python SVM 线性分类模型的实现
运行环境:win10 64位 py 3.6 pycharm 2018.1.1
导入对应的包和数据
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets,linear_model,cross_validation,svm
def load_data_regression():
diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes()
return cross_validation.train_test_split(diabetes,diabetes.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=0)
def load_data_classfication():
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X_train = iris.data
y_train = iris.target
return cross_validation.train_test_split(X_train,y_train,test_size=0.25,random_state=0,stratify=y_train)
#线性分类SVM
def test_LinearSVC(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = data
cls = svm.LinearSVC()
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
print('Coefficients:%s,intercept%s'%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_))
print('Score:%.2f'%cls.score(X_test,y_test))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_LinearSVC(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
def test_LinearSVC_loss(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = data
losses = ['hinge','squared_hinge']
for loss in losses:
cls = svm.LinearSVC(loss=loss)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
print('loss:%s'%loss)
print('Coefficients:%s,intercept%s'%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_))
print('Score:%.2f'%cls.score(X_test,y_test))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_LinearSVC_loss(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
#考察罚项形式的影响
def test_LinearSVC_L12(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = data
L12 = ['l1','l2']
for p in L12:
cls = svm.LinearSVC(penalty=p,dual=False)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
print('penalty:%s'%p)
print('Coefficients:%s,intercept%s'%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_))
print('Score:%.2f'%cls.score(X_test,y_test))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_LinearSVC_L12(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
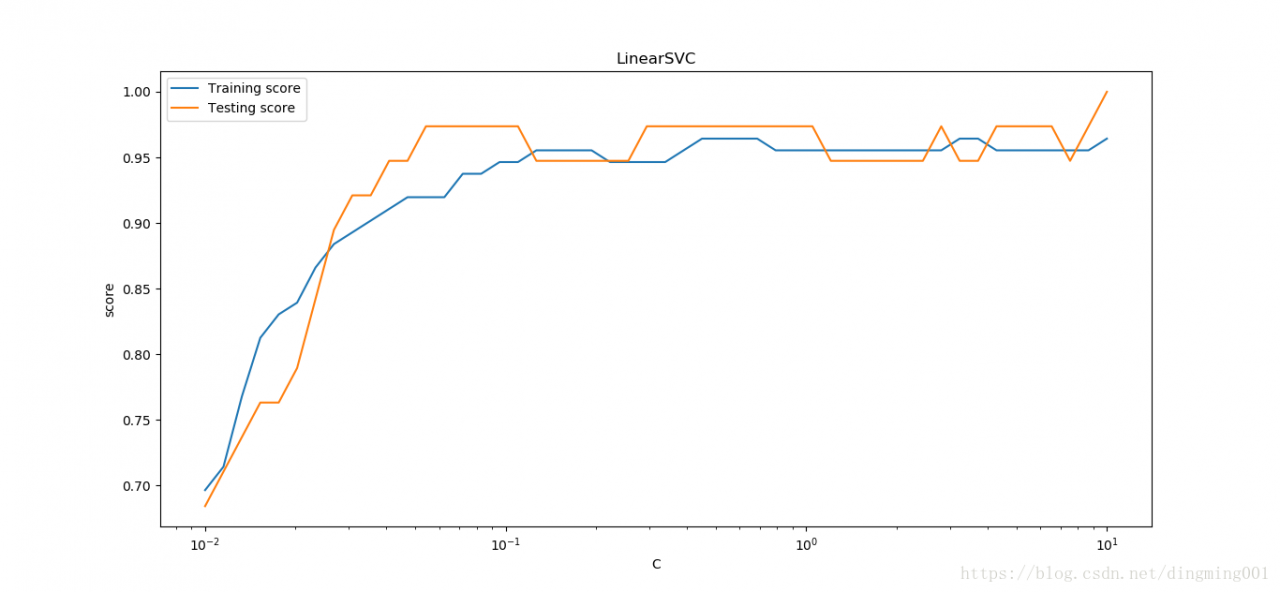
#考察罚项系数C的影响
def test_LinearSVC_C(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = data
Cs = np.logspace(-2,1)
train_scores = []
test_scores = []
for C in Cs:
cls = svm.LinearSVC(C=C)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test,y_test))
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.plot(Cs,train_scores,label = 'Training score')
ax.plot(Cs,test_scores,label = 'Testing score')
ax.set_xlabel(r'C')
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_ylabel(r'score')
ax.set_title('LinearSVC')
ax.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_LinearSVC_C(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
#非线性分类SVM
#线性核
def test_SVC_linear(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
print('Coefficients:%s,intercept%s'%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_))
print('Score:%.2f'%cls.score(X_test,y_test))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_SVC_linear(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
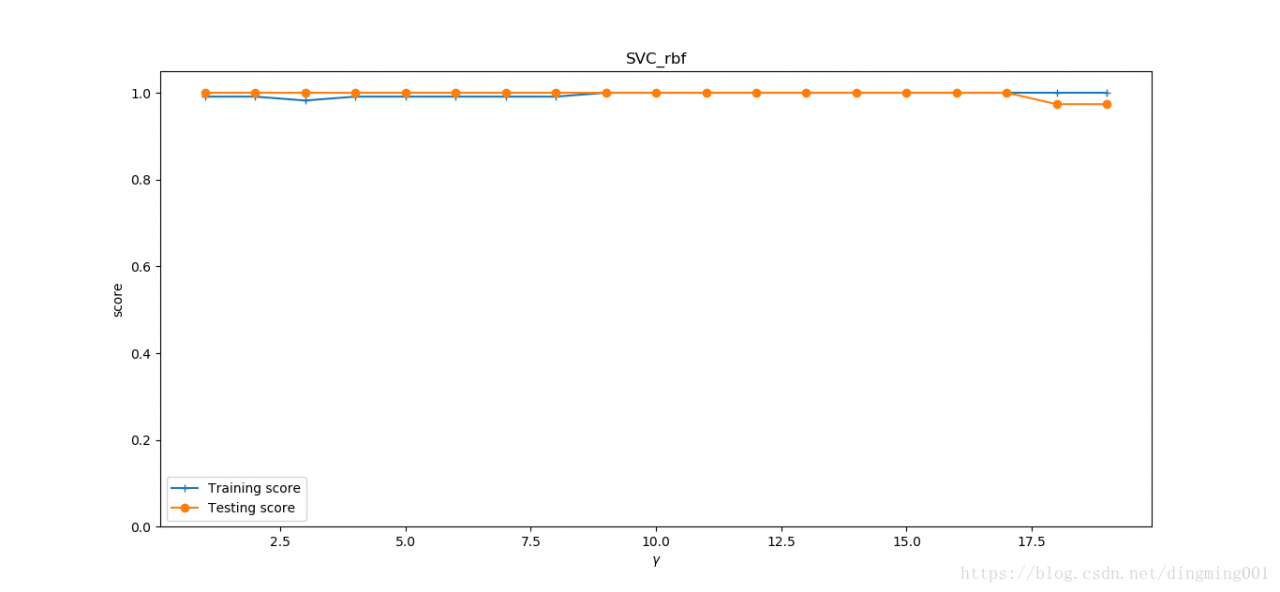
#考察高斯核
def test_SVC_rbf(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
###测试gamm###
gamms = range(1, 20)
train_scores = []
test_scores = []
for gamm in gamms:
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='rbf', gamma=gamm)
cls.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train, y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax.plot(gamms, train_scores, label='Training score', marker='+')
ax.plot(gamms, test_scores, label='Testing score', marker='o')
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\gamma$')
ax.set_ylabel(r'score')
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.05)
ax.set_title('SVC_rbf')
ax.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_SVC_rbf(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
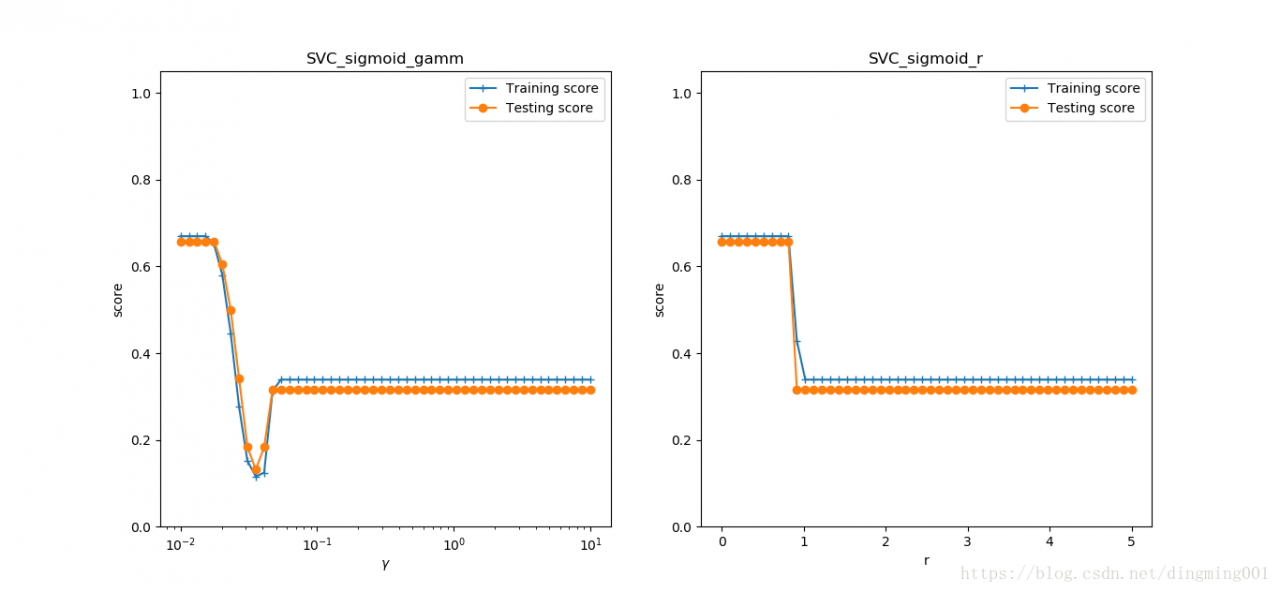
#考察sigmoid核
def test_SVC_sigmod(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
fig = plt.figure()
###测试gamm###
gamms = np.logspace(-2, 1)
train_scores = []
test_scores = []
for gamm in gamms:
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='sigmoid',gamma=gamm,coef0=0)
cls.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train, y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax.plot(gamms, train_scores, label='Training score', marker='+')
ax.plot(gamms, test_scores, label='Testing score', marker='o')
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\gamma$')
ax.set_ylabel(r'score')
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.05)
ax.set_title('SVC_sigmoid_gamm')
ax.legend(loc='best')
#测试r
rs = np.linspace(0,5)
train_scores = []
test_scores = []
for r in rs:
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='sigmoid', gamma=0.01, coef0=r)
cls.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train, y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax.plot(rs, train_scores, label='Training score', marker='+')
ax.plot(rs, test_scores, label='Testing score', marker='o')
ax.set_xlabel(r'r')
ax.set_ylabel(r'score')
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.05)
ax.set_title('SVC_sigmoid_r')
ax.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_SVC_sigmod(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)