跟着Leo机器学习实战--基于概率论的分类方法:朴素贝叶斯
https://github.com/LeoLeos/MachineLearningLeo/tree/master/bayes
核心思想如果我们用p1(x,y)表示数据(x,y)属于类别1的概率,用p2(x,y)表示数据(x,y)属于类别2的概率,那么判别规则如下:
若p1(x,y)>p2(x,y),则判给类别1
若p1(x,y)<p2(x,y),则判给类别2
条件概率是指事件A在另外一个事件B已经发生条件下的发生概率。条件概率表示为:P(A|B)
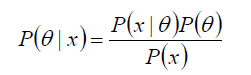
P(θ) 没有数据支持下,θ发生的概率:先验概率
P(θ|x) 在数据X的支持下,θ发生的概率:后验概率,贝叶斯公式也称为后验公式
p(x|θ) 给定某参数θ的概率分布:似然函数
![]()
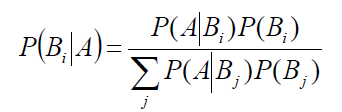
from numpy import *
def loadDataSet():
postingList=[['my', 'dog', 'has', 'flea', 'problems', 'help', 'please'],
['maybe', 'not', 'take', 'him', 'to', 'dog', 'park', 'stupid'],
['my', 'dalmation', 'is', 'so', 'cute', 'I', 'love', 'him'],
['stop', 'posting', 'stupid', 'worthless', 'garbage'],
['mr', 'licks', 'ate', 'my', 'steak', 'how', 'to', 'stop', 'him'],
['quit', 'buying', 'worthless', 'dog', 'food', 'stupid']]
classVec = [0,1,0,1,0,1] #1 标记为侮辱性语言,0标记为不是
return postingList,classVec
def createVocabList(dataSet):
vocabSet = set([]) #create empty set
for document in dataSet:
vocabSet = vocabSet | set(document) #对向量的每一维合并一个不重复的数组
return list(vocabSet)
def setOfWords2Vec(vocabList, inputSet):
returnVec = [0]*len(vocabList)
for word in inputSet:
if word in vocabList:
returnVec[vocabList.index(word)] = 1
else: print("the word: %s is not in my Vocabulary!" % word)
return returnVec #返回词汇列表的每个词汇是否出现在数据集当中,如果是则标记为1
训练算法:从词向量计算概率
此时又需要贝叶斯公式了
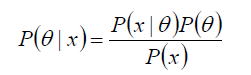
伪代码:
计算每个类别中的文档数目
对每篇训练文档
对每个类别
如果词条出现文档–>增加该词条的计数值
增加所有词条的计数值
对每个类别
对每个词条
将该词条的数目除以总词条数目得到条件概率
返回每个类别的条件概率
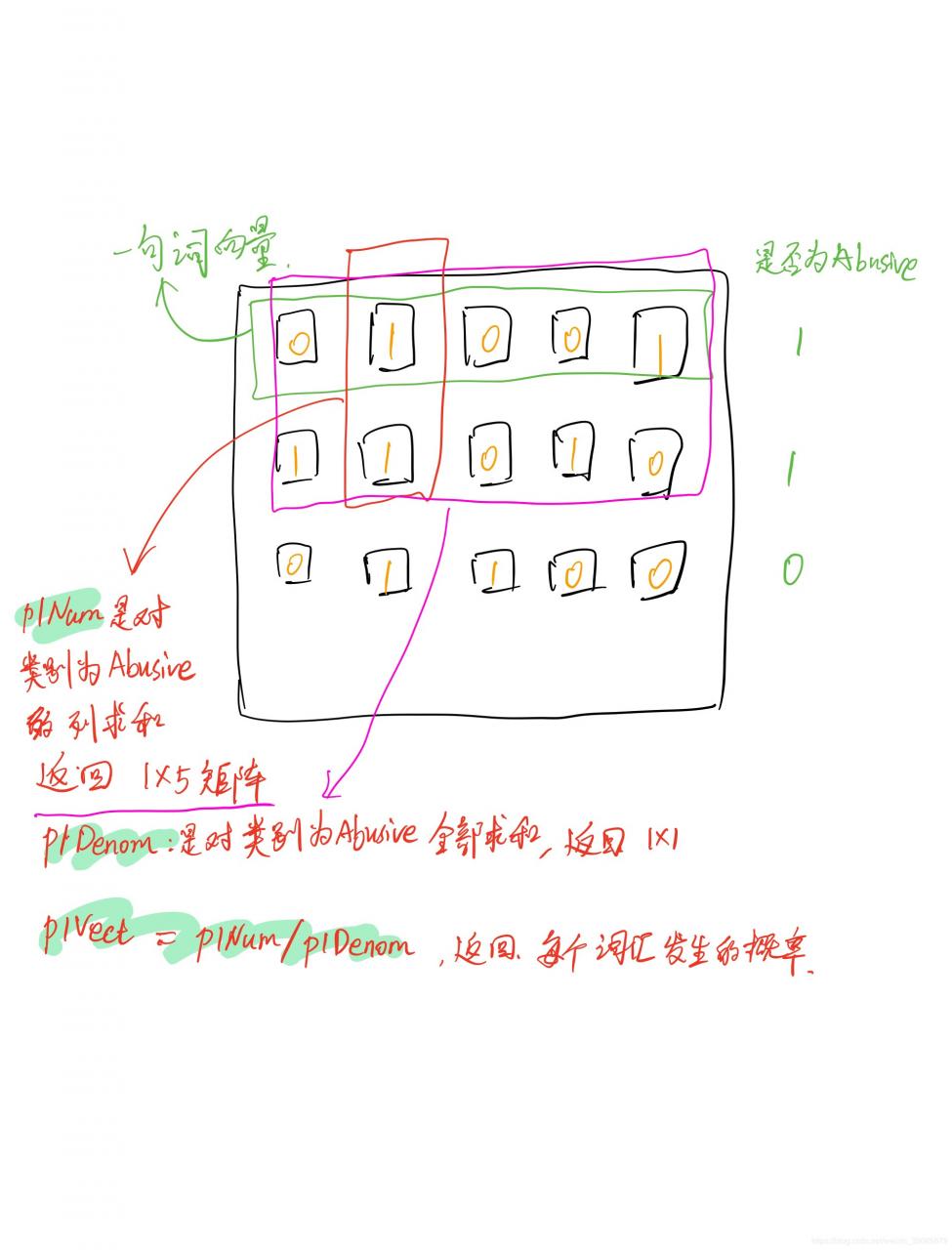
朴素贝叶斯分类器训练函数
def trainNB0(trainMatrix,trainCategory):#trainMatrix文档矩阵,trainCategory每篇文档类别标签构成的向量
numTrainDocs = len(trainMatrix) #len获取行数
print('numTrainDocs',numTrainDocs)
numWords = len(trainMatrix[0]) #第一条词向量的数目
pAbusive = sum(trainCategory)/float(numTrainDocs) #侮辱性语言占总词条的比例
p0Num = ones(numWords); p1Num = ones(numWords) #都设为1是防止相乘之后为0,减少影响
print(p0Num)
p0Denom = 2.0; p1Denom = 2.0 #由于之前设为1了,故此处设为2
for i in range(numTrainDocs): #遍历文档里每一句词向量
if trainCategory[i] == 1: #若1则说明此词向量为侮辱性语言
p1Num += trainMatrix[i] #对所有侮辱性语言的词向量相加
p1Denom += sum(trainMatrix[i]) #获取这一句单词个数,进行累加
else:
p0Num += trainMatrix[i]
p0Denom += sum(trainMatrix[i])
p1Vect = log(p1Num/p1Denom) #change to log()
p0Vect = log(p0Num/p0Denom) #change to log()
return p0Vect,p1Vect,pAbusive
由于都是用很小的数相乘,可能会导致下溢。故需要求对数。
贝叶斯分类器def classifyNB(vec2Classify, p0Vec, p1Vec, pClass1):
#vec2Classify为该词条在词汇表集出现的标记为1的向量,p0Vec为0类词汇的概率向量,p1Vec为1类词汇的概率向量,pClass1类别为1占全部词条的比例
p1 = sum(vec2Classify * p1Vec) + log(pClass1) #element-wise mult
p0 = sum(vec2Classify * p0Vec) + log(1.0 - pClass1)
if p1 > p0:
return 1
else:
return 0
vec2Classify 是0,1向量,p1Vec是前面函数trainNB0()求过的自然对数向量。
sum(vec2Classify * p1Vec) + log(pClass1)表示该词条发生1类的概率乘上1类占全部词条的比例权重,再求其自然对数
sum(vec2Classify * p0Vec) + log(1.0 - pClass1) 表示该词条发生0类的概率乘上0类占全部词条的比例权重,再求其自然对数。
def testingNB():
listOPosts,listClasses = loadDataSet()
myVocabList = createVocabList(listOPosts)
trainMat=[]
for postinDoc in listOPosts:
trainMat.append(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList, postinDoc))
p0V,p1V,pAb = trainNB0(array(trainMat),array(listClasses))
testEntry = ['love', 'my', 'dalmation']
thisDoc = array(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList, testEntry))
print('thisDoc',thisDoc)
print(testEntry,'classified as: ',classifyNB(thisDoc,p0V,p1V,pAb))
testEntry = ['stupid', 'garbage']
thisDoc = array(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList, testEntry))
print('thisDoc',thisDoc)
print(testEntry,'classified as: ',classifyNB(thisDoc,p0V,p1V,pAb))
使用朴素贝叶斯过滤垃圾邮件
词袋模型
#词袋模型
def bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, inputSet):
returnVec = [0]*len(vocabList)
for word in inputSet:
if word in vocabList:
returnVec[vocabList.index(word)] += 1
return returnVec #返回inputSet在vocabList各个出现的个数的矩阵
数据准备(预处理):切分文本
def textParse(bigString): #input is big string, #output is word list
import re
listOfTokens = re.split(r'\W*', bigString)
return [tok.lower() for tok in listOfTokens if len(tok) > 2]
测试算法:使用朴素贝叶斯进行交叉验证
def spamTest():
docList=[]; classList = []; fullText =[]
for i in range(1,26):
wordList = textParse(open('email/spam/%d.txt' % i).read())
docList.append(wordList)
fullText.extend(wordList)
classList.append(1) #侮辱性语言标记为1
wordList = textParse(open('email/ham/%d.txt' % i).read())
docList.append(wordList)
fullText.extend(wordList)
classList.append(0) #非侮辱性语言标记为0
# print('docList',docList)
# print('classList',classList)
# print('fullText',fullText)
vocabList = createVocabList(docList)#创建词汇表
trainingSet = list(range(50)); testSet=[] #初始化训练集和测试集
for i in range(10):
randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(trainingSet))) #随机产生下标
testSet.append(trainingSet[randIndex]) #加到测试集
del(trainingSet[randIndex]) #删除作为测试集的元素
trainMat=[]; trainClasses = []
for docIndex in trainingSet:#对训练集遍历
trainMat.append(bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, docList[docIndex]))#在训练矩阵加入各词条的词包
trainClasses.append(classList[docIndex]) #加入对应的类别
p0V,p1V,pSpam = trainNB0(array(trainMat),array(trainClasses)) #训练算法之后返回参数
errorCount = 0 #初始化错误个数
#交叉验证
for docIndex in testSet: #classify the remaining items
wordVector = bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, docList[docIndex])
if classifyNB(array(wordVector),p0V,p1V,pSpam) != classList[docIndex]:#预测类别
errorCount += 1
print("classification error",docList[docIndex])
print('the error rate is: ',float(errorCount)/len(testSet))
#return vocabList,fullText
核心步骤

def localWords(feed1,feed0):
import feedparser
#与前个函数相同的步骤
docList=[]; classList = []; fullText =[]
minLen = min(len(feed1['entries']),len(feed0['entries']))
for i in range(minLen):
wordList = textParse(feed1['entries'][i]['summary'])
docList.append(wordList)
fullText.extend(wordList)
classList.append(1) #NY is class 1
wordList = textParse(feed0['entries'][i]['summary'])
docList.append(wordList)
fullText.extend(wordList)
classList.append(0)
vocabList = createVocabList(docList)#create vocabulary
top30Words = calcMostFreq(vocabList,fullText) #remove top 30 words
for pairW in top30Words:
if pairW[0] in vocabList: vocabList.remove(pairW[0])
trainingSet = range(2*minLen); testSet=[] #create test set
for i in range(20):
randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(trainingSet)))
testSet.append(trainingSet[randIndex])
del(trainingSet[randIndex])
trainMat=[]; trainClasses = []
for docIndex in trainingSet:#train the classifier (get probs) trainNB0
trainMat.append(bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, docList[docIndex]))
trainClasses.append(classList[docIndex])
p0V,p1V,pSpam = trainNB0(array(trainMat),array(trainClasses)) #训练获取参数
errorCount = 0
for docIndex in testSet: #分类验证
wordVector = bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, docList[docIndex])
if classifyNB(array(wordVector),p0V,p1V,pSpam) != classList[docIndex]:
errorCount += 1
print('the error rate is: ',float(errorCount)/len(testSet))
return vocabList,p0V,p1V
分析数据:显示地域相关用词
def getTopWords(ny,sf):
import operator
vocabList,p0V,p1V=localWords(ny,sf)
topNY=[]; topSF=[]
for i in range(len(p0V)):
if p0V[i] > -6.0 : topSF.append((vocabList[i],p0V[i]))
if p1V[i] > -6.0 : topNY.append((vocabList[i],p1V[i]))
sortedSF = sorted(topSF, key=lambda pair: pair[1], reverse=True)
print("SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**")
for item in sortedSF:
print(item[0])
sortedNY = sorted(topNY, key=lambda pair: pair[1], reverse=True)
print("NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**")
for item in sortedNY:
print(item[0])
参考文献
机器学习实战 Peter Harrington著
作者:LuckyLeo26