强化学习——Sarsa找宝藏
目录
实验结果:
一些有趣的实验现象:
对比Q-Learning和Sarsa公式:
run.py
RL_brain.py
maze_env.py
参考:
实验结果: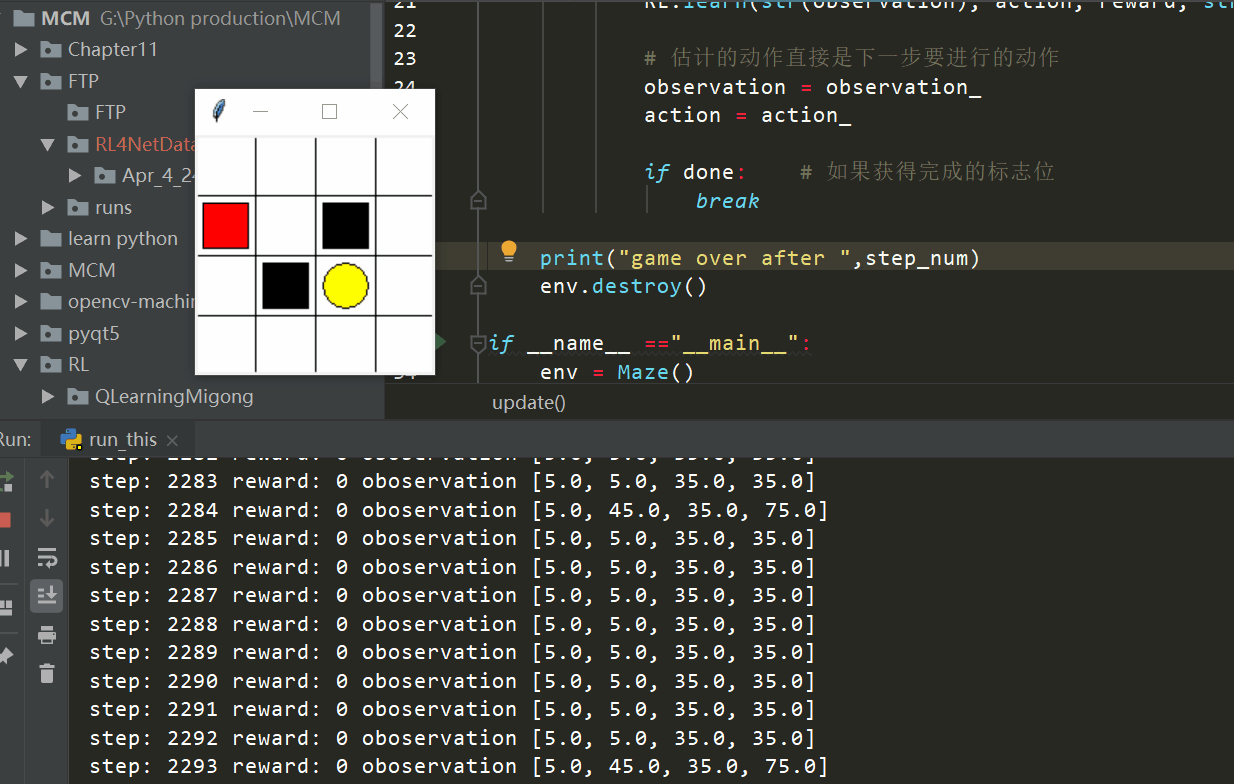
还是经典的二维找宝藏的游戏例子
一些有趣的实验现象: 由于Sarsa比Q-Learning更加安全、更加保守,这是因为Sarsa更新的时候是基于下一个Q,在更新state之前已经想好了state对应的action,而QLearning是基于maxQ的,总是想着要将更新的Q最大化,所以QLeanring更加贪婪!但是这样的后果就是Sarsa会经常处于啥都不寻找的状态,如上面的动图所示!这样的会浪费比较多的资源,也会是训练的回合数更多! 因为 Sarsa 是说到做到型, 所以我们也叫他 on-policy, 在线学习, 学着自己在做的事情. 而 Q learning 是说到但并不一定做到, 所以它也叫作 Off-policy, 离线学习. 而因为有了 maxQ, Q-learning 也是一个特别勇敢的算法. 每次训练的不确定性比较大,有的时候会很快发现一个找到的策略,在大约1000step之内就能完成训练(done为true100个回合),有的时候agent会一直在一处徘徊,浪费很多计算资源(寻找很多个step) 对比Q-Learning和Sarsa公式:


from maze_env import Maze
from RL_brain import SarsaTable
def update():
step_num = 0
for episode in range(100):
observation = env.reset() # 初始得到环境给的初始observation
action = RL.choose_action(str(observation)) # 根据observation选择action
while True:
env.render() # 环境更新部分
observation_, reward, done = env.step(action) # 得到反馈
step_num+=1
print('step:',step_num,'reward:',reward,'oboservation',observation_)
action_ = RL.choose_action(str(observation_)) # 更新下一个回合的action
RL.learn(str(observation), action, reward, str(observation_), action_)
# 估计的动作直接是下一步要进行的动作
observation = observation_
action = action_
if done: # 如果获得完成的标志位
break
print("game over after ",step_num)
env.destroy()
if __name__ =="__main__":
env = Maze()
RL = SarsaTable(actions=list(range(env.n_actions)))
env.after(100, update)
env.mainloop()
RL_brain.py
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
class RL(object):
def __init__(self, action_space, learning_rate=0.01,reward_decay=0.9,e_greedy=0.9):
self.actions = action_space # a list
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.epsilon = e_greedy
self.q_table = pd.DataFrame(columns=self.actions, dtype=np.float64)
def check_state_exist(self, state):
if state not in self.q_table.index:
# append new state to q table
self.q_table = self.q_table.append(
pd.Series(
[0] * len(self.actions),
index=self.q_table.columns,
name=state,
)
)
def choose_action(self, observation):
self.check_state_exist(observation)
# action selection
if np.random.rand() < self.epsilon:
# choose best action
state_action = self.q_table.loc[observation, :]
# some actions may have the same value, randomly choose on in these actions
action = np.random.choice(state_action[state_action == np.max(state_action)].index)
else:
# choose random action
action = np.random.choice(self.actions)
return action
def learn(self, *args):
pass
# 离线学习QLearning
class QLearningTable(RL):
def __init__(self, actions, learning_rate=0.01, reward_decay=0.9, e_greedy=0.9):
super(QLearningTable, self).__init__(actions, learning_rate, reward_decay, e_greedy)
def learn(self, s, a, r, s_):
self.check_state_exist(s_)
q_predict = self.q_table.loc[s, a]
if s_ != 'terminal': # next state is not terminal
q_target = r + self.gamma * self.q_table.loc[s_, :].max() # Q-Learning中是选择最大值
else:
q_target = r # next state is terminal
self.q_table.loc[s, a] += self.lr * (q_target - q_predict) # update
# 在线学习SarsaTable
class SarsaTable(RL):
# 初始化
def __init__(self, actions, learning_rate=0.01, reward_decay=0.9, e_greedy=0.9):
super(SarsaTable, self).__init__(actions, learning_rate, reward_decay, e_greedy)
# 学习更新参数
def learn(self, s, a, r, s_, a_):
self.check_state_exist(s_) # 检查状态是否存在
q_predict = self.q_table.loc[s, a]
if s_ != 'terminal': # next state is not terminal
q_target = r + self.gamma * self.q_table.loc[s_, a_] # 直接选择下一个行动的值
else:
q_target = r # next state is terminal
self.q_table.loc[s, a] += self.lr * (q_target - q_predict) # 更新值
maze_env.py
import numpy as np
import time
import sys
if sys.version_info.major == 2:
import Tkinter as tk
else:
import tkinter as tk
UNIT = 40 # pixels
MAZE_H = 4 # grid height
MAZE_W = 4 # grid width
class Maze(tk.Tk, object):
def __init__(self):
super(Maze, self).__init__()
self.action_space = ['u', 'd', 'l', 'r']
self.n_actions = len(self.action_space)
self.title('maze')
self.geometry('{0}x{1}'.format(MAZE_H * UNIT, MAZE_H * UNIT))
self._build_maze()
def _build_maze(self):
self.canvas = tk.Canvas(self, bg='white',
height=MAZE_H * UNIT,
width=MAZE_W * UNIT)
# create grids
for c in range(0, MAZE_W * UNIT, UNIT):
x0, y0, x1, y1 = c, 0, c, MAZE_H * UNIT
self.canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1)
for r in range(0, MAZE_H * UNIT, UNIT):
x0, y0, x1, y1 = 0, r, MAZE_W * UNIT, r
self.canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1)
# create origin
origin = np.array([20, 20])
# hell
hell1_center = origin + np.array([UNIT * 2, UNIT])
self.hell1 = self.canvas.create_rectangle(
hell1_center[0] - 15, hell1_center[1] - 15,
hell1_center[0] + 15, hell1_center[1] + 15,
fill='black')
# hell
hell2_center = origin + np.array([UNIT, UNIT * 2])
self.hell2 = self.canvas.create_rectangle(
hell2_center[0] - 15, hell2_center[1] - 15,
hell2_center[0] + 15, hell2_center[1] + 15,
fill='black')
# create oval
oval_center = origin + UNIT * 2
self.oval = self.canvas.create_oval(
oval_center[0] - 15, oval_center[1] - 15,
oval_center[0] + 15, oval_center[1] + 15,
fill='yellow')
# create red rect
self.rect = self.canvas.create_rectangle(
origin[0] - 15, origin[1] - 15,
origin[0] + 15, origin[1] + 15,
fill='red')
# pack all
self.canvas.pack()
def reset(self):
self.update()
time.sleep(0.5)
self.canvas.delete(self.rect)
origin = np.array([20, 20])
self.rect = self.canvas.create_rectangle(
origin[0] - 15, origin[1] - 15,
origin[0] + 15, origin[1] + 15,
fill='red')
# return observation
return self.canvas.coords(self.rect)
def step(self, action):
s = self.canvas.coords(self.rect)
base_action = np.array([0, 0])
if action == 0: # up
if s[1] > UNIT:
base_action[1] -= UNIT
elif action == 1: # down
if s[1] < (MAZE_H - 1) * UNIT:
base_action[1] += UNIT
elif action == 2: # right
if s[0] UNIT:
base_action[0] -= UNIT
self.canvas.move(self.rect, base_action[0], base_action[1]) # move agent
s_ = self.canvas.coords(self.rect) # next state
# reward function
if s_ == self.canvas.coords(self.oval):
reward = 1
done = True
s_ = 'terminal'
elif s_ in [self.canvas.coords(self.hell1), self.canvas.coords(self.hell2)]:
reward = -1
done = True
s_ = 'terminal'
else:
reward = 0
done = False
return s_, reward, done
def render(self):
time.sleep(0.1)
self.update()
参考:
主要复现莫烦Python:https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/machine-learning/reinforcement-learning/3-2-tabular-sarsa2/
https://blog.csdn.net/u010223750/article/details/78955807
 沉迷单车的追风少年
沉迷单车的追风少年

 原创文章 381获赞 350访问量 17万+
关注
私信
展开阅读全文
原创文章 381获赞 350访问量 17万+
关注
私信
展开阅读全文
作者:沉迷单车的追风少年
相关文章
Iris
2021-08-03
Laraine
2020-04-28
Adelaide
2020-03-28
Kande
2023-05-13
Ula
2023-05-13
Jacinda
2023-05-13
Winona
2023-05-13
Fawn
2023-05-13
Echo
2023-05-13
Maha
2023-05-13
Kande
2023-05-15
Viridis
2023-05-17
Pandora
2023-07-07
Tallulah
2023-07-17
Janna
2023-07-20
Ophelia
2023-07-20
Natalia
2023-07-20
Irma
2023-07-20