Android 深入探究自定义view之流式布局FlowLayout的使用
文章开始前思考个问题,view到底是如何摆放到屏幕上的?在xml布局中,我们可能用到match_parent、wrap_content或是具体的值,那我们如何转为具体的dp?对于层层嵌套的布局,他们用的都不是具体的dp,我们又该如何确定它们的尺寸?
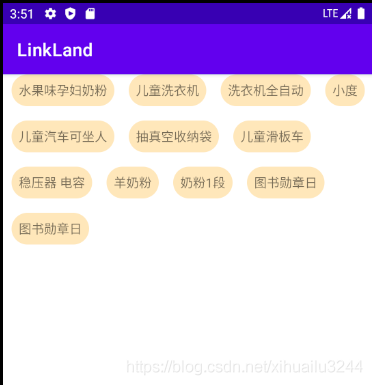
下图是实现效果
想想自定义view我们都要做哪些事情
布局,我们要确定view的尺寸以及要摆放的位置,也就是 onMeasure() 、onLayout() 两方法
显示,布局之后是怎么把它显示出来,主要用的是onDraw,可能用到 :canvas paint matrix clip rect animation path(贝塞尔) line
交互,onTouchEvent
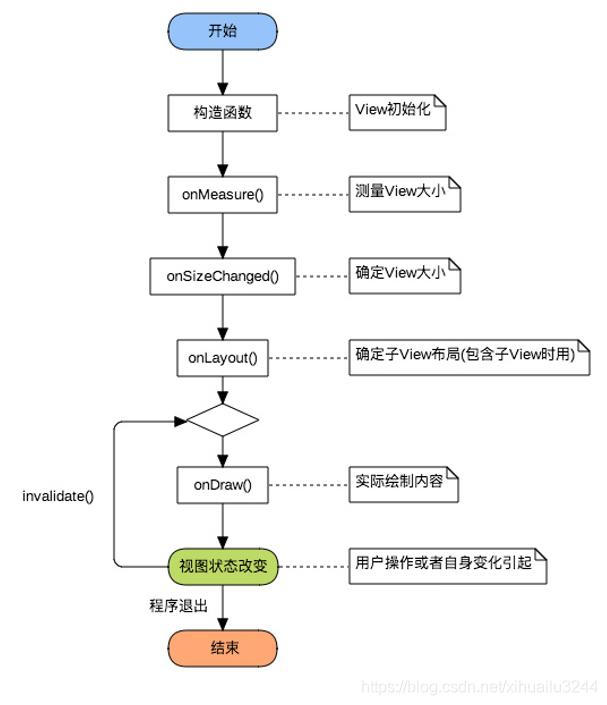
本文要做的是流式布局,继承自ViewGroup,主要实现函数是onMeasure() 、onLayout() 。下图是流程图
onMeasure
onMeasure是测量方法,那测量的是什么?我们不是在xml已经写好view的尺寸了吗,为什么还要测量?
有这么几个问题,我们在xml写view的时候确实写了view的width与height,但那玩意是具体的dp吗?我们可能写的是match_parent,可能是wrap_content,可能是权重,可能是具体的长度。对于不是确定值的我们要给它什么尺寸?哪怕写的是确定值就一定能给它吗,如果父布局最大宽度是100dp,子布局写的是200dp咋办?对于多层级的view,我们只是调用本个view的onMeasure方法吗?
以下面的图为栗子
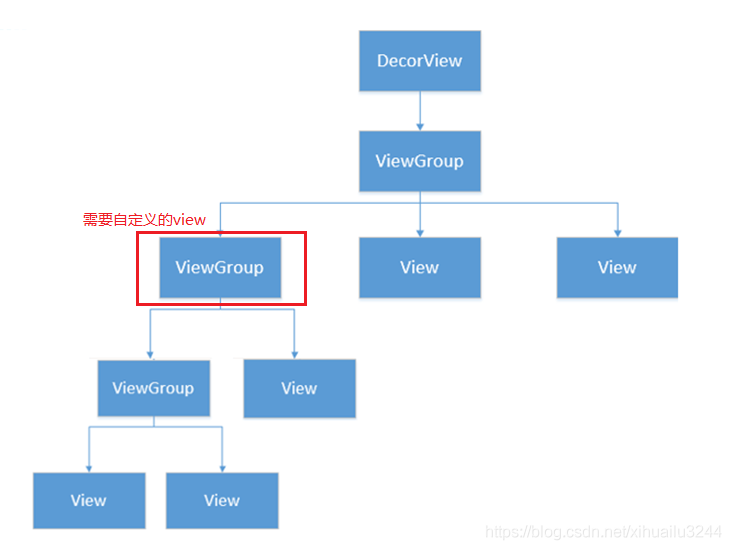
如果上图圈红的View就是我们要自定义的view,我们该怎么测量它?
首先我们要知道它的父布局能给它多大的空间
对于容器类型的view,根据其所有子view需要的空间计算出view所需的尺寸
首先要明确一点:测量是自上而下递归的过程!以FlowLayout的高度举例,它的height要多少合适?根据布局的摆放逐个测量每行的高度得出其所需的height,这个测出的高度再根据父布局给出的参考做计算,最后得到真正的高度。在测量子view的时候,子view可能也是容器,其内部也有很多view,其本身的不确定性需要遍历其子布局,这是一个递归的过程!
下面开始我们的测量过程,假设FlowLayout的父布局是LinearLayout,整体UI布局如下
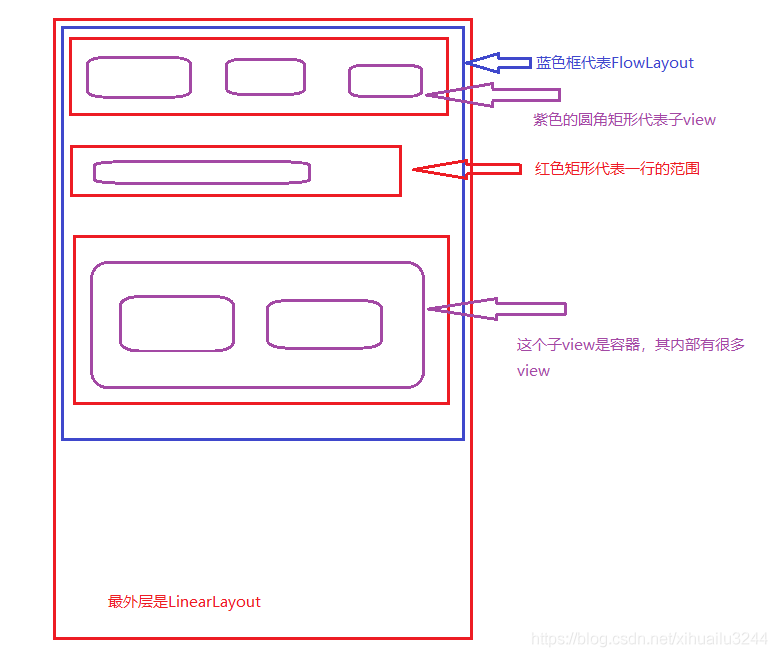
LinearLayout给它的空间有多大,还记得onMeasure的两个参数嘛,这俩是父布局给的参考值,也是父布局对其约束限制
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
MeasureSpec由两部分构成,高2位表示mode,低30位表示size;父布局给的参考宽高
int selfWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int selfHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
由此我们可以得到父布局给的空间大小,也就是FlowLayout的最大空间。那我们实际需要多大空间呢,我们需要测量所以的子view。
子view的摆放逻辑:
本行能放下则放到本行,即满足条件 lineUsed + childWidthMeasured + mHorizontalSpacing < selfWidth
本行放不下则另起一行
摆放逻辑有了,怎么测量子view
获得子view的LayoutParams从而获得xml里设置的layout_width与layout_height
调用getChildMeasureSpec方法算出MeasureSpec
子view调用measure方法测量
//获得LayoutParams
LayoutParams childParams = childView.getLayoutParams();
//计算measureSpec
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec, parentLeft + parentRight, childParams.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec, parentTop + parentBottom, childParams.height);
//测量
childView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
下面是 getChildMeasureSpec 内部实现,以横向尺寸为例
//以横向尺寸为例,第一个参数是父布局给的spec,第二个参数是扣除自己使用的尺寸,第三个是layoutParams
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
//老王的钱是确定的,小王有三种可能
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
//老王的钱最多有多少,小王有三种可能
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
//老王的钱不确定,小王有三种可能
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//noinspection ResourceType
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
上面的算法其实很简单,根据父布局给的mode和size结合自身的尺寸算出自己的mode和size,具体规则如下
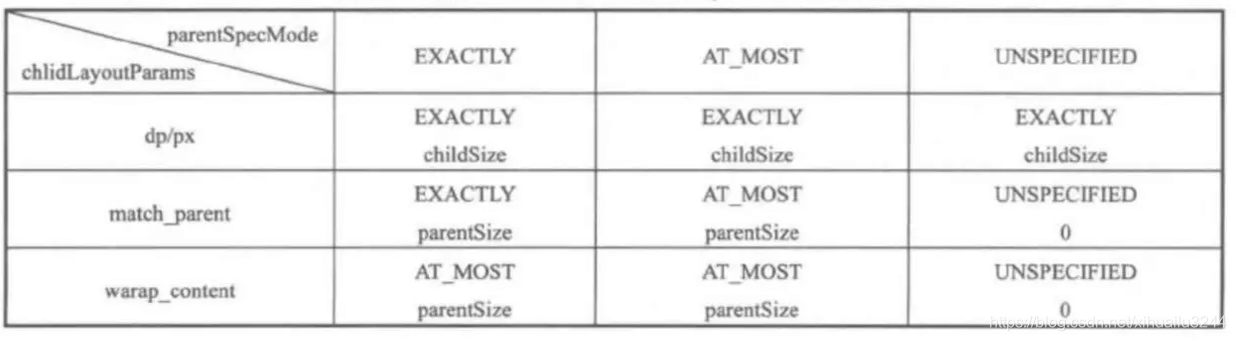
算法的实现是父布局有三种可能,子布局三种可能,总共9种可能。就像下面的小王想跟老王借钱买房,有几种可能?

测量完子view后怎么确定布局的大小?
测量所有行,得到最大的值作为布局的width
测量所有行的高度,高度的总和是布局的height
调用 setMeasuredDimension 函数设置最终的尺寸
onLayout基于测量工作我们基本确定了所有子view的摆放位置,这阶段要做的就是把所有的view摆放上去,调用子view的layout函数即可
具体代码实现
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
private int mHorizontalSpacing = dp2px(16); //每个item横向间距
private int mVerticalSpacing = dp2px(8); //每个item横向间距
// 记录所有的行
private List<List<View>> allLines = new ArrayList<>();
// 记录所有的行高
private List<Integer> lineHeights = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* new FlowLayout(context) 的时候用
* @param context
*/
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* xml是序列化格式,里面都是键值对;所有的都在LayoutInflater解析
*反射
*
* @param context
* @param attrs
*/
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
/**
* 主题style
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @param defStyleAttr
*/
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
/**
* 自定义属性
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @param defStyleAttr
* @param defStyleRes
*/
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
/**
* onMeasure 可能会被调用多次
*/
private void clearMeasureParams() {
// 不断创建回收会造成内存抖动,clear即可
allLines.clear();
lineHeights.clear();
}
/**
* 度量---大部分是先测量孩子再测量自己。孩子的大小可能是一直在变的,父布局随之改变
* 只有ViewPager是先测量自己再测量孩子
* spec 是一个参考值,不是一个具体的值
* @param widthMeasureSpec 父布局给的。这是个递归的过程
* @param heightMeasureSpec 父布局给的
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
clearMeasureParams();
// 先测量孩子
int childCount = getChildCount();
int parentTop = getPaddingTop();
int parentLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int parentRight = getPaddingRight();
int parentBottom = getPaddingBottom();
// 爷爷给的参考值
int selfWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int selfHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// 保存一行所有的 view
List<View> lineViews = new ArrayList<>();
// 记录这行已使用多宽 size
int lineWidthUsed = 0;
// 一行的高
int lineHeight = 0;
// measure过程中,子view要求的父布局宽高
int parentNeedWidth = 0;
int parentNeedHeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
LayoutParams childParams = childView.getLayoutParams();
// 将LayoutParams转为measureSpec
/**
* 测量是个递归的过程,测量子View确定自身大小
* getChildMeasureSpec的三个参数,第一个是父布局传过来的MeasureSpec,第二个参数是去除自身用掉的padding,第三个是子布局需要的宽度或高度
*/
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec, parentLeft + parentRight, childParams.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec, parentTop + parentBottom, childParams.height);
childView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
// 获取子View测量的宽高
int childMeasuredWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int childMeasuredHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
// 需要换行
if (childMeasuredWidth + lineWidthUsed + mHorizontalSpacing > selfWidth) {
// 换行时确定当前需要的宽高
parentNeedHeight = parentNeedHeight + lineHeight + mVerticalSpacing;
parentNeedWidth = Math.max(parentNeedWidth, lineWidthUsed + mHorizontalSpacing);
// 存储每一行的数据 !!! 最后一行会被漏掉
allLines.add(lineViews);
lineHeights.add(lineHeight);
// 数据清空
lineViews = new ArrayList<>();
lineWidthUsed = 0;
lineHeight = 0;
}
lineViews.add(childView);
lineWidthUsed = lineWidthUsed + childMeasuredWidth + mHorizontalSpacing;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childMeasuredHeight);
//处理最后一行数据
if (i == childCount - 1) {
allLines.add(lineViews);
lineHeights.add(lineHeight);
parentNeedHeight = parentNeedHeight + lineHeight + mVerticalSpacing;
parentNeedWidth = Math.max(parentNeedWidth, lineWidthUsed + mHorizontalSpacing);
}
}
// 测量完孩子后再测量自己
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// 如果父布局给的是确切的值,测量子view则变得毫无意义
int realWidth = (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? selfWidth : parentNeedWidth;
int realHeight = (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? selfHeight : parentNeedHeight;
setMeasuredDimension(realWidth, realHeight);
}
/**
* 布局
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int currentL = getPaddingLeft();
int currentT = getPaddingTop();
for (int i = 0; i < allLines.size(); i++) {
List<View> lineViews = allLines.get(i);
int lineHeight = lineHeights.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++) {
View view = lineViews.get(j);
int left = currentL;
int top = currentT;
// 此处为什么不用 int right = view.getWidth(); getWidth是调用完onLayout才有的
int right = left + view.getMeasuredWidth();
int bottom = top + view.getMeasuredHeight();
// 子view位置摆放
view.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
currentL = right + mHorizontalSpacing;
}
currentT = currentT + lineHeight + mVerticalSpacing;
currentL = getPaddingLeft();
}
}
public static int dp2px(int dp) {
return (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, dp, Resources.getSystem().getDisplayMetrics());
}
}
实现效果如文章开头
FlowLayout 的 onMeasure方法是什么时候被调用的FlowLayout的onMeasure是在上面什么调用的,肯定是在其父布局做测量递归的时候调用的。比如FlowLayout的父布局是LinearLayout,咱们去LinearLayout中找实现
LinearLayout.onMeasure()
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
void measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec){
//获取子view 的 LayoutParams
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
...
...
//开始测量
measureChildBeforeLayout(child, i, widthMeasureSpec, 0,heightMeasureSpec, usedHeight);
}
void measureChildBeforeLayout(View child, int childIndex,int widthMeasureSpec, int totalWidth, int heightMeasureSpec,int totalHeight) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, totalWidth, heightMeasureSpec, totalHeight);
}
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//去除自己的使用,padding、margin剩下的再给子view
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
//此处子view调用其测量函数,也就是FlowLayout的测量
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
一些其他概念
MeasureSpec 是什么
自定义view常用的一个属性MeasureSpec,是View的内部类,封装了对子View的布局要求,由尺寸和模式组成。由于int类型由32位构成,所以他用高2位表示 Mode,低30位表示Size。
MeasureMode有三种 00 01 11
UNSPECIFIED:不对View大小做限制,系统使用
EXACTLY:确切的大小,如100dp
AT_MOST:大小不可超过某值,如:matchParent,最大不能超过父布局
LayoutParams 与 MeasureSpec 的关系
我们在xml写的键值对是不能直接转化为具体的dp的,根据父布局给的尺寸与模式计算出自己的MeasureSpec,通过不断的递归测量,得到最后的测量值。LayoutParams.width获取的就是xml里写的或许是match_parent,或许是wrap_content,这些是不能直接用的,根据父布局给出的参考值再通过测量子布局的尺寸最后才能得到一个具体的测量值
onLayout为什么不用 int right = view.getWidth() 而用 getMeasuredWidth
这要对整个流程有完整的理解才能回答,getWidth 是在 onLayout 调用后才有的值,getMeasuredWidth在测量后有值
到此这篇关于Android 深入探究自定义view之流式布局FlowLayout的使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android 流式布局FlowLayout内容请搜索软件开发网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持软件开发网!