基于OpenMV的图像识别之数字识别功能
基于OpenMV的图像识别
一、数字识别
基于OpenMV的图像识别 OpenMV简介什么是OpenMV
OpenMV是由美国克里斯团队基于MicroPython发起的开源机器视觉项目,目的是创建低成本,可扩展,使用python驱动的机器视觉模块。OpenMV搭载了MicroPython解释器,使其可以在嵌入式端进行python开发,关于MicroPython可以参照我之前的博客专栏:MicroPython. OpenMV基于32位,ARM Cortex-M7内核的OpenMV-H7, 并结合各种摄像头,可以进行多种机器视觉应用的实现,比如人脸检测,物体分类等。
OpenMV是一个开源,低成本,功能强大的机器视觉模块,以STM32F427CPU为核心,集成了OV7725摄像头芯片,在小巧的硬件模块上,用C语言高效地实现了核心机器视觉算法,提供Python编程接口 。同时 OpenMV也是一个可编程的摄像头,通过Python语言可实现你想要的逻辑。而且摄像头本身也内置了一些图像处理的算法,使用起来也更加的方便,仅需要写一些简单的Python代码,即可轻松的完成各种机器视觉相关的任务。在此,我们通过OpenMV实现了数字识别。
在打开OpenMV摄像头链接电脑时,会弹出让你升级的窗口
这时切忌一定要选择Cancel键,
不能选择升级!!!
不能选择升级!!!
不能选择升级!!!

然后在进行下一步的操作
OpenMV中文入门视频教程
一、数字识别数字识别的基础是需要配置使用NCC模板匹配。通过NCC模板的匹配可把
需要识别的数字模板图片保存到SD卡中,然后可进行下一步的识别。
1、可以通过打开模板匹配的历程来直接打开代码进行使用


2、如果运行出现这个窗口就说明没有保存模板图片

所以这时就需要创建一个模板图片:创建模板图片的详细视频教程
创建一个模板图片首先要打开一个helloworld历程文件


然后在helloworld历程文件中进行匹配0~9这样的基本数字,对这些数字进
行一一截取,用它们来作为我们的模板图片。
在右边的Frame Buffer框中进行截取,注意:不要点Zoom,因为Zoom展示
的是放大后的效果,在识别时可能会导致失帧。
然后点击左键选出一个框(如图所示)
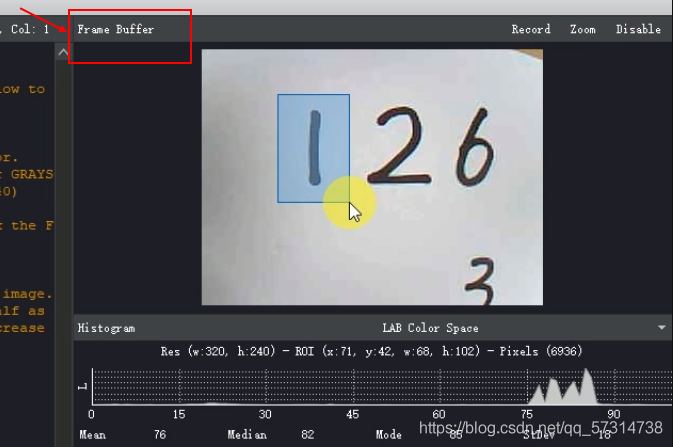
选完框后点击右键选择Save Image selection to PC

最后把截取的数字图片进行保存,一定要保存到OpenMV的SD卡中,保存的文件名可自己
定义

3、把template.pgm改为你创建的模板图片的名称

(注意:模板图片的格式一定要是pgm的格式,转换格式可以在
https://convertio.co/zh/bmp-pgm/网站直接进行转换)
4、改完之后就可以运行
下面展示一些 有关数字识别的代码。
此代码为源代码,可根据自己的需求在上面进行改动。
代码来源:数字识别代码,可直接引用并修改
# Template Matching Example - Normalized Cross Correlation (NCC)
#
# This example shows off how to use the NCC feature of your OpenMV Cam to match
# image patches to parts of an image... expect for extremely controlled enviorments
# NCC is not all to useful.
#
# WARNING: NCC supports needs to be reworked! As of right now this feature needs
# a lot of work to be made into somethin useful. This script will reamin to show
# that the functionality exists, but, in its current state is inadequate.
import time, sensor, image
from image import SEARCH_EX, SEARCH_DS
# Reset sensor
sensor.reset()
# Set sensor settings
sensor.set_contrast(1)
sensor.set_gainceiling(16)
# Max resolution for template matching with SEARCH_EX is QQVGA
sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA)
# You can set windowing to reduce the search image.
#sensor.set_windowing(((640-80)//2, (480-60)//2, 80, 60))
sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.GRAYSCALE)
# Load template.
# Template should be a small (eg. 32x32 pixels) grayscale image.
template8 = image.Image("/8.pgm")
template9 = image.Image("/9.pgm")
clock = time.clock()
# Run template matching
while (True):
clock.tick()
img = sensor.snapshot()
# find_template(template, threshold, [roi, step, search])
# ROI: The region of interest tuple (x, y, w, h).
# Step: The loop step used (y+=step, x+=step) use a bigger step to make it faster.
# Search is either image.SEARCH_EX for exhaustive search or image.SEARCH_DS for diamond search
#
# Note1: ROI has to be smaller than the image and bigger than the template.
# Note2: In diamond search, step and ROI are both ignored.
r 8= img.find_template(template8, 0.70, step=4, search=SEARCH_EX) #, roi=(10, 0, 60, 60))
if r8:
img.draw_rectangle(r8)
r 9= img.find_template(template9, 0.70, step=4, search=SEARCH_EX) #, roi=(10, 0, 60, 60))
if r9:
img.draw_rectangle(r9)
print(clock.fps())
运行的结果如图所示

到此这篇关于基于OpenMV的图像识别之数字识别的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关OpenMV图像识别内容请搜索软件开发网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持软件开发网!