字典学习 (Dictionary Learning) —— K-SVD 算法
文章目录论文问题描述求解原理python 实现KSVD 算法测试结果可视化函数
论文
作者:颹蕭蕭
M. Aharon, M. Elad and A. Bruckstein, “K-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation,” in IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 54, no. 11, pp. 4311-4322, Nov. 2006.
问题描述minD,X∣∣Y−DX∣∣Fs.t.∣∣xi∣∣0<T0,∀i
\begin{array}{ll}
\min_{D,X} & ||Y-DX||_F \\
s.t.& ||x_i||_0 < T_0, \forall i
\end{array}
minD,Xs.t.∣∣Y−DX∣∣F∣∣xi∣∣0<T0,∀i
其中Y∈RM×LY\in R^{M\times L}Y∈RM×L为原始数据,D∈RM×ND\in R^{M\times N}D∈RM×N为字典,X∈RN×LX\in R^{N\times L}X∈RN×L为编码。
MMM 表示数据特征维度,LLL表示样本数,NNN 表示字典大小。
优化的目标是找到原始数据的稀疏表示,要求XXX的每一列xix_ixi的非零元数目小于 T0T_0T0。
交替优化:
固定 DDD,优化 XXX,主要用到正交匹配跟踪 (OMP) 固定 XXX,优化 DDD,主要用到奇异值分解 (SVD)
from sklearn import linear_model
def KSVD(Y, dict_size,
max_iter = 10,
sparse_rate = 0.2,
tolerance = 1e-6):
assert(dict_size 1e-7)[0]
if len(index) == 0:
continue
d[:, i] = 0
r = (y - np.dot(d, x))[:, index]
u, s, v = np.linalg.svd(r, full_matrices=False)
d[:, i] = u[:, 0]
for j,k in enumerate(index):
x[i, k] = s[0] * v[0, j]
return d, x
# initialize dictionary
if dict_size > Y.shape[0]:
dic = Y[:, np.random.choice(Y.shape[1], dict_size, replace=False)]
else:
u, s, v = np.linalg.svd(Y)
dic = u[:, :dict_size]
print('dict shape:', dic.shape)
n_nonzero_coefs_each_code = int(sparse_rate * dict_size) if int(sparse_rate * dict_size) > 0 else 1
for i in range(max_iter):
x = linear_model.orthogonal_mp(dic, Y, n_nonzero_coefs = n_nonzero_coefs_each_code)
e = np.linalg.norm(Y - dic @ x)
if e < tolerance:
break
dict_update(Y, dic, x)
sparse_code = linear_model.orthogonal_mp(dic, Y, n_nonzero_coefs = n_nonzero_coefs_each_code)
return dic, sparse_code
测试
Y=DXY = D XY=DX
import numpy as np
import scipy.sparse as ss
# 生成随机稀疏矩阵 X
num_col_X = 30
num_row_X = 10
num_ele_X = 40
a = [np.random.randint(0,num_row_X) for _ in range(num_ele_X)]
b = [np.random.randint(0,num_col_X) for _ in range(num_ele_X - num_col_X)] + [i for i in range(num_col_X)]
c = [np.random.rand()*10 for _ in range(num_ele_X)]
rows, cols, v = np.array(a), np.array(b), np.array(c)
sparseX = ss.coo_matrix((v,(rows,cols)))
X = sparseX.todense()
# 随机生成字典 D
num_row_D = 10
num_col_D = num_row_X
D = np.random.random((num_row_D,num_col_D))
# 生成 Y
Y = D @ X
原始数据

完备字典
dic, code = KSVD(Y, 10)
Y_reconstruct = dic @ code

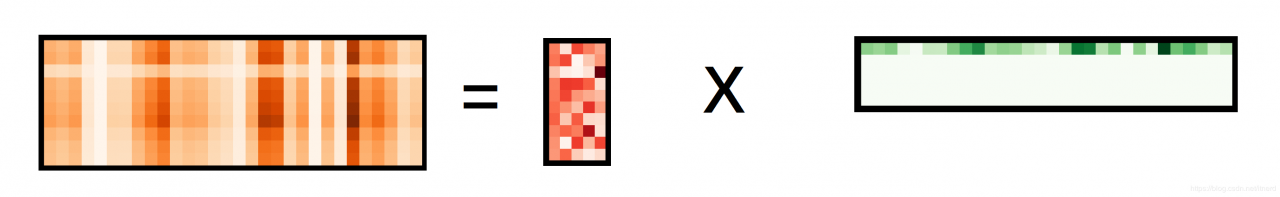
欠完备字典
dic, code = KSVD(Y, 5)
Y_reconstruct = dic @ code
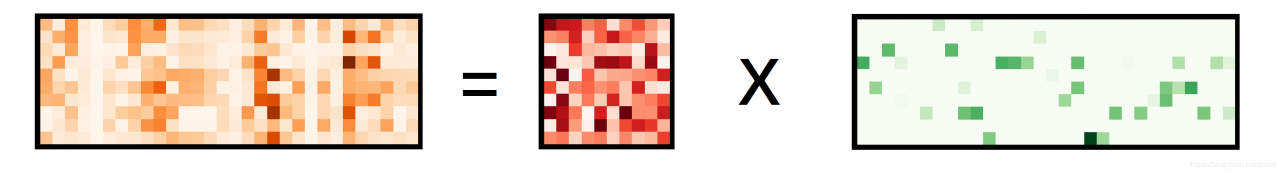
超完备字典
dic, code = KSVD(Y, 15)
Y_reconstruct = dic @ code

def showmat(X, cmap='Oranges'):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
X_abs = np.abs(X)
ax.matshow(X_abs, vmin=np.min(X_abs), vmax=np.max(X_abs), cmap=cmap)
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
showmat(Y_reconstruct), showmat(Y)
showmat(code,'Greens'), showmat(X,'Greens')
showmat(dic,'Reds'), showmat(D, 'Reds')
作者:颹蕭蕭
相关文章
Serafina
2021-03-06
Iris
2021-08-03
Xena
2020-02-28
Naomi
2021-05-04
Rhea
2023-05-31
Pandora
2023-07-07
Tallulah
2023-07-17
Trixie
2023-07-20
Janna
2023-07-20
Ophelia
2023-07-20
Natalia
2023-07-20
Hester
2023-07-20
Ianthe
2023-07-20
Irma
2023-07-20
Valora
2023-07-20
Kirima
2023-07-20
Radinka
2023-07-20
Fawn
2023-07-21
Tertia
2023-07-21