解放双手,Android开发应该尝试的UI自动化测试
人们懒的走路,才创造了汽车;
人们懒的爬楼,才创造了电梯;
人们懒的扫地,才创造了自动扫地机器人。
人类的进步,离不开这些喜欢偷懒的人,Google希望,当Android的开发者利用Espresso写完测试用例后,能一边看着测试用例自动执行,一边享受一杯香醇Espresso(浓咖啡)。
@小创作:为什么要做单元测试
为什么要进行烦人的单元测试?
以下引用Android官方文档对测试的概述
测试应用是应用开发过程中不可或缺的一部分。通过持续对应用运行测试,您可以在公开发布应用之前验证其正确性、功能行为和易用性。
测试还会为您提供以下优势:
快速获得故障反馈。 在开发周期中尽早进行故障检测。 更安全的代码重构,让您可以优化代码而不必担心回归。 稳定的开发速度,帮助您最大限度地减轻技术负担。 关于 EspressoEspresso 是 Google 开源的一款 Android 自动化测试框架,目标是让开发人员能够快速地写出简洁、美观且可靠的 Android 界面测试,特点如下:
规模更小、更简洁,API更加精确,编写测试代码简单,容易快速上手。
提供了自动同步操作,在主线程空闲的时候,运行测试代码,从而提高测试的可靠性。
可以运行在Android2.3.3及其更高版本。
因为是基于Instrumentation的,所以不能跨App。
环境配置作为Google的亲儿子,难免会对其照顾有加,相信有一些朋友已经知道在AndroidStudio2.2版本之后,在新建的项目中,AndroidStudio会默认添加Espresso的依赖。
添加依赖
在build.gradle 文件中添加如下依赖:
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.2.0'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test:runner:1.1.0'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test:rules:1.1.0'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.1'
//espresso-contrib扩展包用于RecyclerView相关操作,不需要可以不用添加
androidTestCompile('com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-contrib:2.0') {
exclude group: 'com.android.support', module: 'appcompat'
exclude group: 'com.android.support', module: 'support-v4'
exclude module: 'recyclerview-v7'
//不导入依赖中的包,避免出现依赖冲突,使用用户自己导入的包
}
除此之外Espresso还有一些扩展包,用于完成一些特殊的测试场景:
espresso-core - 包含核心和基本的 View 匹配器、操作和断言。
espresso-web - 包含 WebView 支持的资源。
espresso-idling-resource - Espresso 与后台作业同步的机制。
espresso-contrib - 外部贡献,包含 DatePicker、RecyclerView 和 Drawer 操作、无障碍功能检查以及 CountingIdlingResource。
espresso-intents - 用于对封闭测试的 intent 进行验证和打桩的扩展。
espresso-remote - Espresso 的多进程功能的位置。
设置 instrumentation runner
在build.gradle 文件的 android.defaultConfig 中添加如下配置:
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
设置测试环境
为了避免测试不稳定,建议在用于测试的虚拟或物理设备上关闭系统动画,在设置 > 开发者选项下,停用以下三项设置:
窗口动画缩放
过渡动画缩放
Animator 时长缩放
Espresso 基本使用
三步曲:
ViewMatchers – 寻找View。
ViewActions – 执行交互事件。
ViewAssertions – 检验测试结果。
示例:
onView(withId(R.id.my_view)) // withId(R.id.my_view) is a ViewMatcher
.perform(click()) // click() is a ViewAction
.check(matches(isDisplayed())); // matches(isDisplayed()) is a ViewAssertion
Espresso 测试代码位置和静态导入
Espresso 测试代码放在 app/src/androidTest 目录下。
为了简化 Espresso API 的使用, 建议使用以下静态导入. 可以允许在没有类前缀的前提下访问这些静态方法。
import static androidx.test.espresso.Espresso.onView;
import static androidx.test.espresso.Espresso.pressBack;
import static androidx.test.espresso.action.ViewActions.click;
import static androidx.test.espresso.assertion.ViewAssertions.matches;
import static androidx.test.espresso.matcher.ViewMatchers.withText;
import static androidx.test.espresso.matcher.ViewMatchers.withId;
寻找 View
ViewMatchers
函数
功能
assertThat()
用于生成断言描述的工具
hasContentDescription()
匹配具有内容描述的view
hasDescendant()
匹配具有特定子视图(直接或间接)的view
hasErrorText()
匹配getError为特定字符串的EditView
hasFocus()
匹配获取焦点的view
hasImeAction()
匹配支持输入,并且具有特定IMEAction的view
hasLinks()
匹配具有超链接的TextView
hasSibling()
匹配具有特定相邻view的view
isAssignableFrom()
匹配继承自特定类的view
isChecked()
匹配实现Checkable接口并且处于选中状态的View
isClickable()
匹配可以点击的view
isCompletelyDisplayed()
匹配全部显示在视图中的view
isDescendantOfA()
匹配具有特定父视图(直接或间接)的view
isDisplayed()
匹配显示在视图中(包括部分)的view
isDisplayingAtLeast()
匹配显示在视图中超过指定比值的view
isEnabled()
匹配当前可用(非灰色)的view
isFocusable()
匹配可以获取焦点的view
isJavascriptEnabled()
匹配开启JS的webView
isNotChecked()
匹配实现Checkable接口并且处于未选中状态的View
isRoot()
匹配本身为root的view
isSelected()
匹配被选中的view
supportsInputMethods()
匹配支持输入的View
withChild()
匹配具有特定直接子视图的view
withClassName()
匹配具有特定类名的view
withContentDescription()
匹配具有特定内容描述的view
withEffectiveVisibility()
匹配显示在屏幕上(所有父视图为Visible)的view
withHint()
匹配getHint为指定字符串的TextView
withId()
匹配具有指定id的view
withInputType()
匹配具有指定输入类型的EditView
withParent()
匹配具有特定直接父视图的view
withResourceName()
匹配具有指定资源名称的view
withSpinnerText()
匹配getSeletedItem为指定文本的view
withTagKey()
匹配getTag为指定值的view
withText()
匹配getText为指定字符串的TextView
RootMatchers
函数
功能
isDialog()
匹配是对话框的root
isFocusable()
匹配拥有焦点的root
isPlatformPopup()
匹配是弹出窗的root
isTouchable()
匹配可以触摸的root
withDecorView()
匹配满足特定条件的root
Matchers
函数
功能
allOf()
将所有matcher合并为一个matcher(必须满足所有matcher)
any()
生成一个判定是否为指定类实例或者子类的matcher
anyOf()
将所有matcher合并为一个matcher(满足至少一个matcher即可)
anything()
生成一个匹配任何对象的matcher(matches写死返回值为true)
array()
由n个matcher生成一个可以对应匹配array[n],中每个data的matcher(必须依次对应)
arrayContaining()
由n个data生成一个可以对应匹配array[n],中每个data的matcher(必须依次对应)
arrayContainingInAnyOrder()
由n个data生成一个可以对应匹配array[n],中每个data的matcher(不必依次对应)
arrayWithSize()
生成匹配指定array.size()的matcher
both()
将两个matcher合并成一个matcher
closeTo()
生成matcher匹配误差范围内的数:num∈[operand-error,operand+error]
comparesEqualTo()
生成matcher匹配指定value
contains()
iterable中每一项符合对应matcher(必须依次匹配)
containsInAnyOrder()
iterable中每一项符合对应matcher(不必依次匹配)
containsString()
包含特定string
describedAs()
更改matcher的描述
either()
指定对象与指定匹配器匹配时匹配
empty()
collection为空
emptyArray()
数组为空
emptyCollectionOf()
collection为空
emptyIterable()
Iterable为空
emptyIterableOf()
Iterable为空
endsWith()
String以指定字符串结尾
equalTo()
封装equalTo
equalToIgnoringCase()
string.equalTo()忽略大小写
equalToIgnoringWhiteSpace()
string.equalTo()忽略大小写和留白
eventFrom()
匹配从指定source中派生的eventObject
everyItem()
Iterable中任何一项都符合目标matcher
greaterThan()
大于指定值
greaterThanOrEqualTo()
大于等于指定值
hasEntry()
匹配指定Map
hasItem()
匹配具有指定item的Iterable
hasItemInArray()
匹配具有指定item的数组
hasItems()
匹配具有指定多个item的Iterable
hasKey()
具有特定K 的Map
hasProperty()
具有指定名称成员变量的对象
hasSize()
Collection为指定size
hasToString()
匹配toString为指定值的对象
hasValue()
具有特定V的Map
hasXPath()
Creates a matcher of {@link org.w3c.dom.Node}s that matches when the examined node contains a node at the specified xPath, with any content.
instanceOf()
为特定class的实例或者子类
is()
封装上文matcher:equalTo
isA()
封装上文matcher:instanceOf
isEmptyOrNullStringv()
""或者空String
isEmptyString()
""(String)
isIn()
匹配指定Array中的item
isOneOf()
匹配列举中的一项
iterableWithSize()
iterable的size为指定值
lessThan()
小于特定值
lessThanOrEqualTo()
小于等于特定值
not()
不匹配指定matcher
notNullValue()
不为空值
nullValue()
空值
sameInstance()
对象相同的
samePropertyValuesAs()
具有相同属性值
startsWith()
String以特定字符串开始
stringContainsInOrder()
具有特定一个字符串的String
theInstance()
对象相同的与上文sameInstance相同
typeCompatibleWith()
当前class是继承自指定class
执行交互事件
ViewActions
函数
功能
addGlobalAssertion()
设置全局断言
actionWithAssertions()
包装 action ,执行前必须满足所有全局断言
removeGlobalAssertion()
删除全局断言
clearGlobalAssertions()
清空全局断言
clearText()
清空文本
click()
单击
click(ViewAction rollbackAction()
单击(防止误判为长按)
closeSoftKeyboard()
关闭软键盘
doubleClick()
双击
longClick()
长按
openLink()
打开连接(TextView)
openLinkWithText()
打开连接(Text)
openLinkWithUri()
打开连接(Uri)
pressBack()
返回键
pressImeActionButton()
pressKey()
根据Key模拟按键
pressMenuKey()
实体键盘菜单键
replaceText()
替换文本
scrollTo()
滑动到
swipeDown()
下滑
swipeLeft()
左滑
swipeRight()
右滑
swipeUp()
上滑
typeText()
获得焦点并注入文本(模拟按键单个输入)
typeTextIntoFocusedView()
在已获得焦点的View上注入文本(模拟按键单个输入)
检验测试结果
ViewAssertions
这里用的最多的时 matches(Matcher) ,可以根据自己的需求情况修改 Matcher 来变更断言。
函数
功能
doesNotExist()
断言目标 view 不存在于当前布局
matches()
断言当前 view 是否匹配指定 matcher
seletedDescendantsMatch()
目标 view 的子视图如果匹配第一个matcher,则一定匹配第二个
LayoutAssertions
函数
功能
noEllipsizedText()
布局不包含椭圆化或剪切的TextView
noMultilineButtons()
布局中不包含具有多行文本的Button
noOverlaps
与匹配的子视图不重叠
PositionAssertions
函数
isAbove(Matcher matcher)
isBelow(Matcher matcher)
isBottomAlignedWith(Matcher matcher)
isLeftAlignedWith(Matcher matcher)
isLeftOf(Matcher matcher)
sRightAlignedWith(Matcher matcher)
isRightOf(Matcher matcher)
isTopAlignedWith(Matcher matcher)
具体案例
TODO:未完待遇
进阶使用
onData的使用
对于ListView,如果要操作其中的某一个item,特别是不可见状态的item,是不能通过上述的ViewMatch来定位的。我们都知道ListView的View是复用的,不可见状态的item并没有把内容绘制到View上。Espresso针对AdapterView(ListView的父类),提供了onData来支持。
Idling Resource的使用
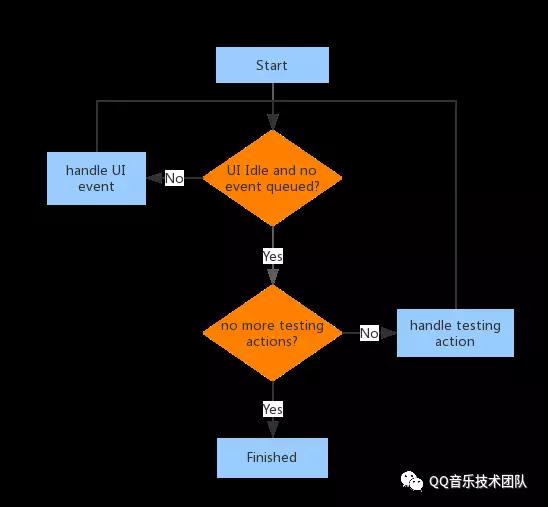
TODO:未完待遇
注意
避免Activity的层级跳转,测试用例尽量只在单个Activity内完成。Activity层级跳转越多,越容易出错
强烈不推荐,直接获取View的对象,调用View的方法来模拟用户操作。应该统一使用Espresso提供的方法
测试用例,特别是UI自动化测试用例,应该尽量保持逻辑简单,覆盖关键路径就足矣。因为UI变动是很频繁的,越复杂,维护成本就越高,投入产出比就会自然降低了。
感想
正如周报中所言,发现自己会和分享给别人完全是两回事,1.首先得让人认可这件事是有意义的 2.这件事用这种方案是最合适的 3.最后才是这个方案分享出去的每一个知识点是正确的。目前我只能做到第三点。
写在最后
引用官方介绍的一段话,Espresso的目标受众是开发者。希望更多的团队能够实现Google的期许最大化利用Espresso,把Bug扼杀在摇篮中。
引用
作者:clwwlc