Python3——bytes和str
Python3——bytes 和str
作者:紫菜花油菜花
参考链接:
Python3种的str和bytes区别、包含python2与python3的区别 Python3中的bytes和str类型 编码方式 ASCII编码:8个比特位代表一个字符的编码,最多表示282^828个字符 UNICODE:规定任何一个字符都用2个字节表示(包括英文),不兼容ASCII UTF-8编码:英文字符系列1字节,汉子3字节表示。兼容ASCII 国产编码:GBK,GB2312,BIG5
方法
>>> dir(bytes)
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'center', 'count', 'decode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'fromhex', 'hex', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdigit', 'islower', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill']
>>> dir(str)
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill']
发现str和bytes有非常相似的方法。
特别的,
str——独有encode
bytes——独有decode
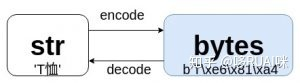
str.encode(‘encoding’) -> bytes
bytes.decode(‘encoding’) -> str
#必须显示地指定编码格式
实例:
'''中文编码'''
>>> a='中文'
>>> type(a)
str
>>> b=bytes(a,encoding='utf-8')
>>> b
b'\xe4\xb8\xad\xe6\x96\x87' #变成了utf-8的编码格式
'''中文解码'''
>>> c=str(b,encoding='utf-8')
>>> type(c)
str
>>> c
'中文' #解码后变成str
'''英文编码,因为英文里,utf-8和ASCII是兼容的,所以显示b'hello',其实也是数字'''
>>> a='hello'
>>> b=bytes(a,encoding='utf-8')
>>> b #输入B,编码为(数字),按照ascii的形式显示
b'hello'
>>> len(b)
5
'''英文解码'''
>>> a=b'hello'
>>> type(a)
bytes
>>> b=str(a,encoding='utf-8')
>>> b
'hello'
bytes与str连接
#bytes连接str
>>> a='中文'
>>> b=bytes(a,encoding='utf-8')
>>> b+=bytes('end','utf-8')
>>> b.strip('end')
未完待续
(a,encoding=‘utf-8’)
b+=bytes(‘end’,‘utf-8’)
b.strip(‘end’)
# 未完待续
作者:紫菜花油菜花