机器学习代码实战——数值计算
文章目录1.上溢和下溢2.优化方法
1.上溢和下溢
作者:程旭员
下溢(Underflow):当接近零的数被四舍五入为零时发生下溢。
上溢(Overflow):当大量级的数被近似为 ∞ 或 −∞ 时发生上溢。
必须对上溢和下溢进行数值稳定的一个例子是 softmax 函数。softmax 函数经常用于预测与范畴分布相关联的概率,定义为:
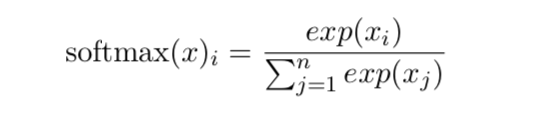
import numpy as np
x = np.array([1e7, 1e8, 2e5, 2e7])
y = np.exp(x) / sum(np.exp(x))
print("上溢:",y)
x = x - np.max(x) # 减去最大值
y = np.exp(x) / sum(np.exp(x))
print("上溢处理:",y)
import numpy as np
x = np.array([-1e10, -1e9, -2e10, -1e10])
y = np.exp(x) / sum(np.exp(x))
print("下溢:",y)
x = x - np.max(x)
y = np.exp(x) / sum(np.exp(x))
print("下溢处理:",y)
print("log softmax(x):", np.log(y))
def logsoftmax(x):
y = x - np.log(sum(np.exp(x)))
return y
print("logsoftmax(x):", logsoftmax(x))
2.优化方法
梯度下降法

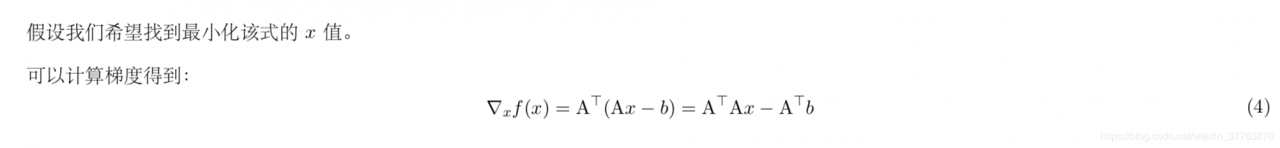
x0 = np.array([1.0,1.0,1.0])
A = np.array([[1.0, -2.0, 1.0],[0.0, 2.0, -8.0], [-4.0, 5.0, 9.0]])
b = np.array([0.0, 8.0, -9.0])
epsilon = 0.001
delta = 1e-3
def matmul_chain(*args):
if len(args) == 0:
return np.nan
result = args[0]
for x in args[1:]:
result += x
return result
def gradient_decent(x, A,b,epsilon,delta):
while np.linalg.norm(matmul_chain(A.T,A,x) - matmul_chain(A.T,b)) > delta:
x -= epsilon*(matmul_chain(A.T,A,x) - matmul_chain(A.T,b))
return x
gradient_decent(x0,A,b,epsilon,delta)
作者:程旭员