叁拾肆- sklearn 根据样本对文本情绪进行分类
通过 sklearn 对从爬虫捉取的网页文本进行情绪分类,只是简单化的工科内容而不是理科内容(无理论分析)。
从 MongoDB 中随机抽取数据,然后用jieba分词再进行分词,然后用 sklearn 做学习样本进行分类。
jieba分词后可能会多达4、5万个词,所以必须计算各词信息熵,把信息熵高的词汇剔除掉。
剩余信息熵低的关键字用 sklearn 包进行学习。
廿捌-原爬虫项目加入客制化内容,Python 读取 URL 域名
通过前期爬虫项目捉取内容,并且手动对接近1000多条数据进行人工情绪分类。
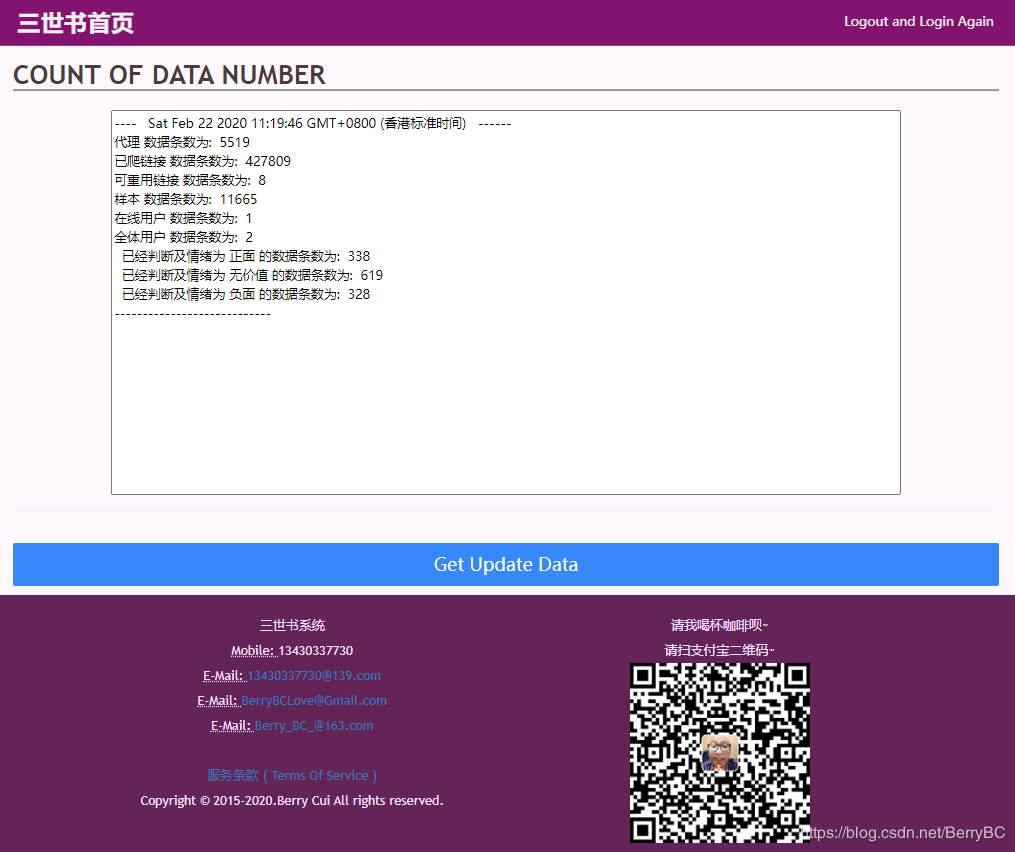
人工分类页如下:
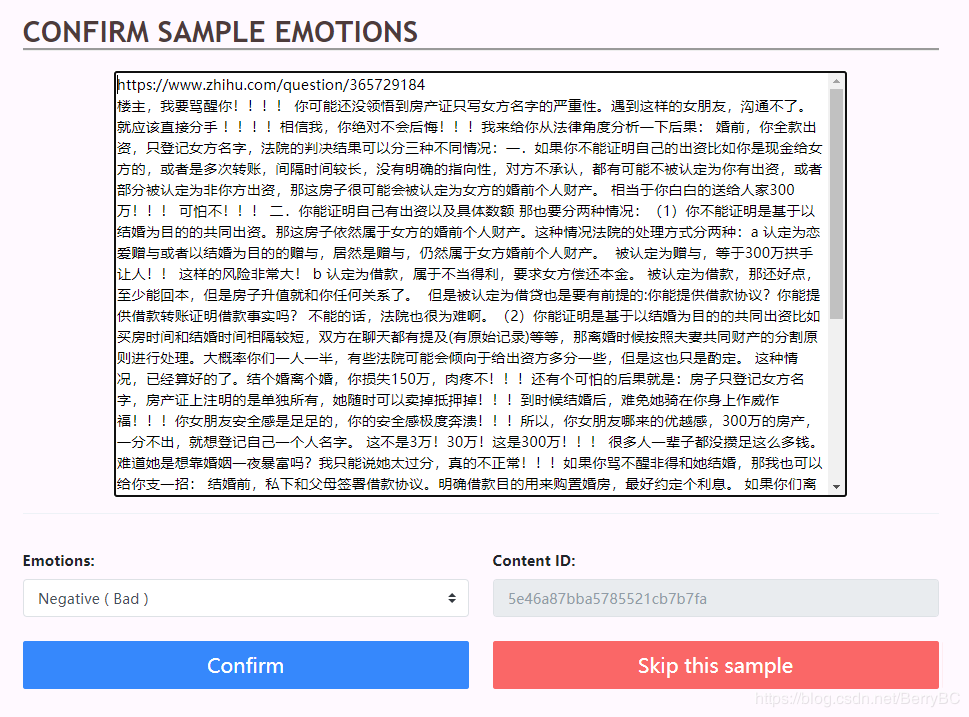
这个其实就从数据库抽样。通过以下 MongoDB Filiter:
curPos = colSample.aggregate(
[{'$match': {'cf': True, 'e': 1}}, {'$sample': {'size': 300}}])
4-2) 分词并整理为相应关键字
分词是用jieba包进行分词的,我只是简单做,并没用比较复杂的分词方式。
遍历3个(正面、负面、无用)情绪集之后,把他们按分词之后的词按统一顺序排,代码如下:
# 初始化定义
# dictSampleOfNew={'kw':[],'e':1}
arrXPreTrain = []
arrYPreTrain = []
# 定义数据记录
dictAllResult = {'intIndexNow': 0, 'arrXPreTrain': [], 'arrYPreTrain': [], 'dictKW': {}, 'arrSample': [], 'arrColunms': []}
# 把 MongoDB 的 Cursor 遍历转为数组
def ToGrepSampleKW(curSamples, dictInAllResult):
for eleSamples in curSamples:
# 不设睡眠时间很容易 CPU 爆掉
time.sleep(0.05)
genSampleWord = jieba.cut(eleSamples['ct'], cut_all=False)
dictSampleOfNew = {'kw': [], 'e': eleSamples['e']}
# 对分词之后的每个关键字进行处理
for eleKW in genSampleWord:
# 如果前期没有该关键字即进行下一步
if not eleKW in dictSampleOfNew['kw']:
dictSampleOfNew['kw'].append(eleKW)
# 如果所有样本都不存在此关键字即存在全局字典内
if not eleKW in dictInAllResult['dictKW'].keys():
dictInAllResult['dictKW'][eleKW] = dictInAllResult['intIndexNow']
dictInAllResult['intIndexNow'] += 1
dictInAllResult['arrColunms'].append(eleKW)
dictInAllResult['arrSample'].append(dictSampleOfNew)
return dictInAllResult
# 做成一个矩阵,如果该样本含有该关键字,即对应位置为 True,否则为 False
# 样本大致为
# 我 爱 中国
# 样本1 True False True
# 样本2 False True True
def ToArraySample(dictInAllResult):
for dictEle in dictInAllResult['arrSample']:
arrNewSample = [False for intX in range(
dictInAllResult['intIndexNow'])]
for eleKWFI in dictEle['kw']:
arrNewSample[dictInAllResult['dictKW'][eleKWFI]] = True
dictInAllResult['arrXPreTrain'].append(arrNewSample)
dictInAllResult['arrYPreTrain'].append(dictEle['e'])
return dictInAllResult
dictAllResult = ToGrepSampleKW(curPos, dictAllResult)
print('Done Pos ' + time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
dictAllResult = ToGrepSampleKW(curUseless, dictAllResult)
print('Done Useless '+time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
dictAllResult = ToGrepSampleKW(curNeg, dictAllResult)
print('Done Neg '+time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
dictAllResult = ToArraySample(dictAllResult)
print('Done Arr '+time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
4-3) 计算关键字信息熵
关于信息熵的计算我是参考了:
python, pandas 实现信息熵计算
代码为:
# DataFrame 中第几列
def get_entropy(data_df, columns=None):
time.sleep(0.01)
if (columns is None):
raise "the columns must be not empty!"
# Information Entropy
pe_value_array = data_df[columns].unique()
ent = 0.0
for x_value in pe_value_array:
p = float(data_df[data_df[columns] ==
x_value].shape[0]) / data_df.shape[0]
logp = np.log2(p)
ent -= p * logp
return ent
# 有多少条样本
intLenOfXPreT = len(arrXPreTrain)
arrKWForEntropy = []
# 遍历每一个关键字
for intI in range(dictAllResult['intIndexNow']):
# 所有样本中该关键字是否存在
arrTmp = [arrXPreTrain[intJ][intI] for intJ in range(intLenOfXPreT)]
dfX = pd.DataFrame(arrTmp)
# 打印现在进度
if intI % 1000 ==0:
print(intI)
# 打印该关键字信息熵
print( dictAllResult['arrColunms'][intI]+' 信息熵为: ' +
str(get_entropy(dfY[dfX[dictAllResult['arrColunms'][intI]]==True],0)))
# 在数组 arrKWForEntropy 中插入一个关键字以及对应信息熵
if dfY[dfX[0]].shape[0] > 1:
arrKWForEntropy.append(
[dictAllResult['arrColunms'][intI], get_entropy(dfY[dfX[0]], 0)])
4-4) 关键字信息熵分桶
关于 pandas 的 分桶其实可以参考很多文章,在此我就不再写了,此段代码主要是为了把高信息熵跟低信息熵区分开:
dfEntropy = pd.DataFrame(arrKWForEntropy, columns=['KW', 'IE'])
print(dfEntropy.head(10))
# 分桶
cutB = pd.cut(dfEntropy['IE'], 2, labels=['L', 'H'])
dfEntropy['IEBin'] = cutB
print(dfEntropy[dfEntropy['IEBin'] == 'L'])
nparrKWWaitFor = dfEntropy[dfEntropy['IEBin'] == 'L']['KW'].values
关于分桶使用 cut还是 qcut,我当初有想过使用 qcut,但 qcut 可能会造成关键字过多,对后续处理很麻烦,而且有些高熵的都会混进去。
使用sklearn 的 train_test_split 进行交叉验证分开。
# 重新对低熵关键字在样本中排序
arrForTrain = [[] for intI in range(len(arrXPreTrain))]
for nparrEle in nparrKWWaitFor:
intJ = dictAllResult['dictKW'][nparrEle]
for intK in range(intLenOfXPreT):
arrForTrain[intK].append(arrXPreTrain[intK][intJ])
# 过滤无用的样本
arrXForTrainReal = []
arrYForTrainReal = []
for intI in range(len(arrYPreTrain)):
if(arrYPreTrain[intI] != 0):
arrXForTrainReal.append(arrForTrain[intI])
arrYForTrainReal.append(arrYPreTrain[intI])
# 交叉验证脚本
arrXtrain, arrXtest, arrYtrain, arrYtest = train_test_split(
arrXForTrainReal, arrYForTrainReal, test_size=0.2)
4-6) 评分
只是一段评分的代码。
其实并没有对比过很多的方法,也没用调参包。
主要我是思路我是觉得不同词语的存在与否,是多维的,而并不是统一的,所以用决策树可能会出现有某些词语出现而出现误导的情况。
所以就随便选几个根据维度进行学习的算法。
# ------- SKLearn 测试开始 ------
rcfClassifier = RandomForestClassifier()
rcfClassifier = rcfClassifier.fit(arrXtrain,arrYtrain)
clfScore = rcfClassifier.score(arrXtest,arrYtest)
print("随机森林评分: "+str(clfScore))
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
clfBagging = BaggingClassifier(base_estimator=LinearSVC(
random_state=0, tol=1e-05, max_iter=10000))
clfBagging.fit(arrXtrain, arrYtrain)
clfScore = clfBagging.score(arrXtest, arrYtest)
print("装袋 SVC 评分: "+str(clfScore))
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
clfAdaB = AdaBoostClassifier()
clfAdaB.fit(arrXtrain, arrYtrain)
clfScore = clfAdaB.score(arrXtest,arrYtest)
print("AdaBoost 评分: "+str(clScore))
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
# # ----------------------------------
4-7) 输出结果
看到结果,那我就直接用 SVC了~
# # ----------------------------------
>>> clfScore = rcfClassifier.score(arrXtest,arrYtest)
>>>
>>> print("随机森林评分: "+str(clfScore))
随机森林评分: 0.7916666666666666
>>> print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
2020-02-22 15:10:16
>>>
>>> clfBagging = BaggingClassifier(base_estimator=LinearSVC(
... random_state=0, tol=1e-05, max_iter=10000))
>>> clfBagging.fit(arrXtrain, arrYtrain)
BaggingClassifier(base_estimator=LinearSVC(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=True,
fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1,
loss='squared_hinge', max_iter=10000,
multi_class='ovr', penalty='l2',
random_state=0, tol=1e-05,
verbose=0),
bootstrap=True, bootstrap_features=False, max_features=1.0,
max_samples=1.0, n_estimators=10, n_jobs=None,
oob_score=False, random_state=None, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
>>> clfScore = clfBagging.score(arrXtest, arrYtest)
>>>
>>> print("装袋 SVC 评分: "+str(clfScore))
装袋 SVC 评分: 0.825
>>> print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
2020-02-22 15:10:17
>>>
>>> clfAdaB = AdaBoostClassifier()
>>> clfAdaB.fit(arrXtrain, arrYtrain)
AdaBoostClassifier(algorithm='SAMME.R', base_estimator=None, learning_rate=1.0,
n_estimators=50, random_state=None)
>>> clfScore = clfAdaB.score(arrXtest,arrYtest)
>>>
>>> print("AdaBoost 评分: "+str(clfScore))
AdaBoost 评分: 0.725
>>> print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
2020-02-22 15:10:20
4-8) 完整代码
import jieba
import pymongo
import time
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
dbClient = pymongo.MongoClient('mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/')
dbMongo = dbClient['dbSample']
dbMongo.authenticate('Berry', 'Berry')
colSample = dbMongo['tbSample']
curPos = colSample.aggregate(
[{'$match': {'cf': True, 'e': 1}}, {'$sample': {'size': 300}}])
curUseless = colSample.aggregate(
[{'$match': {'cf': True, 'e': 0}}, {'$sample': {'size': 200}}])
curNeg = colSample.aggregate(
[{'$match': {'cf': True, 'e': -1}}, {'$sample': {'size': 300}}])
dictKW = {}
arrSample = []
# dictSampleOfNew={'kw':[],'e':1}
intIndexNow = 0
arrXPreTrain = []
arrYPreTrain = []
dictAllResult = {'intIndexNow': 0, 'arrXPreTrain': [], 'arrYPreTrain': [], 'dictKW': {}, 'arrSample': [], 'arrColunms': []}
def ToGrepSampleKW(curSamples, dictInAllResult):
for eleSamples in curSamples:
time.sleep(0.05)
genSampleWord = jieba.cut(eleSamples['ct'], cut_all=False)
dictSampleOfNew = {'kw': [], 'e': eleSamples['e']}
for eleKW in genSampleWord:
if not eleKW in dictSampleOfNew['kw']:
dictSampleOfNew['kw'].append(eleKW)
if not eleKW in dictInAllResult['dictKW'].keys():
dictInAllResult['dictKW'][eleKW] = dictInAllResult['intIndexNow']
dictInAllResult['intIndexNow'] += 1
dictInAllResult['arrColunms'].append(eleKW)
dictInAllResult['arrSample'].append(dictSampleOfNew)
return dictInAllResult
def ToArraySample(dictInAllResult):
for dictEle in dictInAllResult['arrSample']:
arrNewSample = [False for intX in range(
dictInAllResult['intIndexNow'])]
for eleKWFI in dictEle['kw']:
arrNewSample[dictInAllResult['dictKW'][eleKWFI]] = True
dictInAllResult['arrXPreTrain'].append(arrNewSample)
dictInAllResult['arrYPreTrain'].append(dictEle['e'])
return dictInAllResult
dictAllResult = ToGrepSampleKW(curPos, dictAllResult)
print('Done Pos ' + time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
dictAllResult = ToGrepSampleKW(curUseless, dictAllResult)
print('Done Useless '+time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
dictAllResult = ToGrepSampleKW(curNeg, dictAllResult)
print('Done Neg '+time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
dictAllResult = ToArraySample(dictAllResult)
print('Done Arr '+time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
curPos.close()
curUseless.close()
curNeg.close()
dbClient.close()
arrXPreTrain = dictAllResult['arrXPreTrain']
arrYPreTrain = dictAllResult['arrYPreTrain']
dfY = pd.DataFrame(arrYPreTrain)
def get_entropy(data_df, columns=None):
time.sleep(0.01)
if (columns is None):
raise "the columns must be not empty!"
# Information Entropy
pe_value_array = data_df[columns].unique()
ent = 0.0
for x_value in pe_value_array:
p = float(data_df[data_df[columns] ==
x_value].shape[0]) / data_df.shape[0]
logp = np.log2(p)
ent -= p * logp
return ent
intLenOfXPreT = len(arrXPreTrain)
arrKWForEntropy = []
for intI in range(dictAllResult['intIndexNow']):
arrTmp = [arrXPreTrain[intJ][intI] for intJ in range(intLenOfXPreT)]
dfX = pd.DataFrame(arrTmp)
# if intI % 1000 ==0:
# print(intI)
# print( dictAllResult['arrColunms'][intI]+' 信息熵为: ' +
# str(get_entropy(dfY[dfX[dictAllResult['arrColunms'][intI]]==True],0)))
if dfY[dfX[0]].shape[0] > 1:
arrKWForEntropy.append(
[dictAllResult['arrColunms'][intI], get_entropy(dfY[dfX[0]], 0)])
dfEntropy = pd.DataFrame(arrKWForEntropy, columns=['KW', 'IE'])
print(dfEntropy.head(10))
cutB = pd.cut(dfEntropy['IE'], 2, labels=['L', 'H'])
dfEntropy['IEBin'] = cutB
print(dfEntropy[dfEntropy['IEBin'] == 'L'])
nparrKWWaitFor = dfEntropy[dfEntropy['IEBin'] == 'L']['KW'].values
arrForTrain = [[] for intI in range(len(arrXPreTrain))]
for nparrEle in nparrKWWaitFor:
intJ = dictAllResult['dictKW'][nparrEle]
for intK in range(intLenOfXPreT):
arrForTrain[intK].append(arrXPreTrain[intK][intJ])
arrXForTrainReal = []
arrYForTrainReal = []
for intI in range(len(arrYPreTrain)):
if(arrYPreTrain[intI] != 0):
arrXForTrainReal.append(arrForTrain[intI])
arrYForTrainReal.append(arrYPreTrain[intI])
arrXtrain, arrXtest, arrYtrain, arrYtest = train_test_split(
arrXForTrainReal, arrYForTrainReal, test_size=0.2)
# ------- SKLearn 测试开始 ------
rcfClassifier = RandomForestClassifier()
rcfClassifier = rcfClassifier.fit(arrXtrain,arrYtrain)
clfScore = rcfClassifier.score(arrXtest,arrYtest)
print("随机森林评分: "+str(clfScore))
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
clfBagging = BaggingClassifier(base_estimator=LinearSVC(
random_state=0, tol=1e-05, max_iter=10000))
clfBagging.fit(arrXtrain, arrYtrain)
clfScore = clfBagging.score(arrXtest, arrYtest)
print("装袋 SVC 评分: "+str(clfScore))
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
clfAdaB = AdaBoostClassifier()
clfAdaB.fit(arrXtrain, arrYtrain)
clfScore = clfAdaB.score(arrXtest,arrYtest)
print("AdaBoost 评分: "+str(clScore))
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
# # ----------------------------------
5。后续
保存 sklearn 生成的模型之后,直接以后就能用了。
打算以后对新捉取的信息进行识别之后再作为样本,重新再生成新的模型。
以后再说吧。
作者:BerryBC