手把手教你实现Python重试超时装饰器
一、前言
二、简单分析
三、代码模拟实现
重试装饰器-初版
重试装饰器-改进版
重试装饰器-加强版
重试装饰器-最终版
修改记录
一、前言在写业务代码时候,有许多场景需要重试某块业务逻辑,例如网络请求、购物下单等,希望发生异常的时候多重试几次。本文分享如何利用Python 的装饰器来进行面向切面(AOP)的方式实现自动重试器。
二、简单分析一个重试装饰器,最重要的就是发生意外异常处理失败自动重试,有如下几点需要注意
失败不能一直重试,因为可能会出现死循环浪费资源,因此需要有 最大重试次数 或者 最大超时时间
不能重试太频繁,因为太频繁容易导致重试次数很快用完,却没有成功响应,需要有 重试时间间隔 来限制,有时可以加大成功概率,例如网络请求时有一段时间是堵塞的,或者对方服务负载太高导致一段时间无法响应等。
简单分析完,我们的重试装饰器,就要支持可配置最大重试次数、最大超时时间、重试间隔,所以装饰器就要设计成带参数装饰器。
三、代码模拟实现 重试装饰器-初版分析完毕后,看看第一版的装饰器
import time
from functools import wraps
def task_retry(max_retry_count: int = 5, time_interval: int = 2):
"""
任务重试装饰器
Args:
max_retry_count: 最大重试次数 默认5次
time_interval: 每次重试间隔 默认2s
"""
def _task_retry(task_func):
@wraps(task_func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 函数循环重试
for retry_count in range(max_retry_count):
print(f"execute count {retry_count + 1}")
try:
task_result = task_func(*args, **kwargs)
return task_result
except Exception as e:
print(f"fail {str(e)}")
time.sleep(time_interval)
return wrapper
return _task_retry
装饰器内部闭包,就简单通过 for 循环 来执行指定重试次数,成功获取结果就直接 return 返回,发生异常则睡眠配置重试间隔时间后继续循环
写个例子来模拟测试下看看效果
没有异常正常执行,在函数中模拟一个异常来进行重试看看
@task_retry(max_retry_count=3, time_interval=1)
def user_place_order():
a = 1 / 0
print("user place order success")
return {"code": 0, "msg": "ok"}
ret = user_place_order()
print("user place order ret", ret)
>>>out
fail division by zero
execute count 2
fail division by zero
execute count 3
fail division by zero
user place order ret None
可以看到 user_place_order 函数执行了三遍,都发生了除零异常,最后超过最大执行次数,返回了 None 值,我们可以在主逻辑中来判断返回值是否为 None 来进行超过最大重试次数失败的业务逻辑处理
ret = user_place_order()
print("user place order ret", ret)
if not ret:
print("user place order failed")
...
重试装饰器-改进版
现在只能配置 最大重试次数 没有最大超时时间,有时候我们想不但有重试,还得在规定时间内完成,不想浪费太多试错时间。所以增加一个 最大超时时间配置选项默认为None,有值时超过最大超时时间退出重试。
def task_retry(max_retry_count: int = 5, time_interval: int = 2, max_timeout: int = None):
"""
任务重试装饰器
Args:
max_retry_count: 最大重试次数 默认 5 次
time_interval: 每次重试间隔 默认 2s
max_timeout: 最大超时时间,单位s 默认为 None,
"""
def _task_retry(task_func):
@wraps(task_func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 函数循环重试
start_time = time.time()
for retry_count in range(max_retry_count):
print(f"execute count {retry_count + 1}")
use_time = time.time() - start_time
if max_timeout and use_time > max_timeout:
# 超出最大超时时间
print(f"execute timeout, use time {use_time}s, max timeout {max_timeout}")
return
try:
return task_func(*args, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
print(f"fail {str(e)}")
time.sleep(time_interval)
return wrapper
return _task_retry
看看效果
# 超时
@task_retry(max_retry_count=3, time_interval=1, max_timeout=2)
def user_place_order():
a = 1 / 0
print("user place order success")
return {"code": 0, "msg": "ok"}
>>>out
execute count 1
fail division by zero
execute count 2
fail division by zero
execute count 3
execute timeout, use time 2.010528802871704s, max timeout 2
user place order ret None
# 超过最大重试次数
@task_retry(max_retry_count=3, time_interval=1)
def user_place_order():
a = 1 / 0
print("user place order success")
return {"code": 0, "msg": "ok"}
>>>out
execute count 1
fail division by zero
execute count 2
fail division by zero
execute count 3
fail division by zero
user place order ret None
# 正常
@task_retry(max_retry_count=3, time_interval=1, max_timeout=2)
def user_place_order():
# a = 1 / 0
print("user place order success")
return {"code": 0, "msg": "ok"}
>>>out
execute count 1
user place order success
user place order ret {'code': 0, 'msg': 'ok'}
重试装饰器-加强版
到这重试装饰器基本功能就实现了,但还可以加强,Python现在支持 async 异步方式写法,因此要是可以兼容异步写法那就更好了。先看看装饰异步函数会是什么样的效果
import time
import asyncio
import functools
def task_retry(max_retry_count: int = 5, time_interval: int = 2, max_timeout: int = None):
"""
任务重试装饰器
Args:
max_retry_count: 最大重试次数 默认 5 次
time_interval: 每次重试间隔 默认 2s
max_timeout: 最大超时时间,单位s 默认为 None,
"""
def _task_retry(task_func):
@wraps(task_func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 函数循环重试
start_time = time.time()
for retry_count in range(max_retry_count):
print(f"execute count {retry_count + 1}")
use_time = time.time() - start_time
if max_timeout and use_time > max_timeout:
# 超出最大超时时间
print(f"execute timeout, use time {use_time}s, max timeout {max_timeout}")
return
try:
return task_func(*args, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
print(f"fail {str(e)}")
time.sleep(time_interval)
return wrapper
return _task_retry
@task_retry(max_retry_count=3, time_interval=1, max_timeout=2)
def user_place_order():
# a = 1 / 0
print("user place order success")
return {"code": 0, "msg": "ok"}
@task_retry(max_retry_count=3, time_interval=2, max_timeout=5)
async def user_place_order_async():
"""异步函数重试案例"""
a = 1 / 0
print("user place order success")
return {"code": 0, "msg": "ok"}
async def main():
# 同步案例
# ret = user_place_order()
# print(f"user place order ret {ret}")
# 异步案例
ret = await user_place_order_async()
print(f"user place order ret {ret}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
asyncio.run(main())
# 正常时候
execute count 1
user place order success
user place order ret {'code': 0, 'msg': 'ok'}
# 异常时候
>>>out
execute count 1
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "G:/code/python/py-tools/decorator/base.py", line 138, in <module>
asyncio.run(main())
File "G:\softs\DevEnv\python-3.7.9\lib\asyncio\runners.py", line 43, in run
return loop.run_until_complete(main)
File "G:\softs\DevEnv\python-3.7.9\lib\asyncio\base_events.py", line 587, in run_until_complete
return future.result()
File "G:/code/python/py-tools/decorator/base.py", line 133, in main
ret = await user_place_order_async()
File "G:/code/python/py-tools/decorator/base.py", line 121, in user_place_order_async
a = 1 / 0
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
Process finished with exit code 1
发现发生异常的时候并没有重试,为什么呢?其实在执行 task_func() 它并没有真正的执行内部逻辑,而是返回一个 coroutine 协程对象,并不会报异常,所以再装饰器中执行一遍就成功就出来了,外面 ret = await user_place_order_async(), 后才真正的等待执行,然后执行函数内的逻辑再报异常就没有捕获到。我们可以打断点验证下
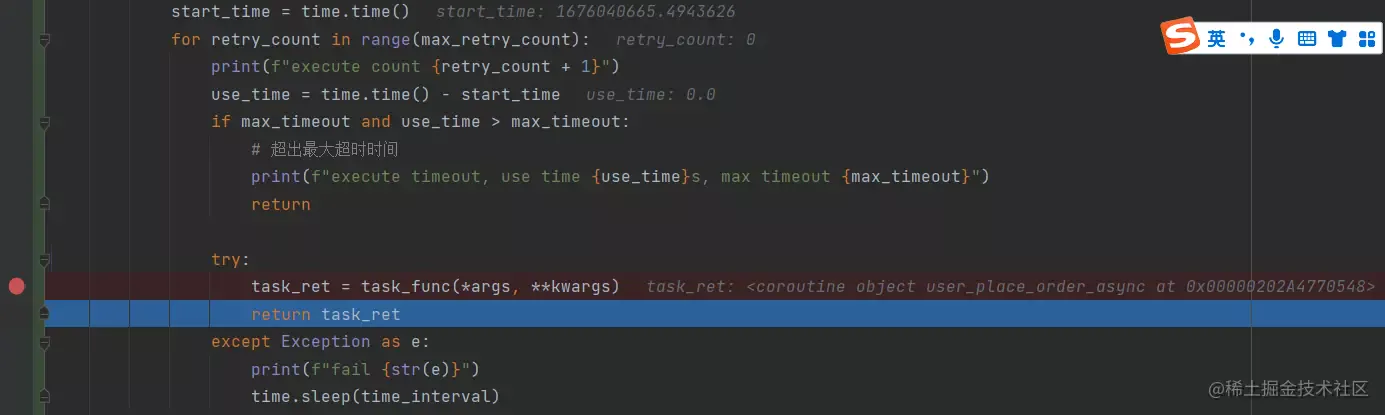
这样装饰器就不支持异步函数的重试,需要加强它,可以使用 asyncio.iscoroutinefunction() 来进行异步函数的判断, 然后再加一个异步函数的闭包就可以实现异步、同步函数都兼容的重试装饰器。
def task_retry(max_retry_count: int = 5, time_interval: int = 2, max_timeout: int = None):
"""
任务重试装饰器
Args:
max_retry_count: 最大重试次数 默认 5 次
time_interval: 每次重试间隔 默认 2s
max_timeout: 最大超时时间,单位s 默认为 None,
"""
def _task_retry(task_func):
@functools.wraps(task_func)
def sync_wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 同步循环重试
start_time = time.time()
for retry_count in range(max_retry_count):
print(f"execute count {retry_count + 1}")
use_time = time.time() - start_time
if max_timeout and use_time > max_timeout:
# 超出最大超时时间
print(f"execute timeout, use time {use_time}s, max timeout {max_timeout}")
return
try:
task_ret = task_func(*args, **kwargs)
return task_ret
except Exception as e:
print(f"fail {str(e)}")
time.sleep(time_interval)
@functools.wraps(task_func)
async def async_wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 异步循环重试
start_time = time.time()
for retry_count in range(max_retry_count):
print(f"execute count {retry_count + 1}")
use_time = time.time() - start_time
if max_timeout and use_time > max_timeout:
# 超出最大超时时间
print(f"execute timeout, use time {use_time}s, max timeout {max_timeout}")
return
try:
return await task_func(*args, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
print(f"fail {str(e)}")
await asyncio.sleep(time_interval)
# 异步函数判断
wrapper_func = async_wrapper if asyncio.iscoroutinefunction(task_func) else sync_wrapper
return wrapper_func
return _task_retry
注意时间等待 await asyncio.sleep(time_interval) 会导致函数挂起,程序不会在这里等待,而是去事件循环loop中执行其他的已经就绪的任务,如果其他函数运行时间太久了才切换回来,会导致时间超时,换成 time.sleep()的话其实也没有用,如果函数内部还有异步函数执行还是会切换出去,因此异步的时候感觉超时参数意义不大。
模拟测试下
@task_retry(max_retry_count=5, time_interval=2, max_timeout=5)
async def user_place_order_async():
"""异步函数重试案例"""
a = 1 / 0
print("user place order success")
return {"code": 0, "msg": "ok"}
async def io_test():
"""模拟io阻塞"""
print("io test start")
time.sleep(3)
print("io test end")
return "io test end"
async def main():
# 同步案例
# ret = user_place_order()
# print(f"user place order ret {ret}")
# 异步案例
# ret = await user_place_order_async()
# print(f"user place order ret {ret}")
# 并发异步
order_ret, io_ret = await asyncio.gather(
user_place_order_async(),
io_test(),
)
print(f"io ret {io_ret}")
print(f"user place order ret {order_ret}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
asyncio.run(main())
>>>out
execute count 1
fail division by zero
io test start
io test end
execute count 2
fail division by zero
execute count 3
execute timeout, use time 5.015768527984619s, max timeout 5
io ret io test end
user place order ret None
可以看出执行一遍后自动切换到了 io_test 中执行由于 io test 中的 time.sleep(3) 会导致整个线程阻塞,一定要等到io_test执行完后才会切换回去,然后再执行两遍就超时了,你可能会说都用异步的库,是的异步的库是可以加速,但我想表达就是这时候统计的耗时是整个程序的而不是单独一个函数的。大家可以在评论区帮我想想有没有其他的方法,要么就不要用这个超时参数。
可以兼容异步函数、然后超时参数可以不配置,影响不大,O(∩_∩)O~
重试装饰器-最终版最终版就是利用抛异常的方式来结束超过最大重试次数、最大超时,而不是直接返回None,然后再添加一个可配置捕获指定异常的参数,当发生特定异常的时候才重试。
import time
import asyncio
import functools
from typing import Type
class MaxRetryException(Exception):
"""最大重试次数异常"""
pass
class MaxTimeoutException(Exception):
"""最大超时异常"""
pass
def task_retry(
max_retry_count: int = 5,
time_interval: int = 2,
max_timeout: int = None,
catch_exc: Type[BaseException] = Exception
):
"""
任务重试装饰器
Args:
max_retry_count: 最大重试次数 默认 5 次
time_interval: 每次重试间隔 默认 2s
max_timeout: 最大超时时间,单位s 默认为 None,
catch_exc: 指定捕获的异常类用于特定的异常重试 默认捕获 Exception
"""
def _task_retry(task_func):
@functools.wraps(task_func)
def sync_wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 函数循环重试
start_time = time.time()
for retry_count in range(max_retry_count):
print(f"execute count {retry_count + 1}")
use_time = time.time() - start_time
if max_timeout and use_time > max_timeout:
# 超出最大超时时间
raise MaxTimeoutException(f"execute timeout, use time {use_time}s, max timeout {max_timeout}")
try:
task_ret = task_func(*args, **kwargs)
return task_ret
except catch_exc as e:
print(f"fail {str(e)}")
time.sleep(time_interval)
else:
# 超过最大重试次数, 抛异常终止
raise MaxRetryException(f"超过最大重试次数失败, max_retry_count {max_retry_count}")
@functools.wraps(task_func)
async def async_wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 异步循环重试
start_time = time.time()
for retry_count in range(max_retry_count):
print(f"execute count {retry_count + 1}")
use_time = time.time() - start_time
if max_timeout and use_time > max_timeout:
# 超出最大超时时间
raise MaxTimeoutException(f"execute timeout, use time {use_time}s, max timeout {max_timeout}")
try:
return await task_func(*args, **kwargs)
except catch_exc as e:
print(f"fail {str(e)}")
await asyncio.sleep(time_interval)
else:
# 超过最大重试次数, 抛异常终止
raise MaxRetryException(f"超过最大重试次数失败, max_retry_count {max_retry_count}")
# 异步函数判断
wrapper_func = async_wrapper if asyncio.iscoroutinefunction(task_func) else sync_wrapper
return wrapper_func
return _task_retry
@task_retry(max_retry_count=3, time_interval=1, catch_exc=ZeroDivisionError,max_timeout=5)
def user_place_order():
a = 1 / 0
print("user place order success")
return {"code": 0, "msg": "ok"}
@task_retry(max_retry_count=5, time_interval=2, max_timeout=5)
async def user_place_order_async():
"""异步函数重试案例"""
a = 1 / 0
print("user place order success")
return {"code": 0, "msg": "ok"}
async def io_test():
"""模拟io阻塞"""
print("io test start")
time.sleep(3)
print("io test end")
return "io test end"
async def main():
# 同步案例
try:
ret = user_place_order()
print(f"user place order ret {ret}")
except MaxRetryException as e:
# 超过最大重试次数处理
print("MaxRetryException", e)
except MaxTimeoutException as e:
# 超过最大超时处理
print("MaxTimeoutException", e)
# 异步案例
# ret = await user_place_order_async()
# print(f"user place order ret {ret}")
# 并发异步
# order_ret, io_ret = await asyncio.gather(
# user_place_order_async(),
# io_test(),
# )
# print(f"io ret {io_ret}")
# print(f"user place order ret {order_ret}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
asyncio.run(main())
测试捕获指定异常
# 指定捕获除零错误,正常捕获重试
@task_retry(max_retry_count=3, time_interval=1, catch_exc=ZeroDivisionError)
def user_place_order():
a = 1 / 0
# a = []
# b = a[0]
print("user place order success")
return {"code": 0, "msg": "ok"}
# out
execute count 1
fail division by zero
execute count 2
fail division by zero
execute count 3
fail division by zero
MaxRetryException 超过最大重试次数失败, max_retry_count 3
# 指定捕获除零错误,报索引越界错误,未正常捕获重试,直接退出
@task_retry(max_retry_count=3, time_interval=1, catch_exc=ZeroDivisionError)
def user_place_order():
# a = 1 / 0
a = []
b = a[0]
print("user place order success")
return {"code": 0, "msg": "ok"}
# out
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "G:/code/python/py-tools/decorator/base.py", line 184, in <module>
asyncio.run(main())
File "G:\softs\DevEnv\python-3.7.9\lib\asyncio\runners.py", line 43, in run
return loop.run_until_complete(main)
File "G:\softs\DevEnv\python-3.7.9\lib\asyncio\base_events.py", line 587, in run_until_complete
return future.result()
File "G:/code/python/py-tools/decorator/base.py", line 161, in main
ret = user_place_order()
File "G:/code/python/py-tools/decorator/base.py", line 97, in sync_wrapper
task_ret = task_func(*args, **kwargs)
File "G:/code/python/py-tools/decorator/base.py", line 137, in user_place_order
b = a[0]
IndexError: list index out of range
Process finished with exit code 1
用抛异常的方式推出更好知道是因为什么原因退出来进行对应的业务逻辑处理。乍一看兼容异步、同步函数导致这个装饰器有点代码冗余,看看大家有没有更好的办法。
到这就结束了,虽然是一个简单的装饰器,但本文还是引伸出很多知识点,望可以帮助到大家。
修改记录2023-05-01
把重试里的超时计算单独抽离出来,这样功能不会太藕合,分两个装饰实现
def set_timeout(timeout: int, use_signal=False):
"""
超时处理装饰器
Args:
timeout: 超时时间,单位秒
use_signal: 使用信号量机制只能在 unix内核上使用,默认False
Raises:
TimeoutException
"""
def _timeout(func: Callable):
def _handle_timeout(signum, frame):
raise MaxTimeoutException(f"Function timed out after {timeout} seconds")
@functools.wraps(func)
def sync_wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 同步函数处理超时
if use_signal:
# 使用信号量计算超时
signal.signal(signal.SIGALRM, _handle_timeout)
signal.alarm(timeout)
try:
return func(*args, **kwargs)
finally:
signal.alarm(0)
else:
# 使用线程
with ThreadPoolExecutor() as executor:
future = executor.submit(func, *args, **kwargs)
try:
return future.result(timeout)
except TimeoutError:
raise MaxTimeoutException(f"Function timed out after {timeout} seconds")
@functools.wraps(func)
async def async_wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 异步函数处理超时
try:
ret = await asyncio.wait_for(func(*args, **kwargs), timeout)
return ret
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
raise MaxTimeoutException(f"Function timed out after {timeout} seconds")
return async_wrapper if asyncio.iscoroutinefunction(func) else sync_wrapper
return _timeout
def retry(
max_count: int = 5,
interval: int = 2,
catch_exc: Type[BaseException] = Exception
):
"""
重试装饰器
Args:
max_count: 最大重试次数 默认 5 次
interval: 每次异常重试间隔 默认 2s
catch_exc: 指定捕获的异常类用于特定的异常重试 默认捕获 Exception
Raises:
MaxRetryException
"""
def _retry(task_func):
@functools.wraps(task_func)
def sync_wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 函数循环重试
for retry_count in range(max_count):
logger.info(f"{task_func} execute count {retry_count + 1}")
try:
return task_func(*args, **kwargs)
except catch_exc:
logger.error(f"fail {traceback.print_exc()}")
if retry_count < max_count - 1:
# 最后一次异常不等待
time.sleep(interval)
# 超过最大重试次数, 抛异常终止
raise MaxRetryException(f"超过最大重试次数失败, max_retry_count {max_count}")
@functools.wraps(task_func)
async def async_wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 异步循环重试
for retry_count in range(max_count):
logger.info(f"{task_func} execute count {retry_count + 1}")
try:
return await task_func(*args, **kwargs)
except catch_exc as e:
logger.error(f"fail {str(e)}")
if retry_count < max_count - 1:
await asyncio.sleep(interval)
# 超过最大重试次数, 抛异常终止
raise MaxRetryException(f"超过最大重试次数失败, max_retry_count {max_count}")
# 异步函数判断
wrapper_func = async_wrapper if asyncio.iscoroutinefunction(task_func) else sync_wrapper
return wrapper_func
return _retry
源代码
HuiDBK/py-tools: 打造 Python 开发常用的工具,让Coding变得更简单 (github.com)
以上就是手把手教你实现Python重试超时装饰器,的详细内容,更多关于Python重试超时装饰器的资料请关注软件开发网其它相关文章!