Gin Web框架 核心源码分析
看到在Gin Web框架中 路由tree 中 的priority字段 并不是很了解作用 就单独拿出来了解了下 实际上就是对数组里面子节点 进行排序 使它索引变小 这样在 下移插入路由时 能更快找到。
type node struct {
children []node
path string
priority uint32
indices string
}
以上是 简化的数据结构
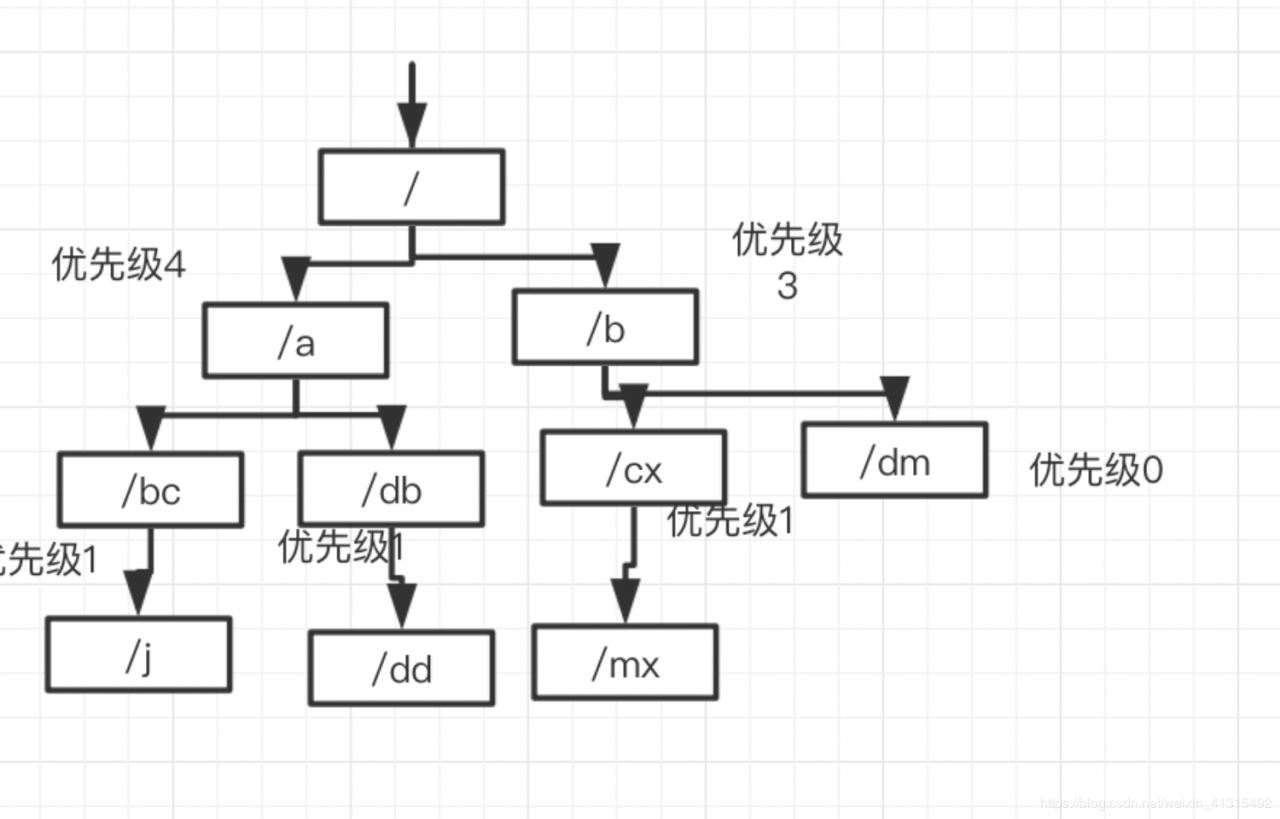
使用数组存储了 路由节点 如果一颗路由下面有很多节点那么被访问到的频率也会变高 所以 子节点较多的数 进行排序。
每次添加节点时 会对当前 节点 向索引0方向冒泡 调换 直到碰到优先级高于当前节点的节点。
package main
import "fmt"
func main(){
n0 := node{
children: make([]node,0),
priority: 1,
indices: "glxh",
path:"/heall",
}
n1 := node{
children: nil,
priority: 1,
indices: "e",
path:"/go",
}
n2 := node{
children: nil,
priority: 1,
indices: "l",
path:"lang",
}
n3 := node{
children: nil,
priority: 1,
indices: "l",
path:"xi",
}
n4 := node{
children: nil,
priority: 1,
indices: "o",
path:"ha",
}
n0.children = append(n0.children, n1)
n0.children = append(n0.children, n2)
n0.children = append(n0.children, n3)
n0.children = append(n0.children, n4)
n0.incrementChildPrio(1)
}
type node struct {
children []node
path string
priority uint32
indices string
}
// 类似于冒泡算法
func (n *node) incrementChildPrio(pos int) int {
cs := n.children
cs[pos].priority++
prio := cs[pos].priority
// Adjust position (move to front)
newPos := pos
for ; newPos > 0 && cs[newPos-1].priority < prio; newPos-- {
// Swap node positions
cs[newPos-1], cs[newPos] = cs[newPos], cs[newPos-1]
}
// Build new index char string
//当 成功交换了 之后 newPos 就会变小
if newPos != pos {
fmt.Println("经过交换后的字符",n.indices[pos:pos+1])
fmt.Println("被交换后的字符",n.indices[newPos:pos])
fmt.Println("[newPos:pos]",n.indices[newPos:pos])
fmt.Println("n.indices[pos+1:]",n.indices[pos+1:])
n.indices = n.indices[:newPos] + // Unchanged prefix, might be empty
n.indices[pos:pos+1] + // The index char we move
n.indices[newPos:pos] + n.indices[pos+1:] // Rest without char at 'pos'
}
return newPos
}
作者:草帽boy7