Linux基础-shell Script
自动化测试的基础是什么,我认为就是linux shell Script脚本语言,与jenkins pipeline的语法相似,另外docker的部署很大程度也仰赖脚本语言,这次的坑很早之前就已经开了,但是因为一直在重构官网,所以拖到了现在,嘿嘿,探索开始。
学习自鸟哥的linux私房菜
1. 什么是Shell Scripts什么是shell Scripts(程序化脚本)呢?就是字面的意义,我们把它分为两个部分。在shell部分,我们在BASH中已经提过了,那是一个文字接口底下让我们与系统沟通的一个工具接口。那么Scripts是什么呢?字面上的意思,scripts是脚本和剧本的意思,shell Script就是针对shell所写的剧本了
其实就是一个程序program,这个程序是一个纯文本文件,将一些shell语法与指令(含有外部指令)卸载里面,搭配正则表达式,管线命令与数据流重导向的功能,以达到我们所需要的处理目的。
所以,简单的说,shell Script就像是早期的批处理文件。而且shell Script更是提供了数组,循环,条件与逻辑判断登重要功能,让用户也可以直接以shell来来撰写命令,而不必使用类似C程序语言登传统程序撰写语法。
shell Script的最大作用就是帮助系统管理员更好的管理主机
1.1. 干嘛学习shell Scripts?
自动化管理的重要依据
追踪与管理系统的重要工作 简单入侵检测功能 连续指令的单一化 简单的数据处理 跨平台支持与学习历程较短 1.2. 第一支script的编写撰写过程中注意事项:
1. 指令的执行是从上而下,从左而右的分析和执行。
2. 指令的下达时,指令,选项与参数间的多个空白都会被忽略掉。
3. 空白行也被忽略掉,并且tab按键开头的空白同样是为空格键
4. 如果读取到一个Enter符号, 就尝试执行该行命令或该串命令。
5. 如果一行的内容过多,则使用[\ Enter]来延伸到下一行
6. #可以作为批注,任何加载#后面的资料全部被视为批注文字而被省略。
如此一来,我们在scripts内所撰写的所有程序,就会被一行行的执行。现在我们假设你写的这个程序文件名式 /home/dm/shell.sh好了,那么如何执行这个文件很简单,可以有底下几个方法:
7. 直接指令下达: shell.sh文件必须具备可读与可执行(rx)的权限,然后:
- 绝对路径:使用/home/dm/shell.sh来下达指令
- 相对路径:假设工作目录在/home/dm/下。则使用./shell.sh来执行。
- 变量PATH的功能:将shell.sh放在PATH镇定的目录内。例如:~/bin/shell.sh
8. 以bash程序来执行:透过“bash shell.sh”或者“sh shell.sh”来执行
反正重点就是让那个 shell.sh内的指令可以被执行的意思。
由于centos默认用户家目录下的~/bin目录会被设定到${PATH}内,所以你也可以将shell.sh建立在/home/dm/bin/底下(~/bin目录需要自己设定)。此时若shell.sh在~/bin内有且具有rx权限,那么直接输入shell.sh即可即可执行该脚本程序
那为何 sh shell.sh 也可以执行呢?这是因为~/bin/sh, 其实就是/bin/bash,使用sh shell.sh亦即告诉系统,我想要直接以bash的功能来执行shell.sh这个文件内的相关指令的意思,所以此时你的shell.sh只要有r权限即可被执行。而我们也利用sh 的参数,如-n, -x来执行检查与追踪shell.sh的语法是否正确!
撰写第一支script在武侠世界,不论什么门派都需要从扫地和蹲马步开始,那么学程序呢?呵呵,肯定是有hello World开始了,第一个script
#!/bin/bash
#Program:
# This Program shows "Hello World !" in your screen.
# History:
# 2020/04/02 lidengiyn First release
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin/:usr/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
echo -e "Hello World! \a \n"
exit 0
这段程序分为数段,大致如下:
第一行#!/bin/bash宣告这个script使用的shell名称。 程序内容说明整个script当中,除了第一行的#!用来宣告shell之外,其他的#都是批注用途!所以上面的程序当中,第二行以下就是说明这个程序的数据。易班来说,建议你一定要养成说明该script的:1.内容和功能,2.版本信息, 3.作者与联络方式, 4.建档日期, 5.历史记录等等。 主要环境变量的宣告
建议务必将一些重要哦的环境变量设置好,鸟哥个人人为,PATH与LANG(如果有输出信息是非常重要的),如此一来,我们可以以直接下达一些外部指令,而不必写绝对路径。 主要程序部分
就是将主要的程序写好即可,在这个例子中,就是echo那一行 执行结果告知(定义反传值)
一个指令执行成功与否可以用?这个变量来观察,那么我们也可以用exit这个指令让程序中断,并f返回一个数值给系统,所以我执行之后下达?这个变量来观察,那么我们也可以用exit这个指令让程序中断,并f返回一个数值给系统,所以我执行之后下达?这个变量来观察,那么我们也可以用exit这个指令让程序中断,并f返回一个数值给系统,所以我执行之后下达?得到的就是0了,更可以利用exit(n)来自定义错误,让程序变得更加智能。
执行结果:
[lidengyin@study bin]$ sh hello.sh
Hello World!
你会看到屏幕东东的一声,只需要echo+ -e选项即可
另外,也可以通过:
[lidengyin@study bin]$ chmod a+x hello.sh
[lidengyin@study bin]$ ./hello.sh
来执行。
1.3. 撰写shell Script的良好习惯的建立在每个script的文件开头处记录好:
- script的功能。
- script的版本信息
- script的作者和联系方式
- script的History
- script内比较特殊的指令,使用[绝对路径]来下达
- 内推最好用TAB
- 撰写script最好的工具是而不是vi,因为vim有额外的语法检查机制,能够在第一阶段时发现语法方面的问题。
2. 简单的script练习
2.1. 简单范例
- 对谈式脚本
你应该记得read指令,请你以read指令的用途,撰写一个script,它可以使使用者输入:1.firstname与2.lastname。并且最后在屏幕显示:Your fullname is 的内容:
#!/bin/bash
#Program:
# User inputs his first name and last name. Program shows his full name.
#History:
# 2020/04/03 lidengiyn@2743853037@qq.com release
PATH=/bin:/sbin/:usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
read -p "Please input your first name :" firstname #tishi shuruzhe shuru
read -p "Please input your last name :" lastname #tishi shuru
echo -e "\nYour name is : ${firstname} ${lastname}" #screen output
随日期变化主要用于备份
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# Program creates three files, which named by user's input and date command
# History:
# 2020/02/24 LDY First release
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
#1
echo -e "I will use 'touch' command to create 3 files." #chuncuixianshi
read -p "Please input your filename: " fileuser #input
#2.
filename=${fileuser:-"filename"} #kai shi pan duan shi fou you wen jian ming
#3.
date1=$(date --date='2 days ago' +%Y%m%d)
date2=$(date --date='1 days ago' +%Y%m%d)
date3=$(date +%Y%m%d)
file1=${filename}${date1}
file2=${filename}${date2}
file3=${filename}${date3}
#4.
touch "${file1}"
数值运算:简单的加减惩处可以通过$((计算式))来进行数值的计算,可惜只能到整数位。
! /bin/bash
# Program:
# User inputs 2 integer numbers;
# Program will cross these two numbers
# History:
# 2020/02/24 LDY First Release
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:~/bin
export PATH
echo -e "You should input 2 numbers, I will multiplying them! \n"
read -p "first number: " firstnu
read -p "second number: " secnu
total=$((${firstnu}* ${secnu}))
echo -e "\nThe result of ${firstnu} * ${secnu} is => ${total}"
推荐的运算方式:
var=$((运算内容))
数值运算:透过bc计算pi
#! /bin/bash
# Program:
# User input a scale to calculate pi number
#History:
#2020/02/24 LDY FIRST RELEASE
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:~/bin
export PATH
echo -e "This program will calculate pi value. \n"
echo -e "You should put a float number to calculate pi value.\n"
read -p "The scale number (10~10000) ? " checking
num=${checking:-"10"}
echo -e "Starting calcuate pi value. Be patient."
time echo "scale=${num}; 4*a(1)" | bc -lq
2.2. Script执行方式的差异
利用直接执行的方式来执行
利用source执行
2.3. 善用判断式
1. 利用test测试功能
检查某个目录是否存在`在这里插入代码片`
lidengyin@study bin]$ test -e /home/lidengyin/
执行结果不会显示任何信息,但是可以透过&&以及||来展现整个结果!
[lidengyin@study bin]$ test -e /home/lidengyin/ && echo "exist" || echo "Not exist"
exist
以下是test的常用测试标志:
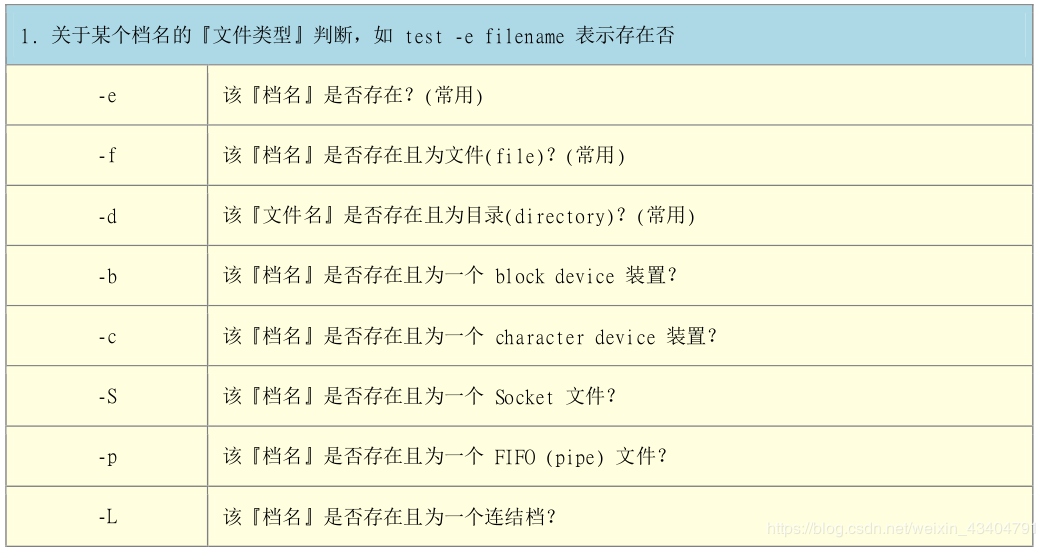

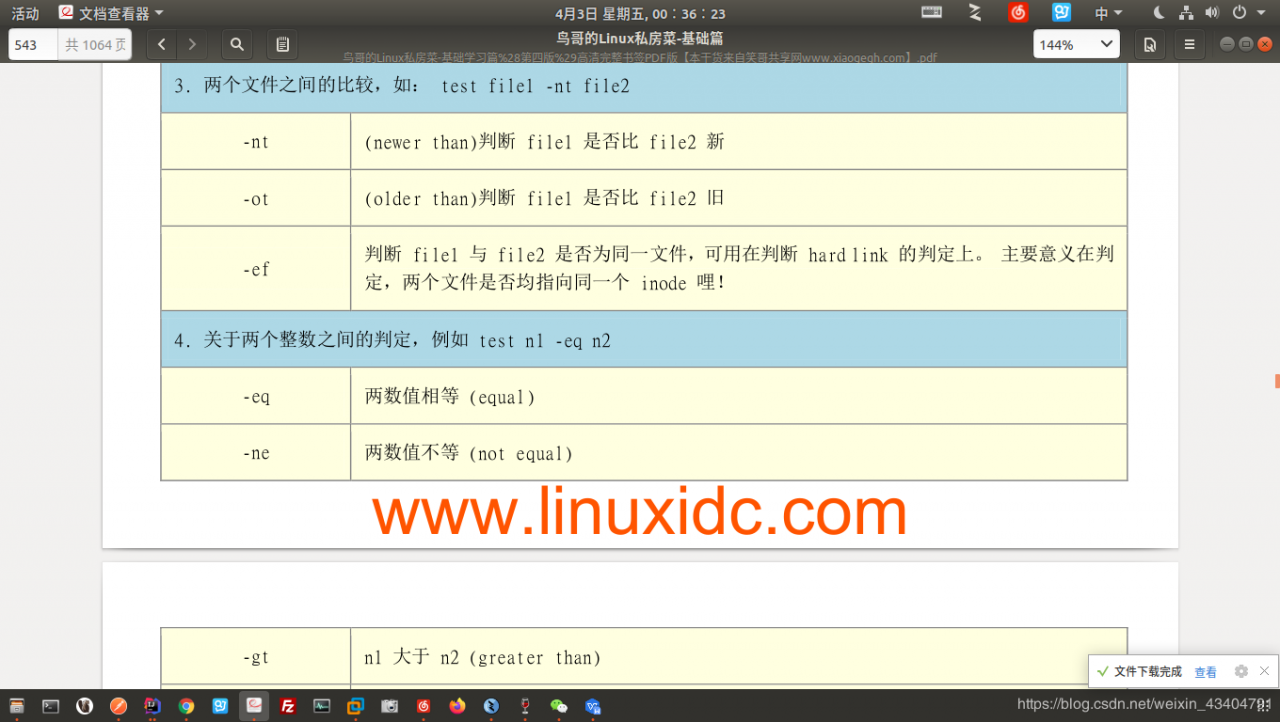


简单例子:
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# User input a filename, program will check the flowing:
# 1.) exist? 2.) file/directory? 3.) file permissions
# History:
# 2020/02/24 LDY FIRST RELEASE
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
# 1.
echo -e "Please input a filename, I will check the filename's type and persmission. \n\n"
read -p "Input a filename: " filename
test -z ${filename} && echo "You MUST input a filename." && exit 0
#2.
test ! -e ${filename} && echo "The filename '${filename}' Do NOT exist" && exit 0
#3.
test -f ${filename} && filetype="regulare file"
test -d ${filename} && filetype="directory"
test -r ${filename} && perm="readable"
test -w ${filename} && perm="writable"
test -x ${filename} && perm="executable"
#4.
echo "The filename: ${filename} is a ${filetype}"
echo "And the permissions for you are : ${perm}"
利用判断符号[]中括号判断${HOME}是否为空
lidengyin@study bin]$ [ -z "${HOME}" ] && echo "exist"
[lidengyin@study bin]$ [ -z "${HOME}" ] ; echo $?
1
[lidengyin@study bin]$ test -d /home
[lidengyin@study bin]$ echo -e $?
0
[lidengyin@study bin]$ [ -z "${HOME}" ] || echo "not exist"
not exist
注意:
在中括号[]之中的每个组件都需要有空格键来分隔 在中括号内的变数,最好都用双引号括号起来 在中括号内的常数,最好都以单或双引号括号起来例如:
[lidengyin@study bin]$ name="lasy 1"
[lidengyin@study bin]$ echo ${name}
lasy 1
[lidengyin@study bin]$ [ ${name} == "ldy" ]
bash: [: too many arguments
见鬼了,这是由于太多参数导致的,因为电脑认定的判断是:
[ lsy 1=="ldy" ]
多了一个参数肯定不对啊
正确写法:
[lidengyin@study bin]$ [ "${name}" == "ldy" ]
[lidengyin@study bin]$
3. shell Script的默认变数($0, $1)
执行的脚本当名,就是$0这个变量, 第一个接的参数就是$1,所以只要善用$1就可以很简单的下达某些指令功能了。除了数字变量,还有一下一些特殊变量:
$#:代表后街参数的个数 $@:代表[ “$1” “$2” “$3” “$4” ]之意,每个变量独立(双引号)例子:
bash
#Program:
# Program shows the script name, parameters..
# History
# 2020/04/03 lidengyin First Release
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
echo "The script name is ==> ${0}"
echo "THe parameter number is ==> $#"
[ "${#}" -lt 2 ] && echo "The number of parameter is less than 2, Stop here" && exit 0
echo "Your whole parameter is ==> ${@}"
echo "THe 1st parameter ==>${1}"
echo "the 2nd parameter ==>${2}"
执行结果
tudy bin]$ sh how_pass.sh theone haha quot
The script name is ==> how_pass.sh
THe parameter number is ==> 3
Your whole parameter is ==> theone haha quot
THe 1st parameter ==>theone
the 2nd parameter ==>haha
[lidengyin@study bin]$
4. 条件判断式
4.1. 利用if…then
if [ 条件判断式 ]; then
当条件判断式成立时,可以进行的指令工作内容。
fi
除了将条件判断式写入一个中括号,还可以用多个中括号隔开多个条件,括号与括号之间用&&或者||隔开,他们的意义是:
&&代表AND || 代表OR所以下面的例子
[ "${yn}" == "Y" -o "${yn}" == "y" ]
可以改为:
[ "${yn}" == "Y" ] || [ "${yn}" == "y" ]
具体例子:
#/bin/bash
#Program
# THe program shows the user's choice
#History:
#2020/04/03 Lidengyin First Release
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
read -p "Please input (Y/N):" yn
if [ "${yn}" == "Y" ] || [ "${yn}" == "y" ]; then
echo "OK, continue"
exit 0
fi
echo "I don't know what your choice is " && exit 0
~
~
执行结果:
[lidengyin@study bin]$ sh ans_yn-2.sh
Please input (Y/N):y
OK, continue
多重,复杂条件判断式基本语法
if [ 条件判断式 ]; then
当条件判断式成立时,可以进行的指令工作内容。
else
当条件判断式成立时,可以进行的指令工作内容。
fi
如果更加复杂考虑这个:
if [ 条件判断式 ]; then
当条件判断式成立时,可以进行的指令工作内容。
elif [ 条件判断式 ]; then
当条件判断式成立时,可以进行的指令工作内容。
else
当条件判断式成立时,可以进行的指令工作内容。
fi
4.2. 利用case …esac判断
case $变量名称 in 《==关键词为case,还有变数钱有钱符号
"第一个变量内容")<==每一个变量内容建议用双引号引起来,变量为单括号
程序段
;; 《==每个类的结尾使用两个连续的分号来处理
"第二个变量内容")
程序段
;;
*)
不包含第一个变量美容与第二个变量内容的其他程序执行段。 《==最后一个变量内容都用*来表示所有其他值
exit 1
;;
esca <===最终结尾
实例:
#!/bin/bash
# Program:
# SHow "hello form $1 ... by using case ..esac"
#History:
# 2020/04/03 lidengyin@2743853037@qq.com First Release
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
case ${1} in
"hello")
echo "Hello , how are you ?"
;;
"")
echo "You must input parameters, ex> {${0} someword}"
;;
*)
echo "Usage ${0} {hello}"
;;
esac
输出
[lidengyin@study bin]$ sh hello-3.sh hello
Hello , how are you ?
一般来说,使用case 变量in这个语法中,当中的那个变量 in这个语法中, 当中的那个变量in这个语法中,当中的那个{变量}大致有两种取得的方式:
直接下达式, 例如利用 sh hello-3.sh hello 交互式:透过read 4.3. 利用fucntion功能function语法
function fname() {
程序段
}
实例:
#Program:
# Using function to repeat information
#History:
# 2020/04/03 Lidengyin First Release
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
function printit(){
echo -n "Your choice is "
}
echo "The program will print your selection !"
case ${1} in
"one")
printit; echo ${1} | tr 'a-z' 'A-Z'
;;
"two")
printit; echo ${1} | tr 'a-z' 'A-Z'
;;
"three")
printit; echo ${1} | tr 'a-z' 'A-Z'
;;
*)
echo "Usage ${0} {one|two|three}"
;;
esac
输出:
[lidengyin@study bin]$ sh show123-2.sh one
The program will print your selection !
Your choice is ONE
[lidengyin@study bin]$ sh show123-2.sh sd
The program will print your selection !
Usage show123-2.sh {one|two|three}
另外,function也是拥有内建变量的~他的内建变量与shell script很类似, 函数名称代表$0, 而后续接的变量也是以$1, $2来取代的, 这很容易搞错,因为
function fname() {
程序段
}
内的$0, $1等等与shell Script的$0是不同的。改写例子:
#Program:
# Using function to repeat information
#History:
# 2020/04/03 Lidengyin First Release
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
function printit(){
echo "Your choice is ${1}"
}
echo "The program will print your selection !"
case ${1} in
"one")
printit 1
;;
"two")
printit 2
;;
"three")
printit 3
;;
*)
echo "Usage ${0} {one|two|three}"
;;
esac
输出:
[lidengyin@study bin]$ sh show123-3.sh one
The program will print your selection !
Your choice is 1
5. 循环(loop)
5.1 while do done, until do done(不定循环)
while [condition]
do
程序段落
done
或者
until [condition]
do
程序段落
done
实例:
#!bin/bash
#Program:
# Repeat question until user input correct answer;
#History:
# 2020/04/03 Lidengyin First Release
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
while [ "${yn}" != "yes" -a "${yn}" != "YES" ]
do
read -p "Please input yes/YES to stop this program: " yn
done
echo "OK! you input the correct answer."
输出:
[lidengyin@study bin]$ sh yes_to_stop.sh
Please input yes/YES to stop this program: y
Please input yes/YES to stop this program: yes
OK! you input the correct answer.
until类似
5.2. 固定循环for…do…done语法:
for var in con; con2 con3。。。
do
程序段
done
以上面例子来说,这个$var的变量内容在循环工作时:
第一次循环, $var的内容是con1 第二次循环, $var的内容是con2 。。。。实例:
#!bin/bash
#Program:
# Using for ... loop to print 3 animals
#Histroy
# 2020/04/03 Lidengyin First Release
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
for animal in dog cat elephant
do
echo "Threr are ${animal}s..."
done
~
~
~
~
输出:
in@study bin]$ sh show_animal.sh
Threr are dogs...
Threr are cats...
Threr are elephants...
5.3. for do done的数值处理
for((初始值;限制值;执行步阶))
do
程序段
done
实例:
#!bin/bash
#Program:
# Try do calculate 1+2+ .....+${your_input}
#History
# 2020/04/03 Lidengyin rELEASE
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:~/bin
export PATH
read -p "Please input a number , I will count for 1+2+....+your_input:" nu
s=0
for((i=1; i ${s}"
~
输出:
[lidengyin@study bin]$ sh cal_1_100-2.sh
Please input a number , I will count for 1+2+....+your_input:100
THe result of '1+2+3 ...+100' is ==> 5050
5.6. shellScript的追踪与debug
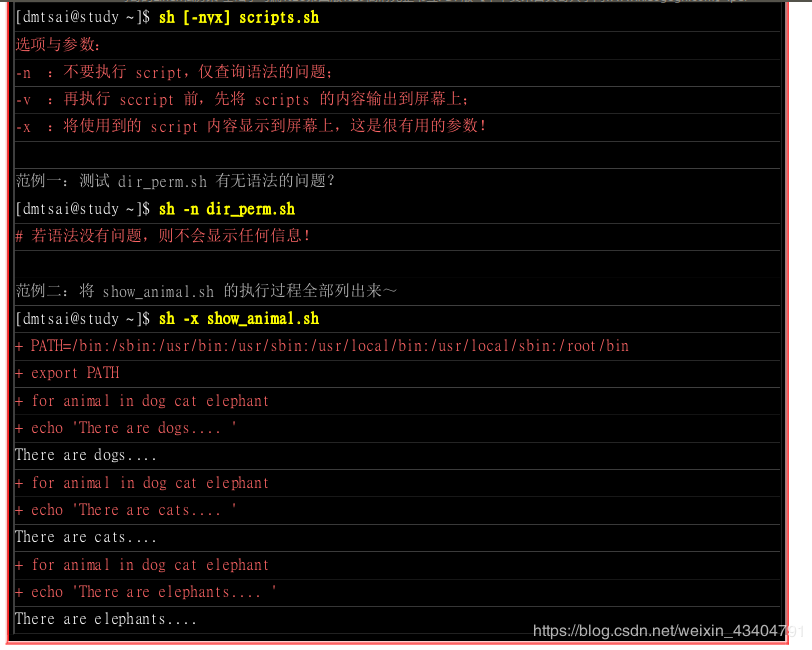
作者:天又热了