SpringBoot集成JWT实现登陆验证的方法详解
1:首先,我们需要在项目中导入两个依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.auth0</groupId>
<artifactId>java-jwt</artifactId>
<version>3.10.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.7.20</version>
</dependency>
2:然后我讲一下需求:前端给后端传入一个form-data类型数据,然后数据库中现在已经有了一条管理员用户(看下面第二个图)

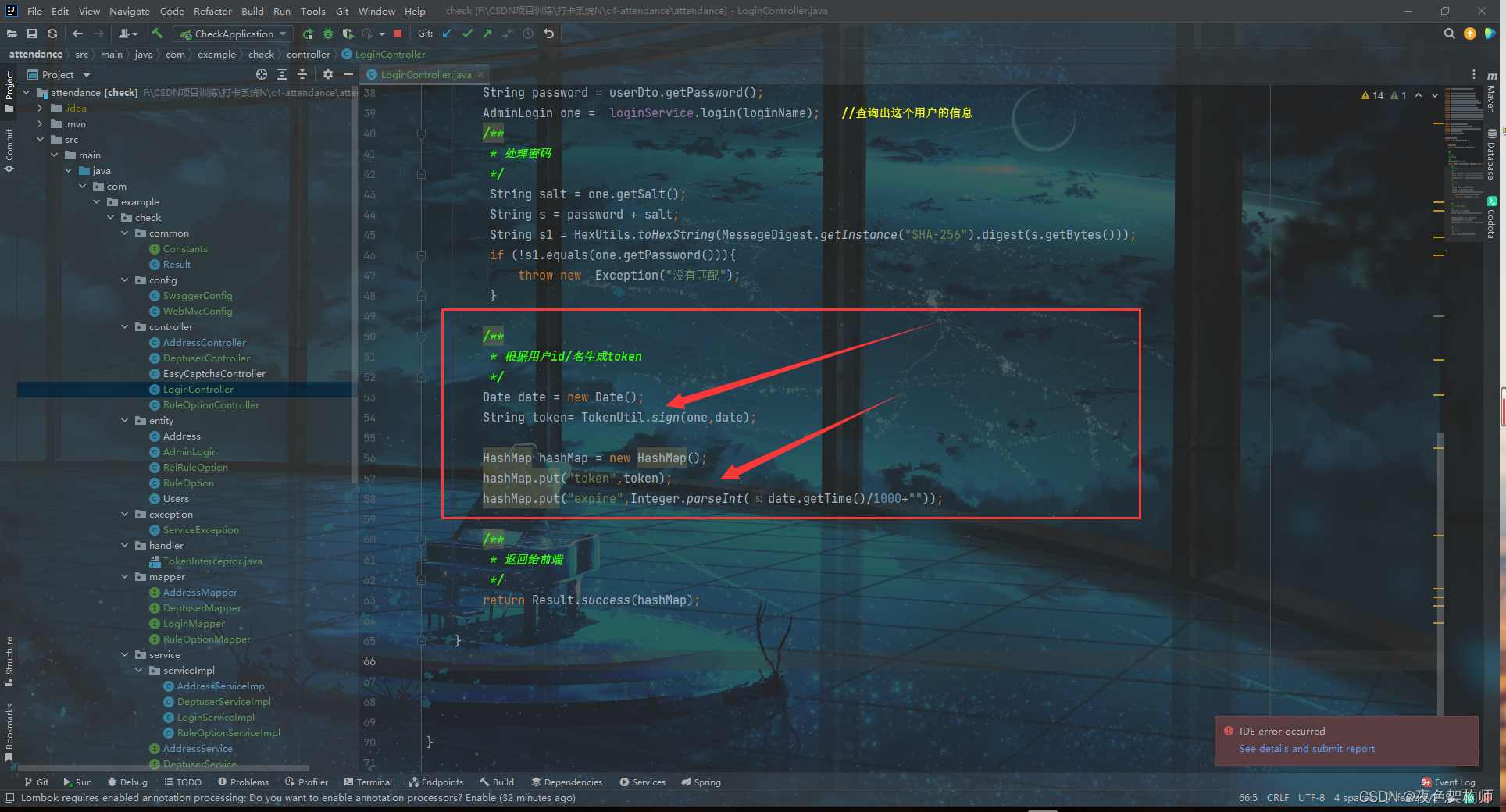
(1):我们的思路就是首先获取到前端传来的值,然后使用前端传来的用户名去数据库中查,我们前端传来的数据我是用了一个封装实体类:UserDto来保存前端传来的值:




(2):然后我们将根据用户名查出来的数据会返回出一个实体类,我们使用get方法得到他的salt:(也就是数据库中的salt)

(3):接下来,我们将前端传来的密码和数据库中查到的salt加起来,组成新的字符串,然后将新的字符串进行SHA-256加密,将加密处理后的密码去和数据库中的密码比对是否相等,这里上面那个图片也圈住了,至于这句话: String s1 = HexUtils.toHexString(MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256").digest(s.getBytes()));就是使用SHA-256加密
如果相等就返回给前端数据:下图是前端需要响应的代码示例,所以我们将中间的data返回数据使用HashMap封装起来,至于外面的code和msg就是使用一个封装类:

3:涉及到的一些工具类和跨域: TokenUtils:创建token中的sign,我们传入的第一个就是数据库中实体类,这里一定不要混淆,数据库中数据的实体类和前端传来参数的封装实体类,我这里数据库中的实体类是:AdminLogin:,然后第二个参数expires是指过期时间,这个我们自己设置就好,需要自己修改的地方还有就是:
.withClaim("username",user.getLoginName()) //存放数据
.withClaim("password",user.getPassword())
这里的user.getxxxxxx根据自己去调整

package com.example.check.util;
import com.auth0.jwt.JWT;
import com.auth0.jwt.JWTVerifier;
import com.auth0.jwt.algorithms.Algorithm;
import com.auth0.jwt.exceptions.JWTCreationException;
import com.auth0.jwt.exceptions.JWTDecodeException;
import com.auth0.jwt.exceptions.JWTVerificationException;
import com.auth0.jwt.interfaces.Claim;
import com.auth0.jwt.interfaces.DecodedJWT;
import com.example.check.entity.AdminLogin;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author quxiang
* @date 2021/12/30 13:53
*/
public class TokenUtil {
private static final long EXPIRE_TIME= 60*1000;//token到期时间60s
private static final String TOKEN_SECRET="l122adasw532df"; //密钥盐
/**
* 创建一个token
* @param user
* @return
*/
public static String sign(AdminLogin user,Date expires){
String token=null;
try {
token = JWT.create()
.withIssuer("auth0")//发行人
.withClaim("username",user.getLoginName()) //存放数据
.withClaim("password",user.getPassword())
.withExpiresAt(expires)//过期时间
.sign(Algorithm.HMAC256(TOKEN_SECRET));
} catch (IllegalArgumentException|JWTCreationException je) {
}
return token;
}
/**
* 对token进行验证
* @param token
* @return
*/
public static Boolean verify(String token){
try {
JWTVerifier jwtVerifier=JWT.require(Algorithm.HMAC256(TOKEN_SECRET)).withIssuer("auth0").build();//创建token验证器
DecodedJWT decodedJWT=jwtVerifier.verify(token);
System.out.println("认证通过:");
System.out.println("username: " + TokenUtil.getUsername(token));
System.out.println("过期时间: " + decodedJWT.getExpiresAt());
} catch (IllegalArgumentException |JWTVerificationException e) {
//抛出错误即为验证不通过
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 获取用户名
*/
public static String getUsername(String token)
{
try{
DecodedJWT jwt=JWT.decode(token);
return jwt.getClaim("username").asString();
}catch (JWTDecodeException e)
{
return null;
}
}
}
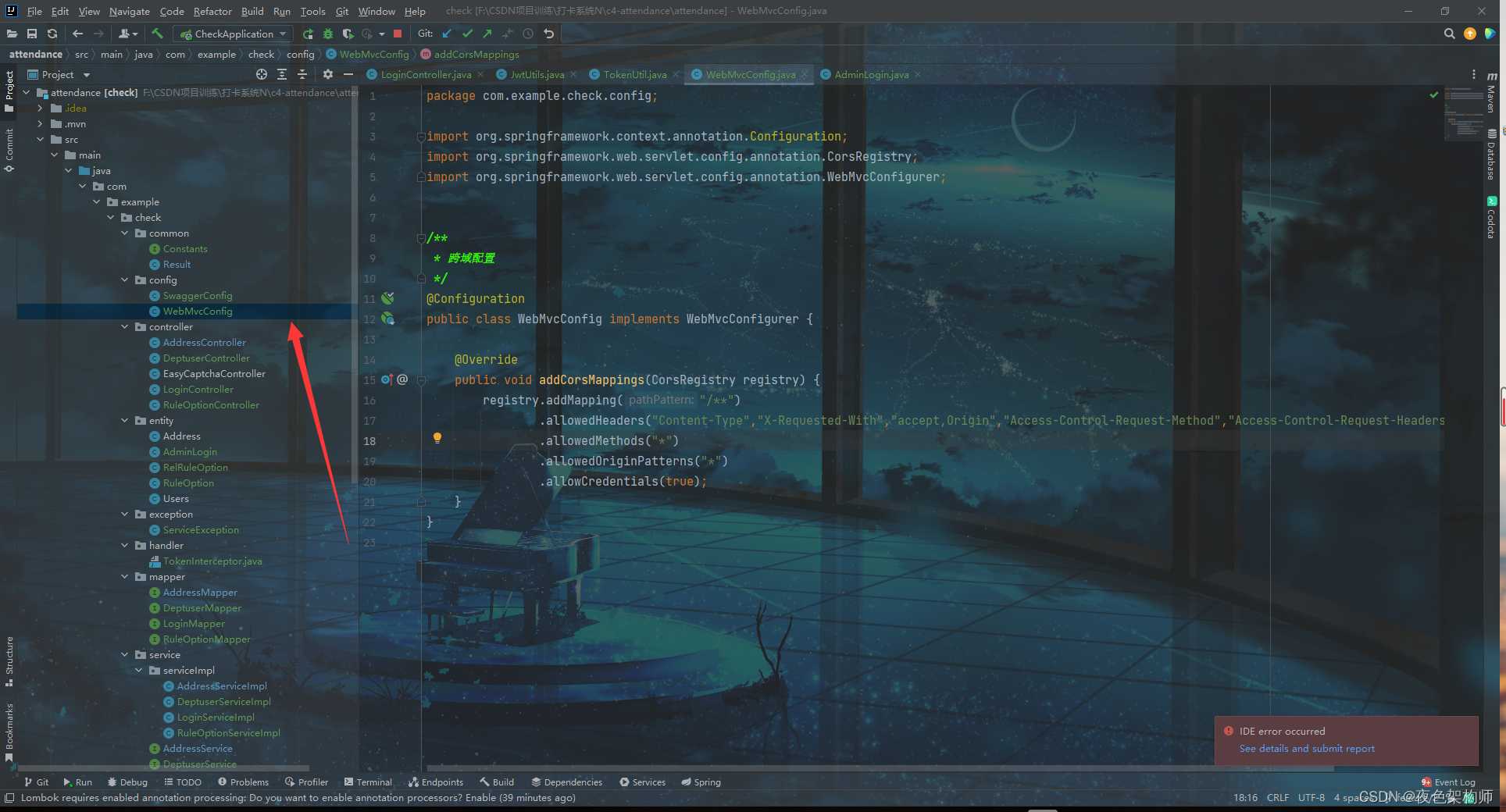
跨域:
package com.example.check.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
/**
* 跨域配置
*/
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedHeaders("Content-Type","X-Requested-With","accept,Origin","Access-Control-Request-Method","Access-Control-Request-Headers","token")
.allowedMethods("*")
.allowedOriginPatterns("*")
.allowCredentials(true);
}
}
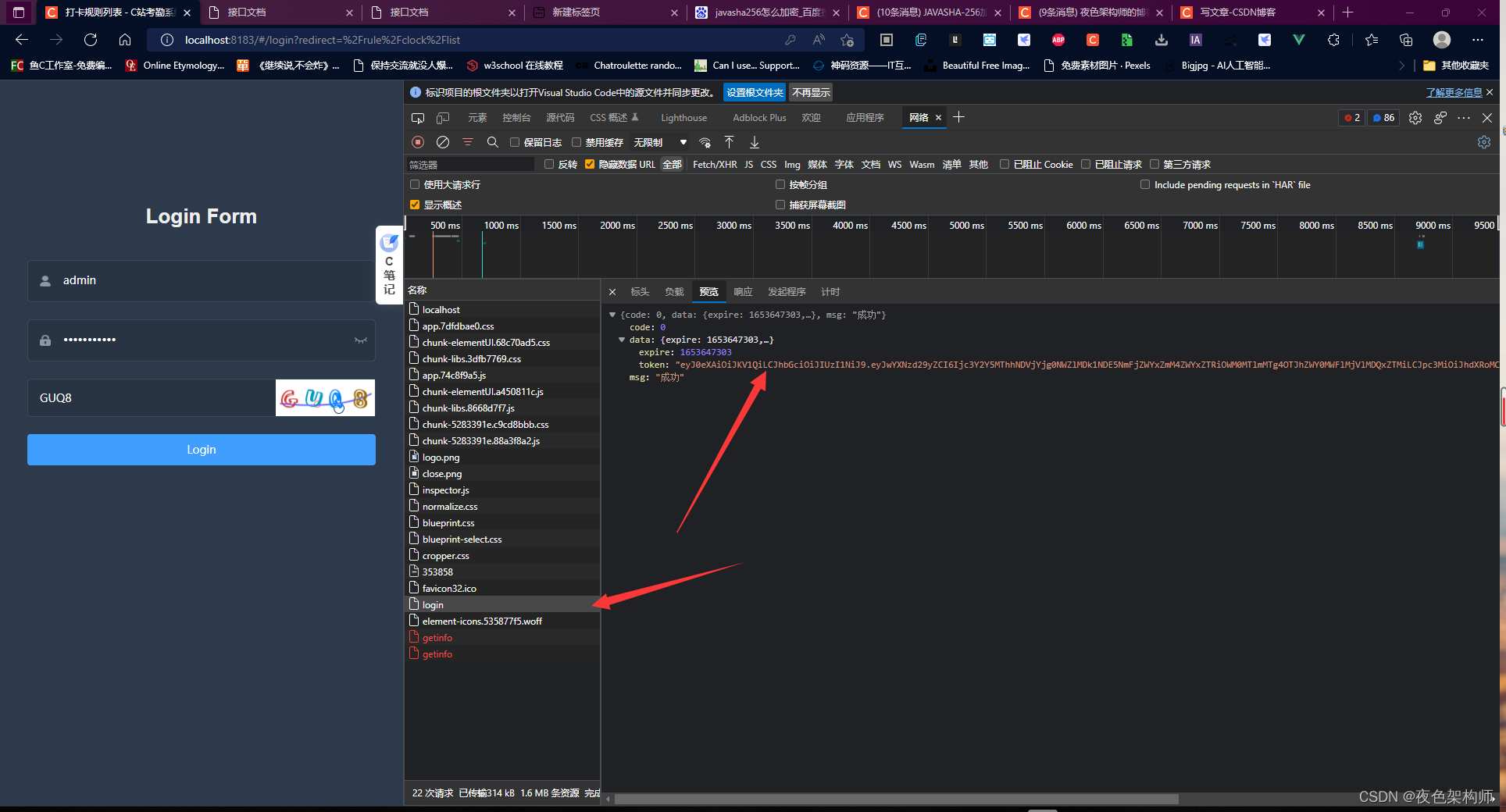
然后我们打开前端界面:点击登录后就可以在后台看到已经传过去的参数:
以上就是SpringBoot集成JWT实现登陆验证的方法详解的详细内容,更多关于SpringBoot JWT登陆验证的资料请关注软件开发网其它相关文章!