3 8 2
输出:
NO
解析:
一开始题目意思理解错误,我以为是像24点用四种运算得到c,结果参考别人才发现是用其中一种方法得到c…还有一个小注意点是,若a,b,c用int型,则在除法中会取整导致判断错误,因此要用double。
有一个巧妙的思路是,通过c * b == a || c * a == b来判断,就不需要double了。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double a,b,c;
scanf("%lf %lf %lf",&a,&b,&c);
if(a+b==c||a*b==c)
{
printf("YES");
}else if(a-b==c||b-a==c)
{
printf("YES");
}else if(a/b==c||b/a==c)
{
printf("YES");
}else{
printf("NO");
}
return 0;
}
3、
题目:
给出优先队列的实现,实现 4 个操作:
1)ADD N P:往队列里加入 id 为 N 的优先级为 P 的任务
2)NEXT:输出下一个最高优先级的任务的 id,如果优先级相同输出 id 小的任务,若队列中没有任务输出-1
3)REMOVE N:移除 id 为 N 的任务
4)COUNT:输出队列中的任务数量
输入:(自编 id和P)
1 2
3 3
4 5
2 5
输出:
next的输入是2
count的输出是4
remove后的count输出是3
解析:
这里主要采用set来进行排序,用map来记录id和优先级的对应。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
作者:考研想喝奶茶