Android内部存储与外部存储的示例讲解
什么是内部存储和外部存储
内部存储与外部存储的代码示例
什么是内部存储和外部存储1.内部存储与外部存储的存储介质:
内部存储的介质:RAM(内存) + 内部ROM
外部存储的介质:外部ROM + SDCard(TS卡等等)。
2.内部存储与外部存储的存储特点:
一般来说,以/data开头的是内部存储。且内部存储不需要任何权限。
例如:
/data/data/< applicationId >/shared_prefs
/data/data/< applicationId >/databases
/data/data/< applicationId >/files // 通过context.getFilesDir() 获取该目录
/data/data/< applicationId >/cache //通过context.getCacheDir() 获取该目录
内部存储需要关注的文件夹:
app文件夹(未root无法打开):存放着所有app的apk文件夹
data文件夹:内部都是app的包名,存储着应用程序相关的数据,例如 data/data/包名/(shared_prefs、database、files、cache)
Android SDK提供了几个常见的内部存储文件的权限
Context.MODE_PRIVATE :私有方式存储,其他应用无法访问,覆盖旧的同名文件
Context.MODE_APPEND:私有方式存储,若有旧的同名文件,则在该文件上追加数据
一般来说,外部存储会放在storage文件夹下或者mnt文件夹下。且需要安卓的权限。
例如:
私有外部存储
/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/< applicationId >/files/Music //Context.getExternalFilesDir() 包含如Music等文件夹
/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/< applicationId >/cache //Context.getExternalCacheDir 外部缓存文件
以及共有外部存储
/storage/emulated/0 Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory()
/storage/emulated/0/Pictures
Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_PICTURES)
外部存储需要注意的文件夹即外部存储的分类:
storage中有一个sdcard文件夹,sdcard下面可以分两类存储:
外部共有存储(共有目录):里面常见的有Pictures、Download等文件夹.
外部私有存储(私有目录):系统中的数据。

内部存储与外部存储的文件夹:
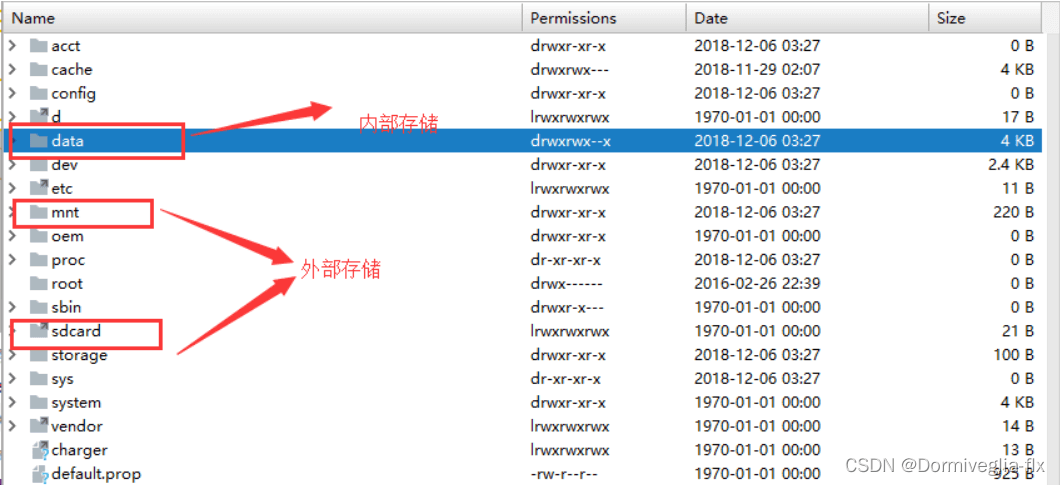
3.内部存储与外部存储,释放内存方面的总结:
内部存储:随应用卸载被删除。外部存储:
1.公有目录:存放一些下载的视频文件等,比如还有movies,fictures,music等公有的一些文件目录。
2.私有目录:随应用卸载被删除。
内部存储与外部存储的代码示例内部存储
// 存
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//第一个参数:文件名
//第二个参数:表示文件输出的类型 这里选择Context.MODE_PRIVATE每次生成相同的文件名,则覆盖原有的文件
fos = openFileOutput('test', Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
String nameAndPassword = username + "." + password;
byte[] bytes = nameAndPassword.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 取
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = openFileInput(fileName);
//fis.available() 判断文件有多少个字节
byte[] bytes = new byte[fis.available()];
while (fis.read(bytes) != -1) {
String message = new String(bytes);
String[] split = message.split("\\.");
tv_message.setText("用户名:" + split[0] + "\n" + "密码:" + split[1]);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
外部存储
// 获取外部存储地址的位置并创建文件:
new File(getExternalFilesDir(Environment.DIRECTORY_DOWNLOADS)
// 存
OutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File(getExternalFilesDir(Environment.DIRECTORY_DOWNLOADS), 'test2'));
String nameAndPassword = username + "." + password;
byte[] bytes = nameAndPassword.getBytes();
outputStream.write(bytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (outputStream != null) {
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 取
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
//第一个参数:文件目录 第二个参数:文件名
//getExternalFilesDir(Environment.DIRECTORY_DOWNLOADS)对应的路径为:
// /storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.example.customviewproject/files/Download
File file = new File(getExternalFilesDir(Environment.DIRECTORY_DOWNLOADS), fileName);
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//判断当前文件的字节个数
byte[] bytes = new byte[fis.available()];
while (fis.read(bytes) != -1) {
String message = new String(bytes);
String[] split = message.split("\\.");
tv_message.setText("用户名:" + split[0] + "\n" + "密码:" + split[1]);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
到此这篇关于Android内部存储与外部存储的示例讲解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android内部存储与外部存储内容请搜索软件开发网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持软件开发网!