OpenCV实现图片编解码实践
原图:

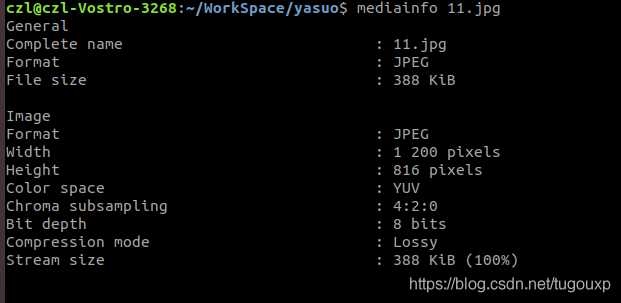
图像信息,可以看到图像是一个816*2100像素的图片:
python代码:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('11.jpg', 0)
img1 = img.astype('float')
img_dct = cv2.dct(img1)
img_dct_log = np.log(abs(img_dct))
img_recor = cv2.idct(img_dct)
recor_temp = img_dct[0:100,0:100]
recor_temp2 = np.zeros(img.shape)
recor_temp2[0:100,0:100] = recor_temp
print recor_temp.shape
print recor_temp2.shape
img_recor1 = cv2.idct(recor_temp2)
plt.subplot(221)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(222)
plt.imshow(img_dct_log)
plt.title('dct transformed')
plt.subplot(223)
plt.imshow(img_recor)
plt.title('idct transformed')
plt.subplot(224)
plt.imshow(img_recor1)
plt.title('idct transformed2')
plt.show()
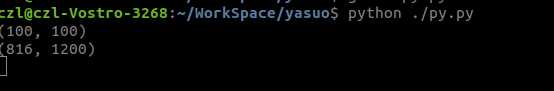
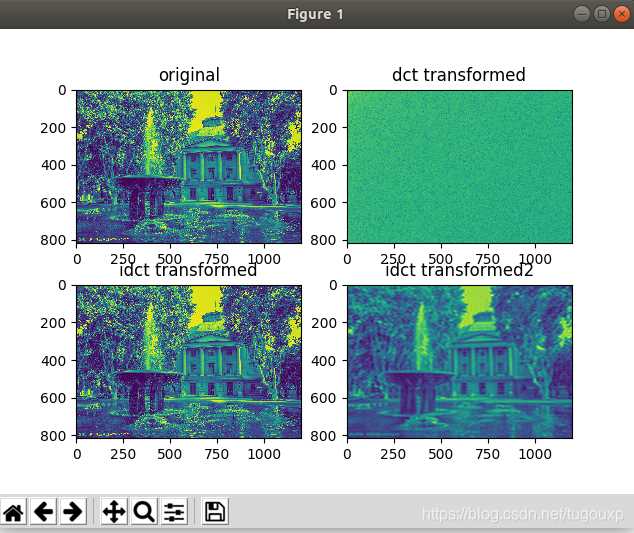
仅仅提取一个100*100的DCT系数后的效果:
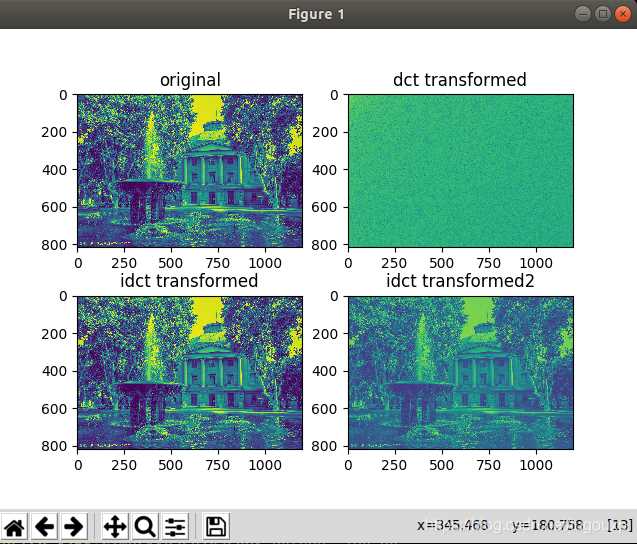
当用800*1000的DCT系数:
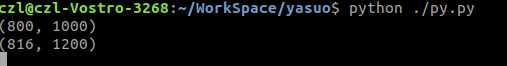
可以看到图像细节更丰富了一些:
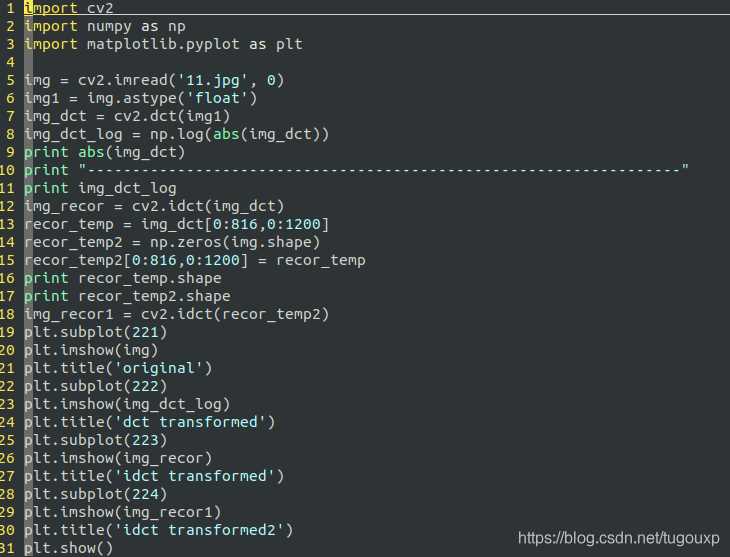
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('11.jpg', 0)
img1 = img.astype('float')
img_dct = cv2.dct(img1)
img_dct_log = np.log(abs(img_dct))
img_recor = cv2.idct(img_dct)
recor_temp = img_dct[0:800,0:1000]
recor_temp2 = np.zeros(img.shape)
recor_temp2[0:800,0:1000] = recor_temp
print recor_temp.shape
print recor_temp2.shape
img_recor1 = cv2.idct(recor_temp2)
plt.subplot(221)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(222)
plt.imshow(img_dct_log)
plt.title('dct transformed')
plt.subplot(223)
plt.imshow(img_recor)
plt.title('idct transformed')
plt.subplot(224)
plt.imshow(img_recor1)
plt.title('idct transformed2')
plt.show()
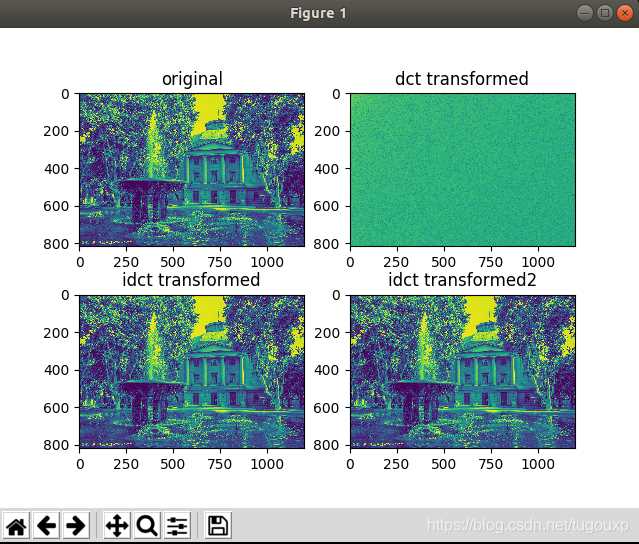
当用816*1200的DCT系数:
可以看出图像恢复到原来的质量了.
分析代码:
img_dct保存的是dct变换后的矩阵,img_dct_log是矩阵中的元素首先取绝对值,再求对数的矩阵.
img_dct_log = np.log(abs(img_dct))
那么对数的底是多少呢?
打印出来img_dct_log和abs(img_dct)看一下:
打印结果:
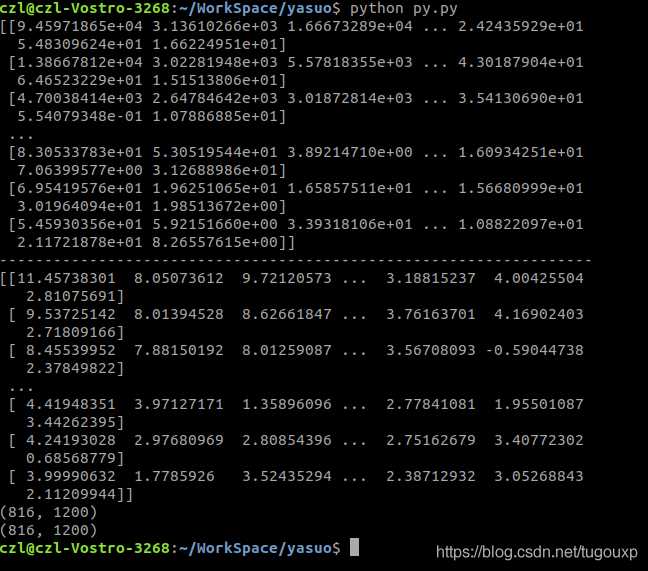
其中9.45971865e+04=9.45971865 x 10^4 =94597.1865表示的是科学计数法.
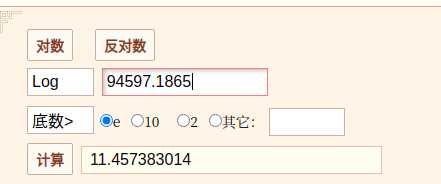
我们看到只有在底数取e的时候,对应的对数才符合题目输出要求,所以,python numpy.log函数取的是以自然常数e为地的对数.
到此这篇关于OpenCV实现图片编解码实践的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关OpenCV 图片编解码内容请搜索软件开发网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持软件开发网!