@NonNull导致无法序列化的问题及解决
@NonNull导致无法序列化的问题
@NonNull修饰Field反序列化部分值为空
分析
建议改进
总结
@NonNull导致无法序列化的问题
以上这个代码在接参的时候报了一个缺少无参构造函数无法序列化的错误
将.class反编译

可以看到编译后的源码中生成了一个有参构造 明显是 用来判空的 假设那么这个构造函数应该就是根据@NonNull生成的
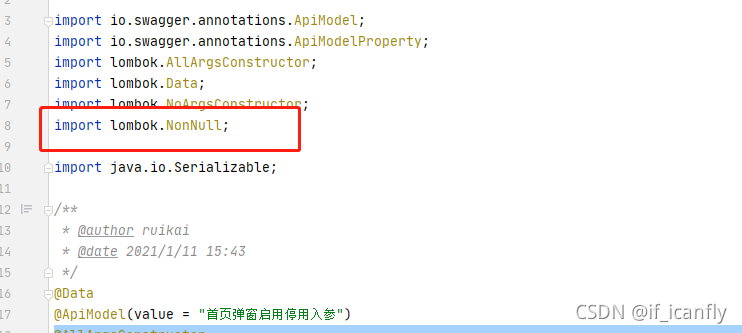
实际上我们治理应该添加的注解是NotNull才对

上面因为lombook根据@NonNull生成了一个有参构造函数,导致jdk不会添加默认的无参构造函数,没有无参构造函数的话 序列化就会失败.
@NonNull修饰Field反序列化部分值为空一般Http接口,为了参数统一管理,定义一个VO用来接收POST过来的字段,常规做法是把参数解析成map,然后反序列化到VO中,早期定义的接口字段都非空,所以VO中都加了@NonNull注解;一直很和谐;
因为需求变化,接口字段需要增加两个,为了版本兼容,新加的两个字段需要可空;于是在VO中增加两个字段,不用@NonNull修饰,但是反序列化后发现这两个字段一直为空!怎么都不能从map中获取到这两个值!
分析版本:
JDK:1.8
lombok:1.18.12
fastjson:1.2.60
原代码
package com.example.demo;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NonNull;
@Data
public class DemoRequestVO {
@NonNull
private String firstParam;
private String SecondParam;
private String thirdParam;
}
public static void testDemo(){
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("firstParam","lllllll");
params.put("secondParam","45454645");
params.put("thirdParam","xx公司");
DemoRequestVO request = JSON.parseObject(JSON.toJSONString(params), DemoRequestVO.class);
System.out.println(request);
}
分析原因
做两方面猜测:
1: 注解提供者问题
2: Json反序列化问题
1: 先看下: 注解提供者 @NonNull
发现其是作用于RetentionPolicy.CLASS的
package lombok;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE, ElementType.TYPE_USE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
@Documented
public @interface NonNull {
}
查看lombok源码可以看到,NonNull注解提供者一共这么多
static {
NONNULL_ANNOTATIONS = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(new String[] {
"androidx.annotation.NonNull",
"android.support.annotation.NonNull",
"com.sun.istack.internal.NotNull",
"edu.umd.cs.findbugs.annotations.NonNull",
"javax.annotation.Nonnull",
// "javax.validation.constraints.NotNull", // The field might contain a null value until it is persisted.
"lombok.NonNull",
"org.checkerframework.checker.nullness.qual.NonNull",
"org.eclipse.jdt.annotation.NonNull",
"org.eclipse.jgit.annotations.NonNull",
"org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull",
"org.jmlspecs.annotation.NonNull",
"org.netbeans.api.annotations.common.NonNull",
"org.springframework.lang.NonNull",
}));
再看下经过注解后编译的CLASS
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package com.example.demo;
import lombok.NonNull;
public class DemoRequestVO {
@NonNull
private String firstParam;
private String SecondParam;
private String thirdParam;
public DemoRequestVO(@NonNull final String firstParam) {
if (firstParam == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("firstParam is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.firstParam = firstParam;
}
}
@NonNull
public String getFirstParam() {
return this.firstParam;
}
public String getSecondParam() {
return this.SecondParam;
}
public String getThirdParam() {
return this.thirdParam;
}
public void setFirstParam(@NonNull final String firstParam) {
if (firstParam == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("firstParam is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.firstParam = firstParam;
}
}
public void setSecondParam(final String SecondParam) {
this.SecondParam = SecondParam;
}
public void setThirdParam(final String thirdParam) {
this.thirdParam = thirdParam;
}
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof DemoRequestVO)) {
return false;
} else {
DemoRequestVO other = (DemoRequestVO)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else {
label47: {
Object this$firstParam = this.getFirstParam();
Object other$firstParam = other.getFirstParam();
if (this$firstParam == null) {
if (other$firstParam == null) {
break label47;
}
} else if (this$firstParam.equals(other$firstParam)) {
break label47;
}
return false;
}
Object this$SecondParam = this.getSecondParam();
Object other$SecondParam = other.getSecondParam();
if (this$SecondParam == null) {
if (other$SecondParam != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$SecondParam.equals(other$SecondParam)) {
return false;
}
Object this$thirdParam = this.getThirdParam();
Object other$thirdParam = other.getThirdParam();
if (this$thirdParam == null) {
if (other$thirdParam != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$thirdParam.equals(other$thirdParam)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(final Object other) {
return other instanceof DemoRequestVO;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $firstParam = this.getFirstParam();
int result = result * 59 + ($firstParam == null ? 43 : $firstParam.hashCode());
Object $SecondParam = this.getSecondParam();
result = result * 59 + ($SecondParam == null ? 43 : $SecondParam.hashCode());
Object $thirdParam = this.getThirdParam();
result = result * 59 + ($thirdParam == null ? 43 : $thirdParam.hashCode());
return result;
}
public String toString() {
return "DemoRequestVO(firstParam=" + this.getFirstParam() + ", SecondParam=" + this.getSecondParam() + ", thirdParam=" + this.getThirdParam() + ")";
}
}
重点是看这个编译后的class的构造方法:只有一个带@NonNull注解参数的构造方法!!!
一般到这里都能想到反序列化后的为啥另外两个未注解NonNull的为啥空值了;如果没想到,也没关系,咱们再来看看JSON反序列化的过程
2: json反序列化;
一系列递进过程不再描述,重点看JavaBeanInfo类中的build方法,这个方法是真正把map反序化到javaBean的过程
public static JavaBeanInfo build(Class<?> clazz, Type type, PropertyNamingStrategy propertyNamingStrategy, boolean fieldBased, boolean compatibleWithJavaBean, boolean jacksonCompatible)
挑几处重要的开看下:
取构造方法list
Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
Constructor<?> defaultConstructor = null;
if (!kotlin || constructors.length == 1) {
if (builderClass == null) {
defaultConstructor = getDefaultConstructor(clazz, constructors);
} else {
defaultConstructor = getDefaultConstructor(builderClass, builderClass.getDeclaredConstructors());
}
}
赋值创建javaBean的构造
boolean is_public = (constructor.getModifiers() & 1) != 0;
if (is_public) {
String[] lookupParameterNames = ASMUtils.lookupParameterNames(constructor);
if (lookupParameterNames != null && lookupParameterNames.length != 0 && (creatorConstructor == null || paramNames == null || lookupParameterNames.length > paramNames.length)) {
paramNames = lookupParameterNames;
creatorConstructor = constructor;
}
}
创建javaBean,看传参; 只有一个构造方法;
if (!kotlin && !clazz.getName().equals("javax.servlet.http.Cookie")) {
return new JavaBeanInfo(clazz, builderClass, (Constructor)null, creatorConstructor, (Method)null, (Method)null, jsonType, fieldList);
}
结论:
使用@NonNull注解,编译后生成的CLASS构造方法只有一个,且只有被注解的字段才能构造时候赋值;此种做法是保证在编译期可以判断非空;
反序列化时候使用了这个构造方法,其他的值没有被赋值;
建议改进1: 使用@NotNull代替
2: 如果修饰的是String类型,推荐使用@NotBlank,好处是可以判断空字符串
3: 在自定义的VO中增加一个无参构造方法;
总结以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持软件开发网。