对象池的实现与性能测试
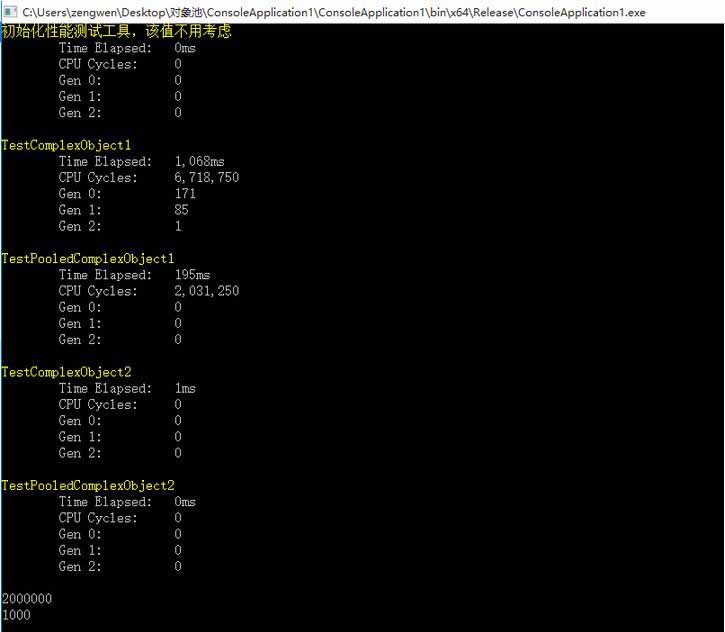
引用对象池的好处:从池中操作对象比直接new、free要性能更快,且能避免内存碎片的堆积 先贴对象池的代码: public abstract class ObjectBase { public abstract void Init(params object[] paramList); } //对象池管理器(采用堆栈存储,支持动态扩容,支持多线程,新扩容的则自动加入到池中能被重复利用) public class ObjectPoolManager<T> where T : ObjectBase, new() { private static ObjectPoolManager<T> instance = null; private int blockCapacity = 1000; private static object doubleCheckLock = new object(); private static object objLock = new object(); private bool inited = false; private ConcurrentDictionary<string, Stack<T>> objectPool = new ConcurrentDictionary<string, Stack<T>>(); private ObjectPoolManager() { } public static ObjectPoolManager<T> Instance { get { if (instance == null) { lock (doubleCheckLock) { if (instance == null) { instance = new ObjectPoolManager<T>(); } } } return instance; } } //初始化对象池 public string Init(int blockCapacity) { lock (objLock) { try { if (blockCapacity < 1 || blockCapacity > int.MaxValue) { this.blockCapacity = 1000; } else { this.blockCapacity = blockCapacity; } Stack<T> freeObjList = new Stack<T>(); for (int index = 0; index < blockCapacity; index++) { T obj = new T(); freeObjList.Push(obj); } objectPool[typeof(T).ToString()] = freeObjList; inited = true; return null; } catch (Exception ex) { return typeof(T).ToString() + " -> ExceptionMessage:" + ex.Message + (ex.InnerException != null ? ("InnerExceptionMessage:" + ex.InnerException.Message) : ""); } } } //取新对象 public T NewObject(params object [] paramList) { lock (objLock) { try { if (!inited) { Init(blockCapacity); } string key = typeof(T).ToString(); Stack<T> objList = objectPool[key]; if (objList.Count > 0) { T obj = objList.Pop(); obj.Init(paramList); return obj; } else { for (int index = 0; index < this.blockCapacity; index++) { T newObj = new T(); objList.Push(newObj); } T obj = objList.Pop(); obj.Init(paramList); return obj; } } catch (Exception ex) { //ServerUtil.RecordLog(LogType.Error, ex); T newObj = new T(); newObj.Init(paramList); return newObj; } } } //释放对象 public void FreeObject(T obj) { lock (objLock) { try { if (obj == default(T)) return; Stack<T> objList = objectPool[typeof(T).ToString()]; if (!objList.Contains(obj)) { objList.Push(obj); } } catch (Exception ex) { //ServerUtil.RecordLog(LogType.Error, ex); } } } } 下一步做与不用池时的性能测试对比: 先提供性能测试的支援函数 //使用方法见本文档末尾 public sealed class CodeElapseChecker { public static void Initialize() { Process.GetCurrentProcess().PriorityClass = ProcessPriorityClass.High; Thread.CurrentThread.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest; Time("初始化性能测试工具,该值不用考虑", 1, () => { }); } public static void Time(string name, Action action, int iterationCnt = 1) { Time(name, iterationCnt, action); } public static void Time(string name, int iteration, Action action) { // 1. ConsoleColor currentForeColor = Console.ForegroundColor; Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow; Console.WriteLine(name); // 2. GC.Collect(GC.MaxGeneration, GCCollectionMode.Forced); int[] gcCounts = new int[GC.MaxGeneration + 1]; for (int i = 0; i <= GC.MaxGeneration; i++) { gcCounts[i] = GC.CollectionCount(i); } // 3. Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); long cycleCount = GetCycleCount(); for (int i = 0; i < iteration; i++) action(); long cpuCycles = GetCycleCount() - cycleCount; watch.Stop(); // 4. Console.ForegroundColor = currentForeColor; Console.WriteLine(" Time Elapsed: " + watch.ElapsedMilliseconds.ToString("N0") + "ms"); Console.WriteLine(" CPU Cycles: " + cpuCycles.ToString("N0")); // 5. for (int i = 0; i <= GC.MaxGeneration; i++) { int count = GC.CollectionCount(i) - gcCounts[i]; Console.WriteLine(" Gen " + i + ": " + count); } Console.WriteLine(); } private static long GetCycleCount() { //ulong cycleCount = 0; //QueryThreadCycleTime(GetCurrentThread(), ref cycleCount); //return cycleCount; return GetCurrentThreadTimes(); } [DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)] static extern bool GetThreadTimes(IntPtr hThread, out long lpCreationTime, out long lpExitTime, out long lpKernelTime, out long lpUserTime); private static long GetCurrentThreadTimes() { long l; long kernelTime, userTimer; GetThreadTimes(GetCurrentThread(), out l, out l, out kernelTime, out userTimer); return kernelTime + userTimer; } //[DllImport("kernel32.dll")] //[return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)] //static extern bool QueryThreadCycleTime(IntPtr threadHandle, ref ulong cycleTime); [DllImport("kernel32.dll")] static extern IntPtr GetCurrentThread(); }建立两个测试对象: //复杂测试对象1 public class ComplexObject1 : ObjectBase { private byte[] data = new byte[1024]; public override void Init(params object[] paramList) { } } //复杂测试对象2 class ComplexObject2 : ObjectBase { private byte[] data = new byte[1024 * 1024]; public override void Init(params object[] paramList) { } } 测试代码: class Program { const int Count1 = 1000000; const int Count2 = 500; static void Main(string[] args) { var list1 = new List<ComplexObject1>(Count1 * 2); var list2 = new List<ComplexObject2>(Count2 * 2); CodeElapseChecker.Initialize(); ObjectPoolManager<ComplexObject1>.Instance.Init(Count1); ObjectPoolManager<ComplexObject2>.Instance.Init(Count2); CodeElapseChecker.Time("TestComplexObject1", () => { list1.Add(new ComplexObject1()); }, Count1); CodeElapseChecker.Time("TestPooledComplexObject1", () => { list1.Add(ObjectPoolManager<ComplexObject1>.Instance.NewObject()); }, Count1); CodeElapseChecker.Time("TestComplexObject2", () => { list2.Add(new ComplexObject2()); }, Count2); CodeElapseChecker.Time("TestPooledComplexObject2", () => { list2.Add(ObjectPoolManager<ComplexObject2>.Instance.NewObject()); }, Count2); Console.WriteLine(list1.Count); Console.WriteLine(list2.Count); } } 运行测试结果:(采用Release、X64编译)