逻辑门的继承层级结构实现-python
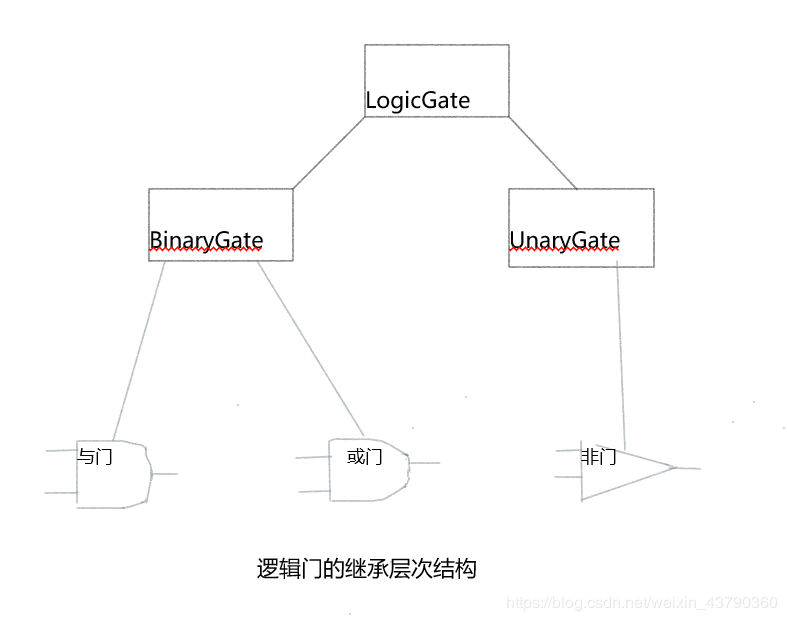
为了实现电路,首先要构建逻辑门的表示。顶部的LogicGate类代表逻辑门的通用特性:逻辑门的标签(label)和一个输出(output)
根据逻辑门接收输入的个数来为逻辑门分类。BinaryGate是LogicGate的一个子类,并且有两个输入。UnaryGatet同样是LogicGate的子类,但只有一个输入。这些输入被称作**‘引脚’(pin)**。
AndGate和OrGate是BinaryGate的子类,NotGate是UnaryGate的子类。AndGate、OrGate和NotGate类需要实现各自的布尔运算行为,这里提供一个函数performGateLogic()。要使用这些逻辑门,可以构建这些类的实例,详见代码。
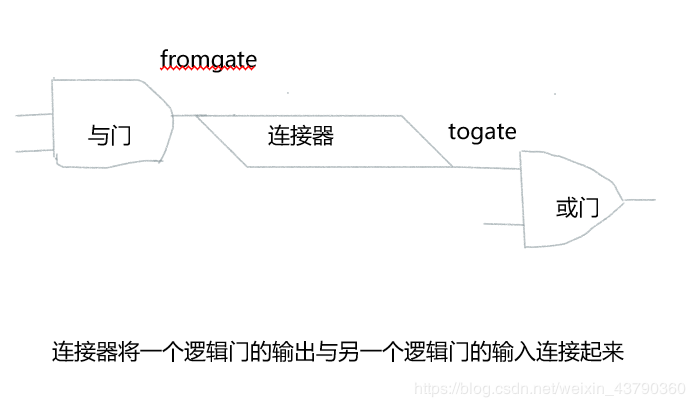
有了基本的逻辑门之后,便可以开始构建电路。为此,需要将逻辑门连接起来,前一个的输出是后一个的输入。因此,要实现一个Connector类。(Connector类与LogicGate类是HAS-A关系,即连接器内部包含LogicGate类的实例,但是不在继承层次结构中)
每一个连接器对象都包含fromgate和togate两个逻辑门实例,数据值会从一个逻辑门的输出‘流向’下一个逻辑门的输入。因此,需要一个函数setNextPin(),将该函数添加到逻辑门类中,以使每一个togate能够选择适当的输入。
# !/user/bin/env python
# coding:utf-8
class LogicGate:
def __init__(self, n):
self.label = n
self.output = None
def getLabel(self):
return self.label
def getOutput(self):
self.output = self.performGateLogic()
return self.output
class BinaryGate(LogicGate):
def __init__(self, n):#子类的构造方法需要先调用父类的构造方法,然后再初始化自己独有的数据
super().__init__(n)#使用super函数调用父类的构造方法
self.pinA = None
self.pinB = None
def getPinA(self):
if self.pinA == None:#输入端没有与任何逻辑门连接,则要求用户输入
return int(input("Enter Pin A input for gate " +
self.getLabel() + '-->'))
else:#输入端有了连接,就访问该连接并且获取fromgate的输出值
return self.pinA.getFrom().getOutput()
def getPinB(self):
if self.pinB == None:
return int(input("Enter Pin B input for gate " +
self.getLabel() + '-->'))
else:
return self.pinB.getFrom().getOutput()
def setNextPin(self, source):
if self.pinA == None:#在Binarygate中,逻辑门有两个输入,都能连接的情况下,默认选择pinA
self.pinA = source
elif self.pinB == None:
self.pinB = source
else:
raise RuntimeError("Error: NO EMPTY PINS")
class UnaryGate(LogicGate):
def __init__(self, n):
super().__init__(n)
self.pin = None
def getPin(self):
if self.pin == None:
return int(input("Enter Pin input for gate " +
self.getLabel() + '-->'))
else:
return self.pin.getFrom().getOutput()
def setNextPin(self, source):
if self.pin == None:
self.pin = source
class AndGate(BinaryGate):
def __init__(self, n):
super().__init__(n)
def performGateLogic(self):
a = self.getPinA()
b = self.getPinB()
if a == 1 and b == 1:
return 1
else:
return 0
class OrGate(BinaryGate):
def __init__(self, n):
super().__init__(n)
def performGateLogic(self):
a = self.getPinA()
b = self.getPinB()
if a == 1 or b == 1:
return 1
else:
return 0
class NotGate(UnaryGate):
def __init__(self, n):
super().__init__(n)
def performGateLogic(self):
a = self.getPin()
if a == 1:
return 0
else:
return 1
class Connector:
def __init__(self, fgate, tgate):
self.fromgate = fgate
self.togate = tgate
tgate.setNextPin(self)
def getFrom(self):
return self.fromgate
def getTo(self):
return self.togate
# instance
'''
g1 = AndGate('G1')
print(g1.getOutput())
'''
'''
g2 = OrGate('G2')
print(g2.getOutput())
'''
'''
g3 = NotGate('G3')
print(g3.getOutput())
'''
以下代码段构造图中的电路:
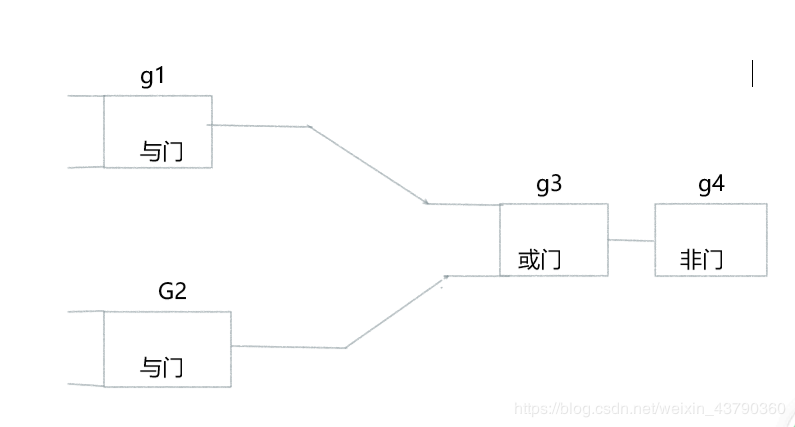
g1 = AndGate('G1')
g2 = AndGate('G2')
g3 = OrGate('G3')
g4 = NotGate('G4')
c1 = Connector(g1, g3)
c2 = Connector(g2, g3)
c3 = Connector(g3, g4)
print(g4.getOutput())
作者:忆木子