Vue.js使用$.ajax和vue-resource实现OAuth的注册、登录、注销和API调用
概述
上一篇我们介绍了如何使用vue resource处理HTTP请求,结合服务端的REST API,就能够很容易地构建一个增删查改应用。
这个应用始终遗留了一个问题,Web App在访问REST API时,没有经过任何认证,这使得服务端的REST API是不安全的,只要有人知道api地址,就可以调用API对服务端的资源进行修改和删除。
今天我们就来探讨一下如何结合Web API来限制资源的访问。
本文的主要内容如下:
介绍传统的Web应用和基于REST服务的Web应用 介绍OAuth认证流程和密码模式 创建一个基于ASP.NET Identity的Web API应用程序 基于$.ajax实现OAuth的注册、登录、注销和API调用 基于vue-resource实现OAuth的注册、登录、注销和API调用本文的最终示例是结合上一篇的CURD,本文的登录、注册、注销和API调用功能实现的。
本文9个示例的源码已放到GitHub:https://github.com/keepfool/vue-tutorials/tree/master/04.OAuth
OAuth介绍
传统的Web应用
在传统的Web应用程序中,前后端是放在一个站点下的,我们可以通过会话(Session)来保存用户的信息。
例如:一个简单的ASP.NET MVC应用程序,用户登录成功后,我们将用户的ID记录在Session中,假设为Session["UserID"]。
前端发送ajax请求时,如果这个请求要求已登录的用户才能访问,我们只需在后台Controller中验证Session["UserID"]是否为空,就可以判断用户是否已经登录了。
这也是传统的Web应用能够逃避HTTP面向无连接的方法。
基于REST服务的Web应用
当今很多应用,客户端和服务端是分离的,服务端是基于REST风格构建的一套Service,客户端是第三方的Web应用,客户端通过跨域的ajax请求获取REST服务的资源。
然而REST Service通常是被设计为无状态的(Stateless),这意味着我们不能依赖于Session来保存用户信息,也不能使用Session["UserID"]这种方式确定用户身份。
解决这个问题的方法是什么呢?常规的方法是使用OAuth 2.0。
对于用户相关的OpenAPI,为了保护用户数据的安全和隐私,第三方Web应用访问用户数据前都需要显式的向用户征求授权。
相比于OAuth 1.0,OAuth 2.0的认证流程更加简单。
专用名词介绍
在了解OAuth 2.0之前,我们先了解几个名词:
Resource:资源,和REST中的资源概念一致,有些资源是访问受保护的 Resource Server:存放资源的服务器 Resource Owner:资源所有者,本文中又称为用户(user) User Agent:用户代理,即浏览器 Client: 访问资源的客户端,也就是应用程序 Authorization Server:认证服务器,用于给Client提供访问令牌的服务器 Access Token:访问资源的令牌,由Authorization Server器授予,Client访问Resource时,需提供Access Token Bearer Token:Bearer Token是Access Token的一种,另一种是Mac Token。 Bearer Token的使用格式为:Bearer XXXXXXXXToken的类型请参考:https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-oauth-v2-15#section-7.1
有时候认证服务器和资源服务器可以是一台服务器,本文中的Web API示例正是这种运用场景。
OAuth认证流程
在知道这几个词以后,我们用这几个名词来编个故事。
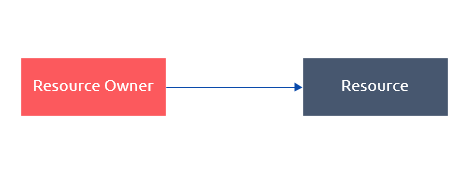
简化版本
这个故事的简化版本是:用户(Resource Owner)访问资源(Resource)。
具体版本
简化版的故事只有一个结果,下面是这个故事的具体版本:
用户通过浏览器打开客户端后,客户端要求用户给予授权。 客户端可以直接将授权请求发给用户(如图所示),或者发送给一个中间媒介,比如认证服务器。 用户同意给予客户端授权,客户端收到用户的授权。 授权模式(Grant Type)取决于客户端使用的模式,以及认证服务器所支持的模式。 客户端提供身份信息,然后向认证服务器发送请求,申请访问令牌 认证服务器验证客户端提供的身份信息,如果验证通过,则向客户端发放令牌 客户端使用访问令牌,向资源服务器请求受保护的资源 资源服务器验证访问令牌,如果有效,则向客户端开放资源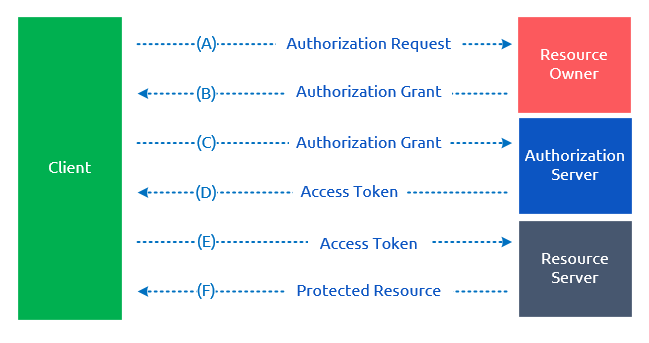
以上几个步骤,(B)是较为关键的一个,即用户怎么样才能给客户端授权。有了这个授权以后,客户端就可以获取令牌,进而通过临牌获取资源。这也是OAuth 2.0的运行流程,详情请参考:https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-oauth-v2-15#section-1.2
客户端的授权模式
客户端必须得到用户的授权(authorization grant),才能获得令牌(access token)。
OAuth 2.0定义了四种授权方式:
授权码模式(authorization code) 简化模式(implicit) 密码模式(resource owner password credentials) 客户端模式(client credentials)本文的示例是基于密码模式的,我就只简单介绍这种模式,其他3我就不介绍了。
密码模式
密码模式(Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant)中,用户向客户端提供自己的用户名和密码。客户端使用这些信息,向服务端申请授权。
在这种模式中,用户必须把自己的密码给客户端,但是客户端不得储存密码。这通常用在用户对客户端高度信任的情况下,比如客户端是操作系统的一部分,或者由一个著名公司出品。
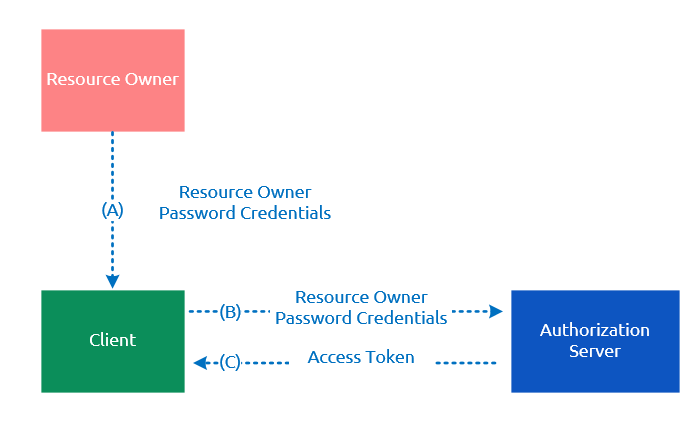
密码嘛事的执行步骤如下:
(A)用户向客户端提供用户名和密码。
(B)客户端将用户名和密码发给认证服务器,向后者请求令牌。
(C)认证服务器确认无误后,向客户端提供访问令牌。
(B)步骤中,客户端发出的HTTP请求,包含以下参数:
grant_type:表示授权类型,此处的值固定为"password",必选项。 username:表示用户名,必选项。 password:表示用户的密码,必选项。 scope:表示权限范围,可选项。注意:在后面的客户端示例中,除了提供username和password,grant_type也是必须指定为"password",否则无法获取服务端的授权。
服务端环境准备
如果您是前端开发人员,并且未接触过ASP.Net Web API,可以跳过此段落。
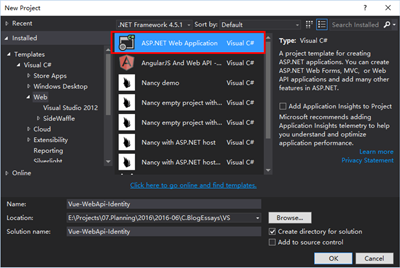
Authentication选择Individual User Accounts
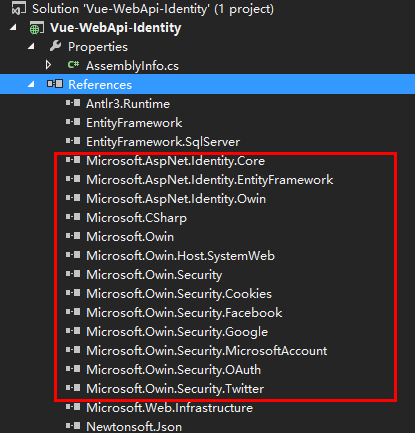
创建这个Web API工程时,VS会自动引入Owin和AspNet.Identity相关的库。
修改ValuesController,除了IEnumerable<string> Get()操作外,其他操作都删除,并为该操作应用[Authorize]特性,这表示客户端必须通过身份验证后才能调用该操作。
public class ValuesController : ApiController
{
// GET: api/Values
[Authorize]
public IEnumerable<string> Get()
{
return new string[] { "value1", "value2" };
}
}
添加Model, Controller
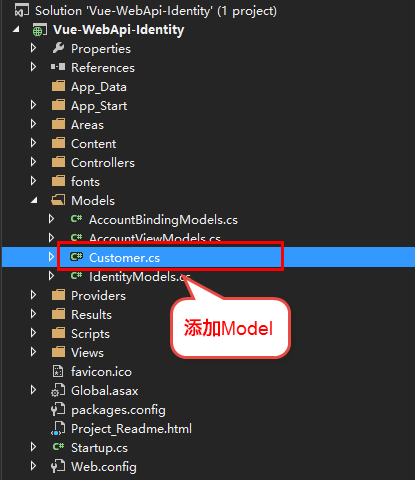
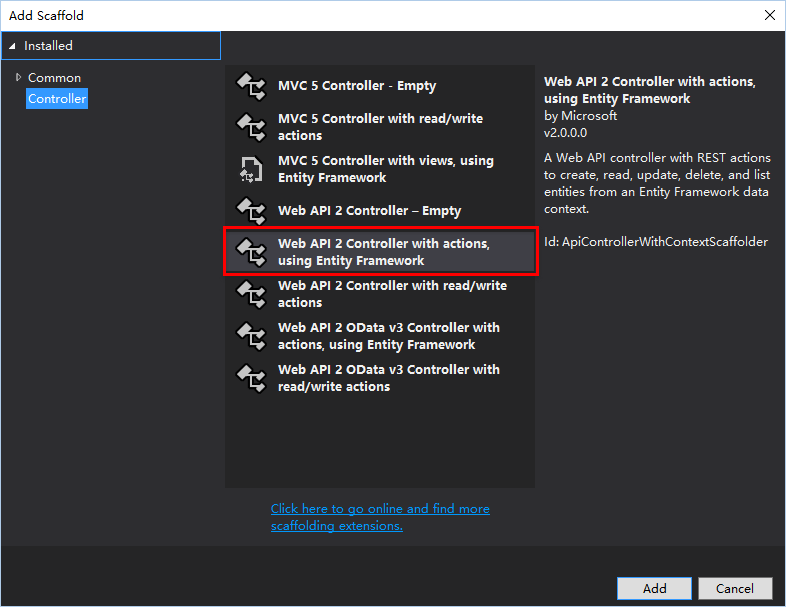
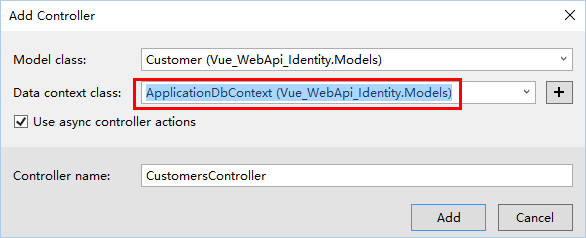
初始化数据库
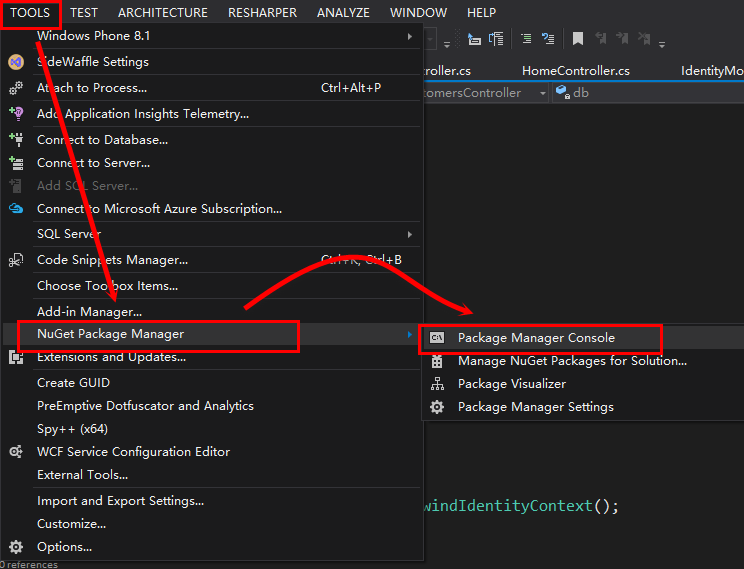
执行以下3个命令
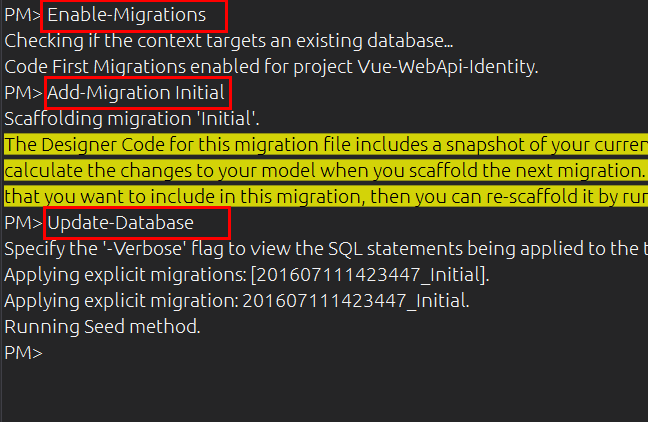
CustomersController类有5个Action,除了2个GET请求外,其他3个请求分别是POST, PUT和DELETE。
为这3个请求添加[Authorize]特性,这3个请求必须通过身份验证才能访问。
public class CustomersController : ApiController
{
private ApplicationDbContext db = new ApplicationDbContext();
// GET: api/Customers
public IQueryable<Customer> GetCustomers()
{
return db.Customers;
}
// GET: api/Customers/5
[ResponseType(typeof(Customer))]
public async Task<IHttpActionResult> GetCustomer(int id)
{
Customer customer = await db.Customers.FindAsync(id);
if (customer == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(customer);
}
// PUT: api/Customers/5
[Authorize]
[ResponseType(typeof(void))]
public async Task<IHttpActionResult> PutCustomer(int id, Customer customer)
{
// ...
}
// POST: api/Customers
[Authorize]
[ResponseType(typeof(Customer))]
public async Task<IHttpActionResult> PostCustomer(Customer customer)
{
// ...
}
// DELETE: api/Customers/5
[ResponseType(typeof(Customer))]
[Authorize]
public async Task<IHttpActionResult> DeleteCustomer(int id)
{
// ...
}
}
让Web API以CamelCase输出JSON
在Global.asax文件中添加以下几行代码:
var formatters = GlobalConfiguration.Configuration.Formatters;
var jsonFormatter = formatters.JsonFormatter;
var settings = jsonFormatter.SerializerSettings;
settings.Formatting = Formatting.Indented;
settings.ContractResolver = new CamelCasePropertyNamesContractResolver();
启用CORS
在Nuget Package Manager Console输入以下命令:
Install-Package Microsoft.AspNet.WebApi.Cors
在WebApiConfig中启用CORS:
public static class WebApiConfig
{
public static void Register(HttpConfiguration config)
{
var cors = new EnableCorsAttribute("*", "*", "*");
config.EnableCors(cors);
// ...
}
}
类说明
在执行上述步骤时,VS已经帮我们生成好了一些类
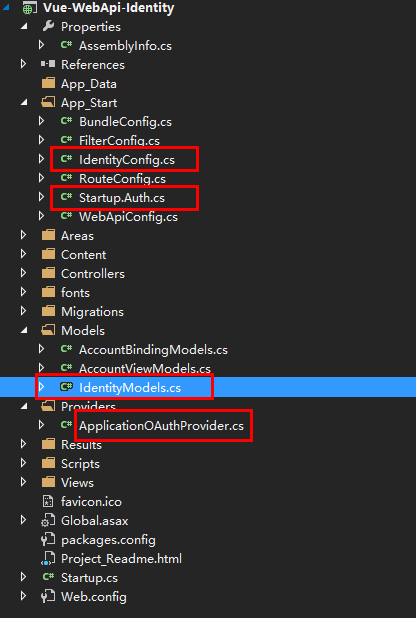
IdentityModels.cs:包含ApplicationDbContext类和ApplicationUser类,无需再创建DbContext类
public class ApplicationUser : IdentityUser
{
// ...
}
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser>
{
// ...
}
Startup.Auth.cs:用于配置OAuth的一些属性。
public partial class Startup
{
public static OAuthAuthorizationServerOptions OAuthOptions { get; private set; }
public static string PublicClientId { get; private set; }
// For more information on configuring authentication, please visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=301864
public void ConfigureAuth(IAppBuilder app)
{
// ..
// Configure the application for OAuth based flow
PublicClientId = "self";
OAuthOptions = new OAuthAuthorizationServerOptions
{
TokenEndpointPath = new PathString("/Token"),
Provider = new ApplicationOAuthProvider(PublicClientId),
AuthorizeEndpointPath = new PathString("/api/Account/ExternalLogin"),
AccessTokenExpireTimeSpan = TimeSpan.FromDays(14),
// In production mode set AllowInsecureHttp = false
AllowInsecureHttp = true
};
// Enable the application to use bearer tokens to authenticate users
app.UseOAuthBearerTokens(OAuthOptions);
// ..
}
}
这些OAuth配置项,我们只用关注其中的两项:
TokenEndpointPath:表示客户端发送验证请求的地址,例如:Web API的站点为www.example.com,验证请求的地址则为www.example.com/token。 UseOAuthBearerTokens:使用Bearer类型的token_type(令牌类型)。ApplicationOAuthProvider.cs:默认的OAuthProvider实现,GrantResourceOwnerCredentials方法用于验证用户身份信息,并返回access_token(访问令牌)。
public override async Task GrantResourceOwnerCredentials(OAuthGrantResourceOwnerCredentialsContext context)
{
// ...
}
通俗地讲,客户端输入用户名、密码,点击登录后,会发起请求到www.example.com/token。
token这个请求在服务端执行的验证方法是什么呢?正是GrantResourceOwnerCredentials方法。
客户端发起验证请求时,必然是跨域的,token这个请求不属于任何ApiController的Action,而在WebApiConfig.cs中启用全局的CORS,只对ApiController有效,对token请求是不起作用的。
所以还需要在GrantResourceOwnerCredentials方法中添加一行代码:
public override async Task GrantResourceOwnerCredentials(OAuthGrantResourceOwnerCredentialsContext context)
{
context.Response.Headers.Add("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", new []{"*"});
// ...
}
IdentityConfig.cs:配置用户名和密码的复杂度,主要用于用户注册时。例如:不允许用户名为纯字母和数字的组合,密码长度至少为6位…。
public static ApplicationUserManager Create(IdentityFactoryOptions<ApplicationUserManager> options, IOwinContext context)
{
var manager = new ApplicationUserManager(new UserStore<ApplicationUser>(context.Get<ApplicationDbContext>()));
// Configure validation logic for usernames
manager.UserValidator = new UserValidator<ApplicationUser>(manager)
{
AllowOnlyAlphanumericUserNames = false,
RequireUniqueEmail = true
};
// Configure validation logic for passwords
manager.PasswordValidator = new PasswordValidator
{
RequiredLength = 6,
RequireNonLetterOrDigit = true,
RequireDigit = true,
RequireLowercase = true,
RequireUppercase = true,
};
// ...
return manager;
}
使用Postman测试GET和POST请求
测试GET请求
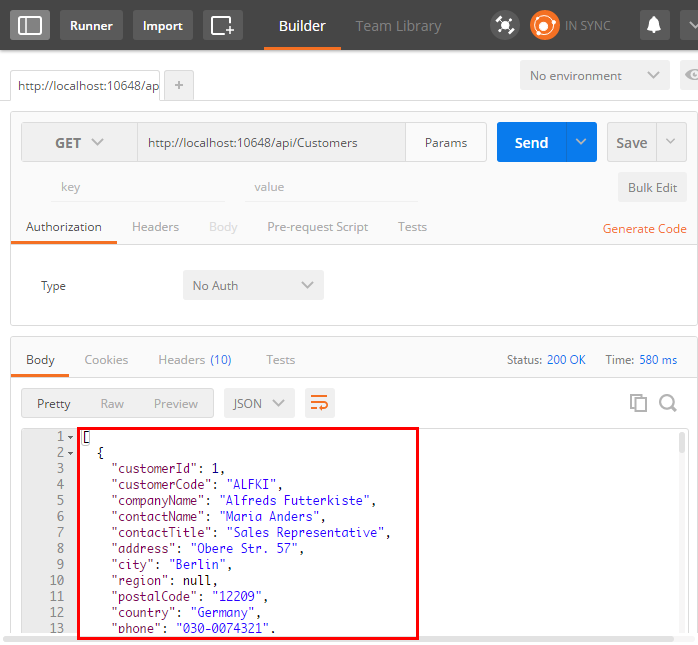
GET请求测试成功,可以获取到JSON数据。
测试POST请求
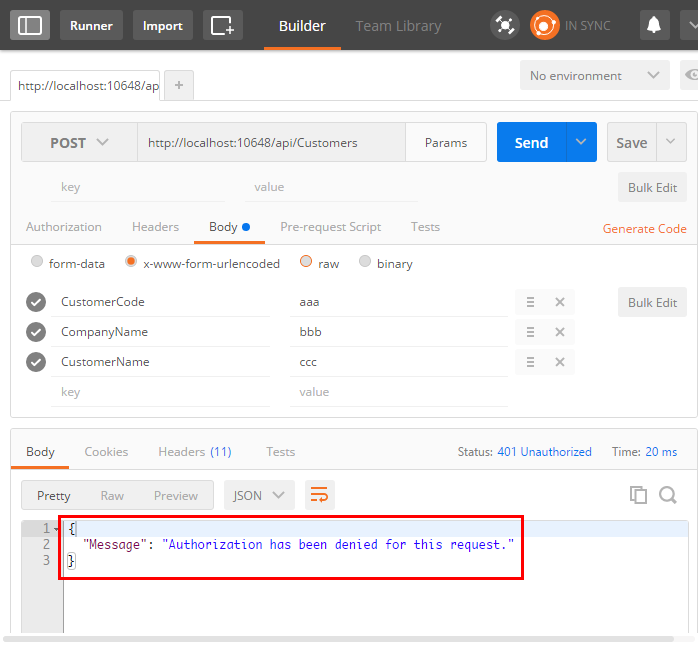
POST请求测试不通过,提示:验证不通过,请求被拒绝。
基于$.ajax实现注册、登录、注销和API调用
服务端的环境已经准备好了,现在我们就逐个实现用户注册、登录,以及API调用功能吧。
注册
页面的HTML代码如下:
<div id="app">
<div class="container">
<span id="message">{{ msg }}</span>
</div>
<div class="container">
<div class="form-group">
<label>电子邮箱</label>
<input type="text" v-model="registerModel.email" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>密码</label>
<input type="text" v-model="registerModel.password" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>确认密码</label>
<input type="text" v-model="registerModel.confirmPassword" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label></label>
<button @click="register">注册</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
创建Vue实例,然后基于$.ajax发送用户注册请求:
var demo = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
registerUrl: 'http://localhost:10648/api/Account/Register',
registerModel: {
email: '',
password: '',
confirmPassword: ''
},
msg: ''
},
methods: {
register: function() {
var vm = this
vm.msg = ''
$.ajax({
url: vm.registerUrl,
type: 'POST',
dataType: 'json',
data: vm.registerModel,
success: function() {
vm.msg = '注册成功!'
},
error: vm.requestError
})
},
requestError: function(xhr, errorType, error) {
this.msg = xhr.responseText
}
}
})
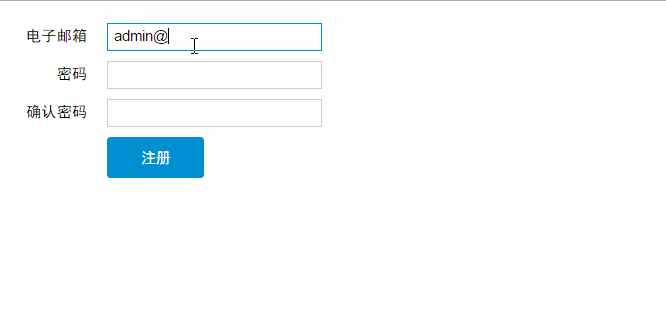
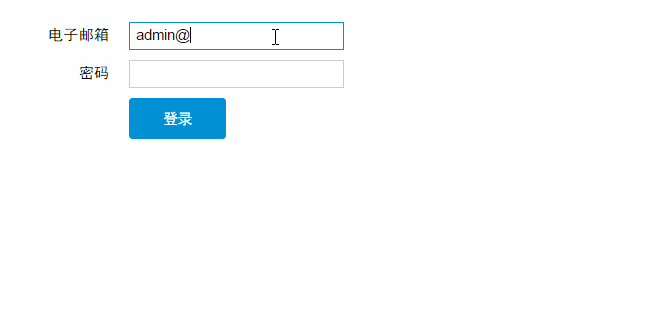
登录和注销
登录的HTML代码:
<div id="app">
<div class="container text-center">
<span id="message">{{ msg }}</span>
</div>
<div class="container">
<div class="account-info">
<span v-if="userName">{{ userName }} | <a href="#" rel="external nofollow" @click="logout">注销</a></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="container">
<div class="form-group">
<label>电子邮箱</label>
<input type="text" v-model="loginModel.username" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>密码</label>
<input type="text" v-model="loginModel.password" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label></label>
<button @click="login">登录</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
创建Vue实例,然后基于$.ajax发送用户登录请求:
var demo = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
loginUrl: 'http://localhost:10648/token',
logoutUrl: 'http://localhost:10648/api/Account/Logout',
loginModel: {
username: '',
password: '',
grant_type: 'password'
},
msg: '',
userName: ''
},
ready: function() {
this.userName = sessionStorage.getItem('userName')
},
methods: {
login: function() {
var vm = this
vm.msg = ''
vm.result = ''
$.ajax({
url: vm.loginUrl,
type: 'POST',
dataType: 'json',
data: vm.loginModel,
success: function(data) {
vm.msg = '登录成功!'
vm.userName = data.userName
sessionStorage.setItem('accessToken', data.access_token)
sessionStorage.setItem('userName', vm.userName)
},
error: vm.requestError
})
},
logout: function() {
var vm = this
vm.msg = ''
$.ajax({
url: vm.logoutUrl,
type: 'POST',
dataType: 'json',
success: function(data) {
vm.msg = '注销成功!'
vm.userName = ''
vm.loginModel.userName = ''
vm.loginModel.password = ''
sessionStorage.removeItem('userName')
sessionStorage.removeItem('accessToken')
},
error: vm.requestError
})
},
requestError: function(xhr, errorType, error) {
this.msg = xhr.responseText
}
}
})
在试验这个示例时,把Fiddler也打开,我们一共进行了3次操作:
第1次操作:输入了错误的密码,服务端响应400的状态码,并提示了错误信息。 第2次操作:输入了正确的用户名和密码,服务端响应200的状态码 第3次操作:点击右上角的注销链接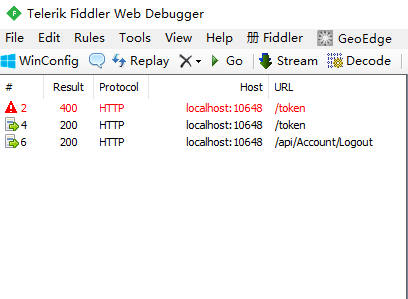
注意第2次操作,在Fiddler中查看服务端返回的内容:
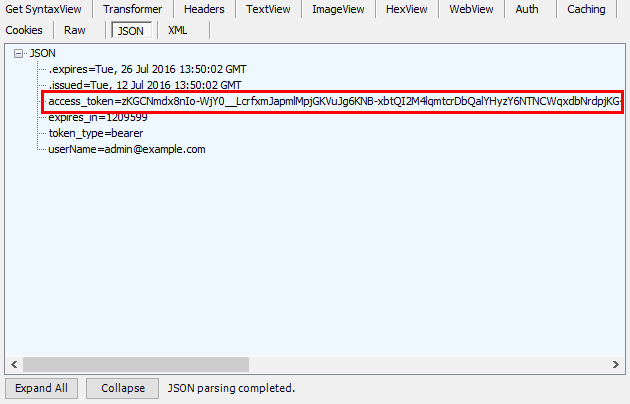
服务端返回了access_token, expires_in, token_type,userName等信息,在客户端可以用sessionStorage或localStorage保存access_token。
调用API
取到了access_token后,我们就可以基于access_token去访问服务端受保护的资源了。
这里我们要访问的资源是/api/Values,它来源于ValuesController的Get操作。
基于注册画面,添加一段HTML代码:
<div class="container text-center">
<div>
<button @click="callApi">调用API</button>
</div>
<div class="result">
API调用结果:{{ result | json }}
</div>
</div>
在Vue实例中添加一个callApi方法:
callApi: function() {
var vm = this
vm.msg = ''
vm.result = ''
headers = {}
headers.Authorization = 'Bearer ' + sessionStorage.getItem('accessToken');
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
dataTye: 'json',
url: vm.apiUrl,
headers: headers,
success: function(data) {
vm.result = data
},
error: vm.requestError
})
}
在调用callApi方法时,设置了请求头的Authorization属性,其格式为:"Bearer access_token"。
由于服务端指定使用了Bearer类型的access token,所以客户端必须使用这种格式将access token传给资源服务器。
在试验这个示例时,我们一共进行了5次操作:
第1次操作:没有输入用户名和密码,直接点击[调用API]按钮,服务端返回401的状态码,表示该请求未授权。 第2次操作:输入用户名和密码,然后店点击登录按钮,登录成功。 第3次操作:点击[调用API]按钮,服务端返回200的状态码,请求成功。 第4次操作:点击[注销]链接,注销成功。 第5次操作:再次点击[调用API]按钮,服务端返回401的状态码,表示该请求未授权。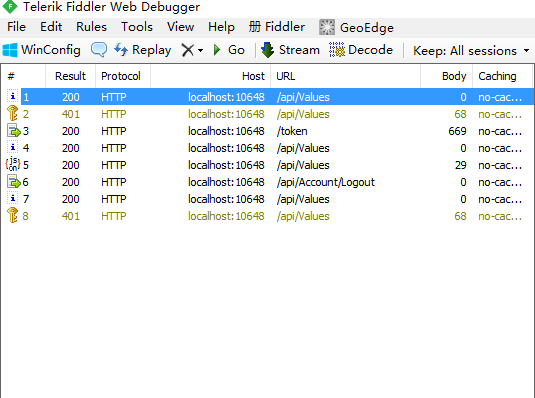
有人可能会注意到,为什么每次点击[调用API]按钮,都发起了两次请求?
这是因为当浏览器发送跨域请求时,浏览器都会先发送一个OPTIONS预请求(preflight request)给目标站点,用于确认目标站点是否接受跨域请求,如果目标站点不支持跨域请求,浏览器会提示错误:
No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource.
如果是POST请求,且数据类型(Content-Type)是application/x-www-form-urlencoded,multipart/form-data 或 text/plain中的一种,则浏览器不会发送预请求,上图的/token请求就是满足该条件的。
zepto会自动将非GET请求的Content-Type设置为application/x-www-form-urlencoded:
if (settings.contentType || (settings.contentType !== false && settings.data && settings.type.toUpperCase() != 'GET'))
setHeader('Content-Type', settings.contentType || 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
image
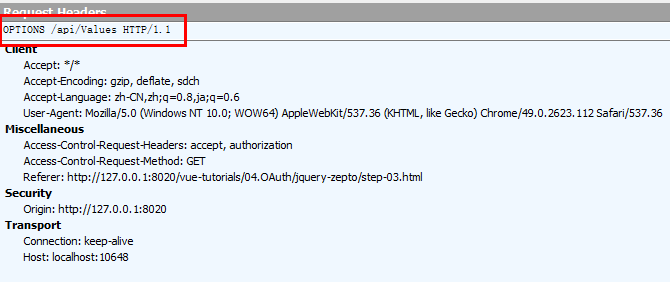
我们还是通过Fidder看一下第1次/api/Values请求和响应的Headers信息
请求的Headers信息,它是一次OPTIONS请求。
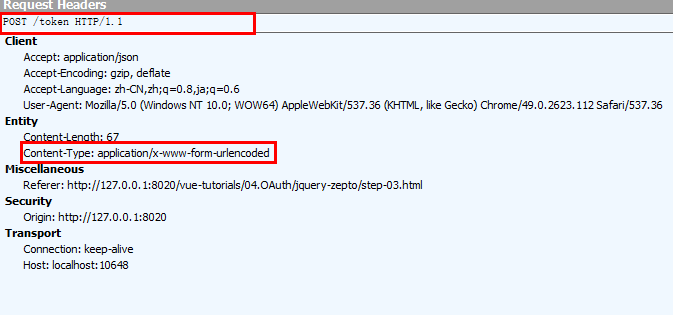
响应的Headers信息,Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *表示允许所有外部站点对目标站点发送跨域请求。
更多CORS的知识,请参考MDN上的说明:
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/HTTP/Access_control_CORS
基于vue-resource实现注册、登录和API调用
基于vue-resource实现这3项功能时,沿用上面的HTML代码。
注册
更为简洁的register方法:
register: function() {
this.$http.post(this.registerUrl, this.registerModel)
.then((response) => {
this.msg = '注册成功!'
}).catch((response) => {
this.msg = response.json()
})
}
注意:当使用vue-resource发送注册的POST请求时,Fiddler捕获到了2次请求,第1次是由浏览器发送的OPTIONS预请求,第2次才是实际的POST请求。这和使用$.ajax时是不一样的,因为$.ajax会将非GET请求的Content-Type设置为application/x-www-form-urlencoded,而vue-resource发送POST请求的Content-Type为application/json;charset=UTF-8。
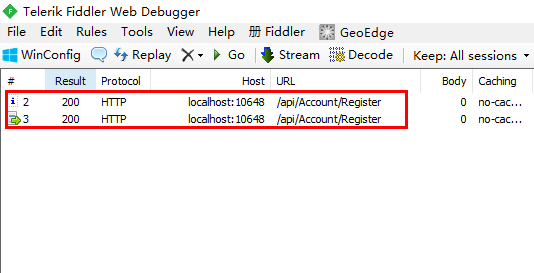
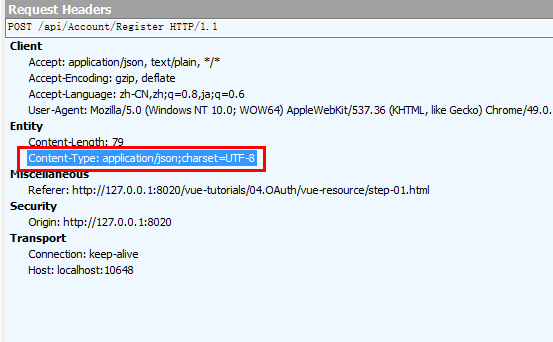
启用emulateJSON选项,可以让浏览器不发送OPTIONS预请求,有两种启用方式。
1.全局启用
Vue.http.options.emulateJSON = true
2.局部启用
this.$http.post(this.registerUrl, this.registerModel ,{ emulateJSON : true})
.then( (response) => {
this.msg = '注册成功!'
})
启用了emulateJSON选项后,使得POST请求的Content-Type变为application/x-www-form-urlencoded
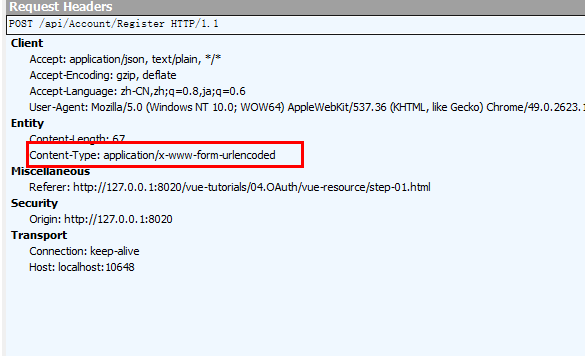
登录和注销
登录和注销的方法:
login: function() {
this.$http.post(this.loginUrl, this.loginModel)
.then((response) => {
var body = response.json()
this.msg = '登录成功!'
this.userName = body.userName
sessionStorage.setItem('accessToken', body.access_token)
sessionStorage.setItem('userName', body.userName)
}).catch(this.requestError)
},
logout: function() {
this.$http.post(this.logoutUrl)
.then((response) => {
this.msg = '注销成功!'
this.userName = ''
this.loginModel.username = ''
this.loginModel.password = ''
sessionStorage.removeItem('userName')
sessionStorage.removeItem('accessToken')
}).catch(this.requestError)
},
requestError: function(response) {
this.msg = response.json()
}
API调用
调用API的方法也更为简洁:
callApi: function() {
var headers = {}
headers.Authorization = 'Bearer ' + sessionStorage.getItem('accessToken')
this.$http.get(this.apiUrl, {
headers: headers
})
.then((response) => {
this.result = response.json()
}).catch(this.requestError)
}
同样的,在发送请求前,需要将access token添加到请求头。
综合示例
本文在准备服务端环境的时候,提供了一个CustomersController,除了GET操作,其他操作的访问都是受保护的,需要用户登录以后才能操作。
现在我们来实现这个示例, 该示例结合了上一篇的CURD示例,以及本文的注册、登录、注销功能。
具体代码我就不再贴出来了,大家结合源代码试一试吧。