SpringBoot注解@ConditionalOnClass底层源码实现
@ConditionalOnClass的底层源码实现
ConditionOutcome对象
ClassNameFilter.MISSING判断某类是否不存在
@ConditionalOnClass的底层源码实现在SpringBoot中,支持了很多种条件注解,@ConditionalOnClass注解就是其中之一,而且及其重要,它主要是用来判断该注解所指定的某个类或某些类,是否在ClassPath中存在,如果存在则符合条件,如果不存在则不符合。
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnClassCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnClass {
Class<?>[] value() default {};
String[] name() default {};
}
这是该注解的源码,可以通过value和name来指定要判断的类,而真正执行判断的逻辑在OnClassCondition类中。
OnClassCondition类继承了FilteringSpringBootCondition类
FilteringSpringBootCondition类又继承了SpringBootCondition类
SpringBootCondition类实现了Condition接口
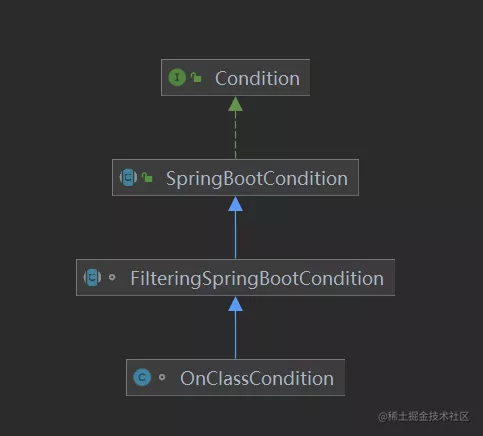
Spring在解析条件注解时,就会调用Condition接口的matches()方法,在上面的类继承关系中,SpringBootCondition类实现了matches()方法,所以会先被调用。
ConditionOutcome对象在matches()方法中,会调用getMatchOutcome()方法,并得到ConditionOutcome对象,ConditionOutcome对象就表示条件判断的结果。
public class ConditionOutcome {
// 表示条件是否匹配
private final boolean match;
// ...
}
getMatchOutcome()方法在SpringBootCondition类中是一个抽象方法,在子类OnClassCondition类中才真正实现了getMatchOutcome()方法,并真正会进行条件判断。
所以核心就是这个getMatchOutcome()方法,在这个方法中会先获取@ConditionalOnClass注解的value和name属性的值,这些值就是待判断的类名集合。
// 调用getCandidates方法
List<String> onClasses = getCandidates(metadata, ConditionalOnClass.class);
private List<String> getCandidates(AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, Class<?> annotationType) {
MultiValueMap<String, Object> attributes =
metadata.getAllAnnotationAttributes(annotationType.getName(), true);
if (attributes == null) {
return null;
}
List<String> candidates = new ArrayList<>();
addAll(candidates, attributes.get("value"));
addAll(candidates, attributes.get("name"));
return candidates;
}
ClassNameFilter.MISSING判断某类是否不存在
接下来就会逐个判断类名集合中的每个类名,判断逻辑为:利用ClassNameFilter.MISSING来判断某类是否不存在?
List<String> missing = filter(onClasses, ClassNameFilter.MISSING, classLoader);
protected final List<String> filter(Collection<String> classNames, ClassNameFilter classNameFilter, ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(classNames)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<String> matches = new ArrayList<>(classNames.size());
for (String candidate : classNames) {
if (classNameFilter.matches(candidate, classLoader)) {
matches.add(candidate);
}
}
return matches;
}
ClassNameFilter.MISSING就是利用ClassLoader来加载类,如果加载到了表示类存在,没加载到就表示不存在。
protected enum ClassNameFilter {
// ...
MISSING {
@Override
public boolean matches(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 是否不存在
return !isPresent(className, classLoader);
}
};
static boolean isPresent(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
try {
resolve(className, classLoader);
return true;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
return false;
}
}
}
protected static Class<?> resolve(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
if (classLoader != null) {
return Class.forName(className, false, classLoader);
}
return Class.forName(className);
}
判断完之后,只要missing集合不为空,那就表示待判断的类中有类不存在,那就返回条件不匹配的ConditionOutcome对象,否则就返回条件匹配的ConditionOutcome对象。
这就是@ConditionalOnClass注解的核心源码流程,期待你的点赞哦。
以上就是SpringBoot注解@ConditionalOnClass底层源码实现的详细内容,更多关于SpringBoot ConditionalOnClass的资料请关注软件开发网其它相关文章!