Windows:定时/进程结束执行命令
1、定时执行脚本2、进程结束执行脚本
训练网络经常半夜才训练完,有时为了不浪费时间,晚上特意调了闹钟起来改代码、继续训练等。大半夜设闹钟起来跑代码太难受了,所以这次写了这两个代码,以后少受点罪。 1、定时执行脚本
作者:zephyrji96
训练网络经常半夜才训练完,有时为了不浪费时间,晚上特意调了闹钟起来改代码、继续训练等。大半夜设闹钟起来跑代码太难受了,所以这次写了这两个代码,以后少受点罪。 1、定时执行脚本
代码:
import os
import time
set_time = '00:00:00' # 此处设置每天定时的时间
cmd = ''
print("——————————waiting to execute task——————————")
while True:
time_now = time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", time.localtime()) # 刷新
if time_now == set_time:
time.sleep(2) # 因为以秒定时,所以暂停2秒,使之不会在1秒内执行多次
subject = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S ", time.localtime()) + " running command"
print(subject)
## 执行命令
os.system(cmd)
break # 执行完毕退出循环
流程:
设置脚本运行时间(如:set_time = '00:00:00')
设置执行脚本命令(如:cmd = 'python 123.py'),可自行添加多条命令
输出:
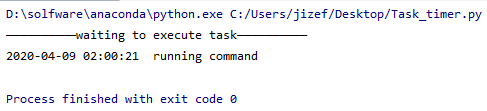
代码:
import os
import time
import psutil
"""
windows查询python.exe进程的ProcessId:
wmic process where name="python.exe" list full
"""
ProcessId = 63112
cmd = ''
pid = psutil.Process(ProcessId)
while True:
time.sleep(5) # 每隔n秒查询一次进程运行情况
if pid.is_running():
p = psutil.Process(ProcessId)
exec_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S ", time.localtime())
print(exec_time + 'pid-%s, pname-%s' % (ProcessId, p.name()))
else:
print('ProcessId is over, running command:')
os.system(cmd)
break
流程:
作者以python.exe为例
1、 WIN+R进入cmd界面,输入命令:wmic process where name="python.exe" list full,获取如下信息:
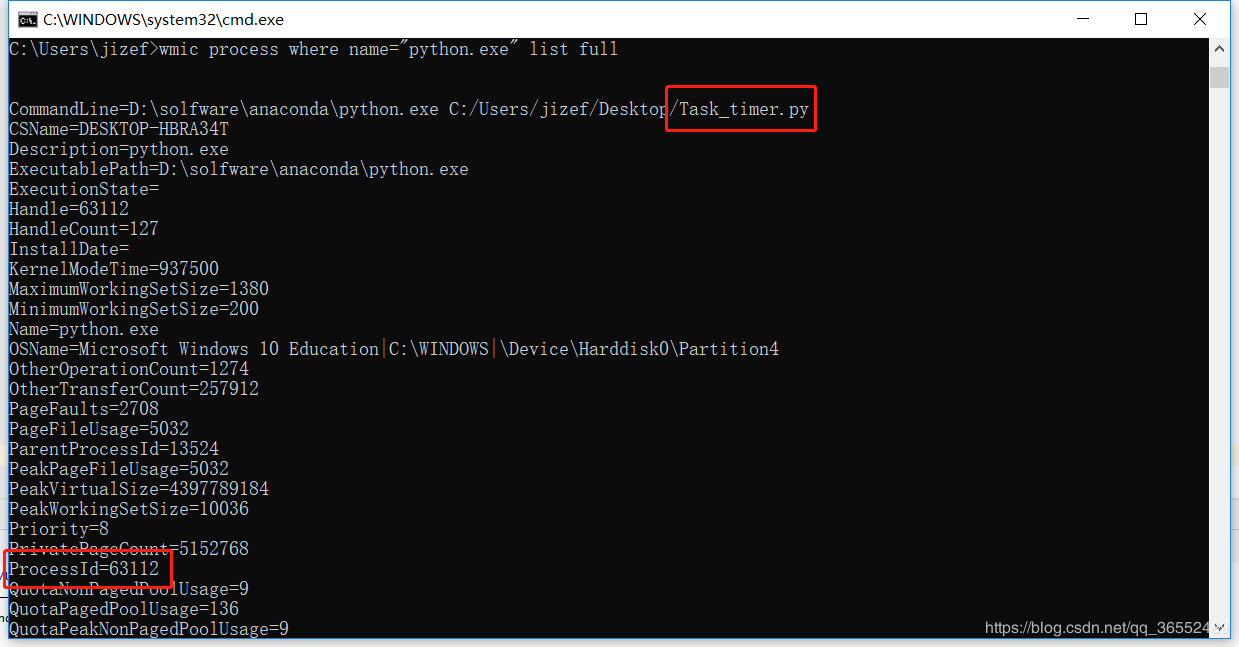
其中主要确定所执行的py文件和对应的进程号。Linux 和 Windows 查看当前运行的 python 进程及 GPU、CPU、磁盘利用率
2、 设置进程ID(如:ProcessId = 63112)
3、 设置执行脚本命令(如:cmd = 'python 123.py'),可自行添加多条命令
运行结果:
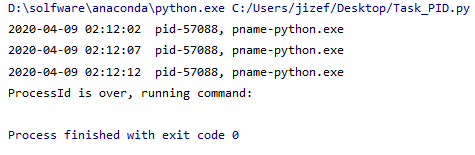
作者:zephyrji96
相关文章
Valencia
2020-07-04
Olinda
2020-03-24
Rhoda
2023-07-20
Sabah
2023-07-20
Oria
2023-07-21
Aine
2023-07-21
Dabria
2023-07-21
Alanni
2023-07-21
Nyako
2023-07-21
Lida
2023-07-21
Grizelda
2023-07-21
Lana
2023-07-21
Heather
2023-07-22
Radinka
2023-07-22
Serafina
2023-07-24
Malinda
2023-08-08
Diane
2023-08-08
Kefira
2023-08-08