PCL 通过室内点云生成房间框架
目录前言基本流程代码wall_dis.pymain.hmain.cpptools.htools.cpp
前言
 代码
代码
作者:3D_DLW
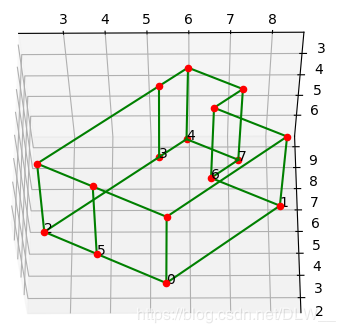
之前我们成功的实现了pcl通过室内点云计算房间参数,但是这个算法无法对较复杂的房间进行参数化,例如这种:
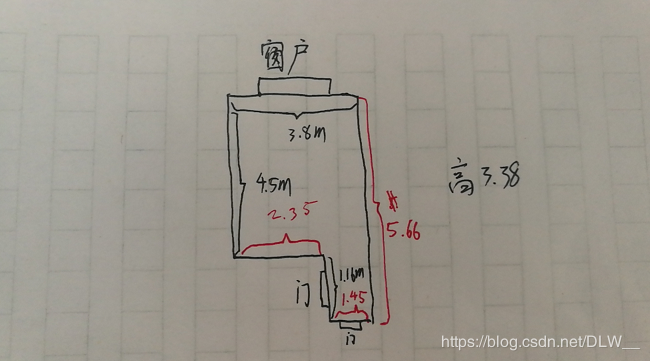
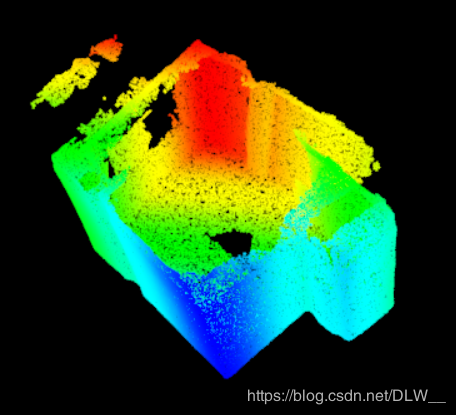
我们使用的原始点云是用RGBD设备扫描室内环境得到的,可见扫描的误差还是非常大的.
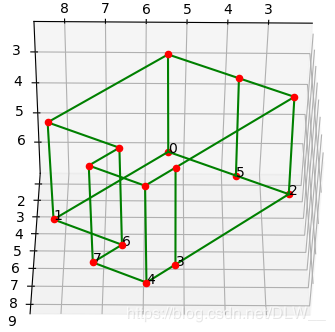
最终我们成功提取了房间的参数:
角点:
[[5.40791146 6.01982222 1.85338407 0. 3. ]
[8.26861105 6.28002276 5.51652248 0. 4. ]
[2.36144057 6.11570359 4.22569127 1. 3. ]
[5.22214015 6.37590413 7.88882968 1. 4. ]
[5.92664598 6.43998384 8.7909525 1. 5. ]
[3.68281987 6.07411591 3.1967244 2. 3. ]
[6.54351945 6.33431645 6.85986281 2. 4. ]
[7.24802527 6.39839616 7.76198562 2. 5. ]]
闭合路线: [0, 1, 6, 7, 4, 3, 2, 5]
路线长度: [4.655092848984463, 2.1871104392584755, 1.1464118939973418, 1.6752747849874787, 1.1464118939973411, 4.655092848984463, 1.6752747849874785, 2.187110439258477]
高: 3.3328831615131667
我们有一个C++程序PointCloud.exe
和一个Python程序wall_dis.py
将他们放在同一个文件夹下,运行wall_dis.py,附带点云文件的路径.\5.pcd作为参数传入
python .\wall_dis.py .\5.pcd
基本执行流程
Python程序检查点云文件路径,如为obj文件会尝试调用pcl_mesh_sampling_release将其转换为点云文件.
调用PointCloud.exe对点云进行平面分割,并生成一个temp.txt文件,文件内容包括
整体点云的重心
分割出15个平面的参数
分割出15个平面的重心
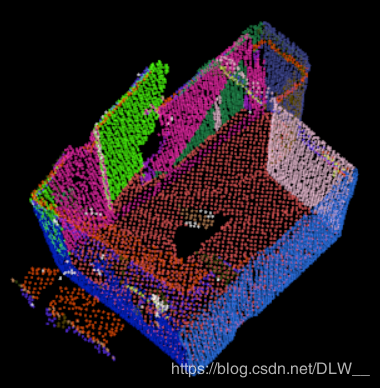
Python读取temp.txt文件,按照角度将墙面分类,然后清理每个分类中靠的太近的墙面,得到3组近乎平行的墙面参数.
根据第一组的第一面墙,对其他组的第一面墙进行校正,使组间墙面正交.
根据每一组的第一面墙,对该组的其他墙进行校正,使组内墙面平行.
计算每面墙和其他墙的交线,选取交线最多的墙面作为底面.
计算底面交线之间的交点,并将这些点写入temp.txt文件.
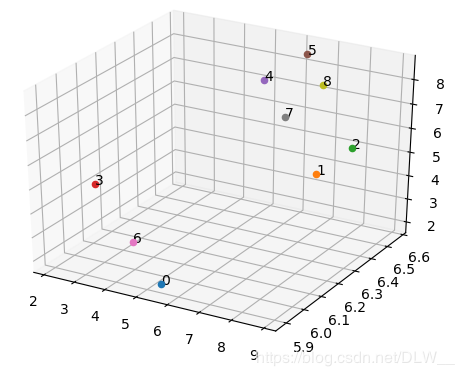
再次调用PointCloud.exe读取temp.txt对每个交点计算半径0.7m内的点云数目,并写回temp.txt.
读取temp.txt根据交点周围点云数目过滤掉错误交点.
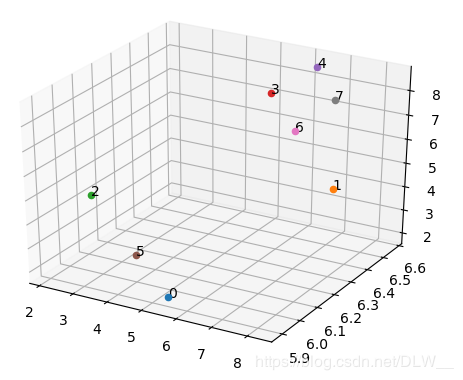
使用深度优先搜索算法计算交点的闭合路径,并输出路径和路线长度等信息.
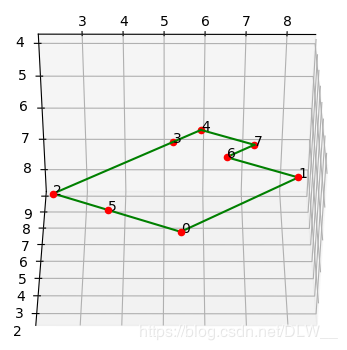
闭合路线: [0, 1, 6, 7, 4, 3, 2, 5]
路线长度: [4.655092848984463, 2.1871104392584755, 1.1464118939973418, 1.6752747849874787, 1.1464118939973411, 4.655092848984463, 1.6752747849874785, 2.187110439258477]
高: 3.3328831615131667
使用底面参数和高,画出房间框架. 代码
代码
警告,在下面你可能会看到:
混乱不堪的代码结构
莫名其妙的函数/变量命名方式
极其不严谨的算法
该删没删的代码和注释
import numpy as np
from numpy import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import subprocess
import sys
import os
# 不使用科学计数法
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)
work_dir = './'
# 计算两个平面的夹角
def angle_plan(a, b):
def s2(a):
return sqrt(a[0] ** 2 + a[1] ** 2 + a[2] ** 2)
c = sum((a * b)[:3]) / s2(a) / s2(b)
if c > 1:
c = 1
return arccos(c) * 180 / pi
# 构造夹角矩阵(显示用)
def angle_mat(coe):
size = coe.shape[0]
newmat = zeros((size, size))
for i in range(size):
for j in range(i, size):
newmat[i, j] = angle_plan(coe[i], coe[j])
return newmat
# 将切片分类
def group_wall(coe, angle_err=20):
size = coe.shape[0]
team = []
free = [i for i in range(size)]
# 添加切片(递归)
def app(i):
free.remove(i)
team[-1].append(i)
for j in range(i + 1, size):
if j in free and angle_plan(coe[i], coe[j]) < angle_err:
app(j)
for i in range(size):
if i in free:
team.append([])
app(i)
if len(free):
print("Error: Free doesn't clear \n")
print(free)
if len(team) < 3:
print("Error: group not enough:", len(group))
return team
# 取每组中最平行的切片(废弃)
def group_best(coe, team):
best_mach = []
for t in team:
best_mach.append([])
best_mach_num = 180
for i in range(len(t)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(t)):
if angle_plan(coe[t[i]], coe[t[j]]) < best_mach_num:
best_mach_num = angle_plan(coe[t[i]], coe[t[j]])
best_mach[-1] = [t[i], t[j]]
return best_mach
# 求三维向量的模
def module(vector):
return sqrt(vector[0] ** 2 + vector[1] ** 2 + vector[2] ** 2)
# 点到平面距离
def dis_dp(cent, plan):
cent = np.append(cent[:3], 1)
return sum(cent * plan) / module(plan)
# 点到直线的距离
def dis_dl(point, line):
t = sum((point[:3]-line[1])*line[0])/module(line[0])**2
return module(point[:3]-(line[0]*t+line[1]))
# 判断点是否在线上
def online(point, line):
return dis_dl(point, line) < 1e-9
# 根据选取的面计算房间长宽高
def distance_wall(cent, coe, group):
distance = []
for g in group[:3]:
distance.append(abs(dis_dp(cent, coe[g[0]]) - dis_dp(cent, coe[g[1]])))
return distance
# 计算房间高
def distance_height(cent, coe, group, top_index):
for g in group:
if top_index in g:
return abs(dis_dp(cent, coe[g[0]]) - dis_dp(cent, coe[g[1]]))
# 清理分组的切片
def clean_group(cent, coe, team, dis_err=0.7):
new_team = []
for t in team[:3]:
new_team.append([t[0]])
for i in range(1, len(t)):
flag = True
for j in range(i):
# 对比距离
dis = abs(dis_dp(cent, coe[t[i]]) - dis_dp(cent, coe[t[j]]))
if dis angle_err:
continue
lines.append(crossline_count(coe[top], coe[i]))
return array(lines)
# 计算交线
def crossline(coe, angle_err=20):
lines = []
top_idx = 0
for i in range(len(coe)):
results = crossline_top(coe, top=i, angle_err=angle_err)
if len(results) > len(lines):
lines = results
top_idx = i
return lines, top_idx
# 计算两线的交点
def crosspoint_count(x, y, angle_err=20):
if abs(angle_plan(x[0], y[0]) - 90) > angle_err:
return "夹角过小"
d = cross(x[0], y[0])
if np.sum(d * y[0]) > 1e-9:
return "两条线不在同一平面内"
d = cross(x[0], d)
t = -(np.sum(d * y[1]) - np.sum(d * x[1])) / np.sum(d * y[0])
return t * y[0] + y[1]
# 计算交点
def crosspoint(lines, angle_err=20):
points = []
for i in range(len(lines)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(lines)):
result = crosspoint_count(lines[i], lines[j], angle_err=angle_err)
if not isinstance(result, str):
points.append(np.append(result, [i, j]))
return array(points)
# 通过几何关系清理无用点(错误)
def clean_points(points, lines):
for i in range(len(lines)):
inline = []
for j in range(len(points)):
if points[j][3]==i or points[j][4]==i:
inline.append(j)
if len(inline) > 2:
max_dis = [0]
for j in range(len(inline)):
for k in range(j+1, len(inline)):
dis = module(points[inline[j]]-points[inline[k]])
if dis > max_dis[0]:
max_dis = [dis, inline[j], inline[k]]
inline.remove(max_dis[-1])
inline.remove(max_dis[-2])
points = np.delete(points, inline, axis=0)
return points
# 计算三个参数(质心,切片)(废弃)
def main_3(cent, coe):
group = group_wall(coe, angle_err=20)
dis = distance_wall(cent, coe, group)
return dis
# 寻找一个点的临近点
def nearest(points, index):
cross = []
for i, p in enumerate(points):
if i == index:
continue
if p[-1] == points[index][-1] or p[-2] == points[index][-2] or p[-1] == points[index][-2] or p[-2] == points[index][-1]:
cross.append(i)
ang = []
dis = []
idx = []
for i in cross:
angle = points[index]-points[i]
flag_ang = True
distence = module(points[index]-points[i])
for j in range(len(ang)):
if angle_plan(ang[j], angle) < 45 and distence < dis[j]:
flag_ang = False
dis[j] = distence
idx[j] = i
break
if flag_ang:
ang.append(angle)
dis.append(distence)
idx.append(i)
return idx
# 递归解算路线
def count_line(points):
def count(points, line):
next_idx = nearest(points, line[-1])
next_idx_res = list(set(next_idx).difference(set(line)))
if len(next_idx_res) == 0:
if len(line) == len(points) and 0 in next_idx:
return line
else:
return
for idx in next_idx_res:
res = count(points, line.copy() + [idx])
if res:
return res
return count(points, [0])
# 校正墙面
def correct_wall(coe, team, coent):
# 校正基准面
idx0 = team[0][0]
idx1 = team[1][0]
idx2 = team[2][0]
dis1 = dis_dp(coent[idx1], coe[idx1])
dis2 = dis_dp(coent[idx2], coe[idx2])
coe[idx2][:3] = cross(coe[idx0][:3], coe[idx1][:3])
coe[idx1][:3] = cross(coe[idx0][:3], coe[idx2][:3])
coe[idx2][3] = dis2 * module(coe[idx2]) - sum(coent[idx2][:3] * coe[idx2][:3])
coe[idx1][3] = dis1 * module(coe[idx1]) - sum(coent[idx1][:3] * coe[idx1][:3])
# 校正平行面
for t in team:
for i in range(1, len(t)):
dis = dis_dp(coent[t[i]], coe[t[i]])
coe[t[i]][:3] = coe[t[0]][:3]
coe[t[i]][3] = dis * module(coe[t[0]]) - sum(coent[t[i]][:3] * coe[t[0]][:3])
# 计算特征点并写入文件
def main_point():
# 读取数据
f = open(work_dir + 'temp.txt', mode='r')
cent = f.readline()
coe = f.readline()
coent = f.readline()
f.close()
cent = array(str.split(cent), dtype=float)
cent = np.append(cent, 1)
coe = array(mat(coe))
coent = array(mat(coent))
# 墙面分类
team = clean_group(cent, coe, group_wall(coe, angle_err=20), dis_err=0.7)
print("墙面分类:", team)
# 校正墙面
correct_wall(coe, team, coent)
# 输出参数
print('三参数: ', distance_wall(cent, coe, team))
teams = []
for t in team:
teams += t
coe_ = coe[teams]
# 计算交线
lines, top_idx = crossline(coe_, angle_err=20)
print("顶点:", top_idx)
height = distance_height(cent, coe, team, top_idx)
# 计算交点
points = crosspoint(lines, angle_err=20)
# 写入文件
f = open(work_dir + 'temp.txt', mode='w')
for p in points:
f.write('%s %s %s\n' % (p[0], p[1], p[2]))
f.close()
return points, (height*coe[top_idx])[:3]
# 规划路线
def main_line(points):
# 读取临近点匹配数据
f = open(work_dir + 'temp.txt', mode='r')
match = f.read()
f.close()
if os.path.exists(work_dir + 'temp.txt'):
os.remove(work_dir + 'temp.txt')
match = [int(x) for x in match.split()]
print(match)
match_err = 10
match_del = []
for i in range(len(match)):
if match[i] < match_err:
match_del.append(i)
points = np.delete(points, match_del, axis=0)
return points, count_line(points)
# 沿线计算长度
def main_lenght(points, line):
lenght = []
for i in range(len(line)-1):
lenght.append(module(points[line[i]] - points[line[i+1]]))
lenght.append(module(points[line[0]] - points[line[-1]]))
return lenght
def main(c_path = r'PointCloud.exe', file_name = '../pcd/5.pcd', visual=False):
# 检查路径
if not os.path.exists(file_name):
print('Error: 文件路径错误')
return
if file_name.endswith('.obj'):
print('正在将obj转换为pcd文件')
if subprocess.call(['pcl_mesh_sampling_release', file_name, os.path.splitext(file_name)[0] + '.pcd']) != 0:
print('Error: 无法成功调用pcl_mesh_sampling_release')
return
file_name = os.path.splitext(file_name)[0] + '.pcd'
elif not file_name.endswith('.pcd'):
print('Error: 文件后缀错误')
return
# C++处理点云
if visual:
rec = subprocess.call([c_path, '0', file_name])
else:
rec = subprocess.call([c_path, '1', file_name])
points, height_vec = main_point()
# C++匹配点云
rec = subprocess.call([c_path, '2', file_name])
points, line = main_line(points)
print('角点: \n', points)
print('闭合路线: ', line)
if line is None:
print('Error: 点云误差较大,数据无法拟合')
return
lenght = main_lenght(points, line)
print('路线长度: ', lenght)
print('高: ', module(height_vec))
# 画图
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
for index in range(len(line)):
i = line[index]
if index + 1 == len(line):
j = line[0]
else:
j = line[index+1]
p = points[i][:3]
d = points[j][:3]
p_ = points[i][:3] + height_vec
d_ = points[j][:3] + height_vec
ax.plot((p[0], p_[0]), (p[1], p_[1]), (p[2], p_[2]), color='green')
ax.plot((p[0], d[0]), (p[1], d[1]), (p[2], d[2]), color='green')
ax.plot((p_[0], d_[0]), (p_[1], d_[1]), (p_[2], d_[2]), color='green')
ax.scatter(p[0], p[1], p[2], color='red')
ax.scatter(p_[0], p_[1], p_[2], color='red')
ax.text(p[0], p[1], p[2], i)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.show()
visual=False
if len(sys.argv) == 3 and sys.argv[2]=='-d':
visual=True
main(file_name=sys.argv[1], visual=visual)
main.h
#ifndef MAIN_H_
#define MAIN_H_
#include "pch.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include //视觉化工具函式库(VTK,Visualization Toolkit) 模型
#include
#include
#include //pcd 读写类相关的头文件。
#include
#include //PCL中支持的点类型头文件。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //点云分割
#include //统计滤波移除离群点
#include //根据半径移除离群点
#include //表面提取
#include //高斯滤波
#include //移除离群点
#include //kd树
#include //最小二乘平滑处理类
#include //计算中心
#endif
main.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include "main.h"
#include "tools.h"
void match(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud)
{
// 读取文件
ifstream infile;
infile.open("temp.txt", ios::in);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr points(new pcl::PointCloud);
while (!infile.eof())
{
pcl::PointXYZ point;
infile >> point.x;
infile >> point.y;
infile >> point.z;
if (infile.eof()) break;
points->points.push_back(point);
}
infile.close();
points->width = (uint32_t)points->points.size();
points->height = 1;
// 检测真角点
cout << "正在匹配角点" << endl;
vector match = in_range(cloud, *points, 0.7);
// 写入文件2
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("temp.txt", ios::out | ios::trunc);
for (int i = 0; i < match.size(); i++)
{
outfile << match[i] << " ";
}
outfile.close();
cout << "匹配数据写入完毕" << endl;
}
void get_faces(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud, bool visual)
{
string work_dir = "./";
// 计算点云中心
Eigen::Vector4f centroid;
pcl::compute3DCentroid(*cloud, centroid);
// cout << "点云质心("
// << centroid[0] << ","
// << centroid[1] << ","
// << centroid[2] << ")." << endl;
// 提取平面
vector<pcl::PointCloud::Ptr> seg_clouds;
vector seg_coefficients;
segment(cloud, seg_clouds, seg_coefficients, 15);
// 输出平面参数
// cout << "Coefficient" << endl;
// for (int i = 0; i < seg_coefficients.size(); i++)
// {
// cout <values[0] << " "
// <values[1] << " "
// <values[2] << " "
// <values[3] << ";";
// }
// cout << endl;
// 输出到文件
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("temp.txt", ios::out | ios::trunc);
outfile << centroid[0] << " "
<< centroid[1] << " "
<< centroid[2] << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < seg_coefficients.size(); i++)
{
outfile <values[0] << " "
<values[1] << " "
<values[2] << " "
<values[3] << ";";
}
outfile.seekp(-1, ios::cur);// 删除最后的";"
outfile << " ";
outfile << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < seg_coefficients.size(); i++)
{
pcl::compute3DCentroid(*seg_clouds[i], centroid);
outfile << centroid[0] << " "
<< centroid[1] << " "
<< centroid[2] << ";";
}
outfile.seekp(-1, ios::cur);// 删除最后的";"
outfile << " ";
outfile.close();
cout << "平面参数写入完毕" << endl;
// 最小二乘平滑
// msl(cloud);
// 剔除离群点
// outliner(cloud);
// 高斯卷积
// gauss_filter(cloud);
// 可视化
if (visual)
{
visual_clouds(seg_clouds);
// 保存
save_clouds(seg_clouds, work_dir + "seg/temp");
}
// while (true) {
// ransac();
// }
// 显示点云
// pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("pointcloud viewer");
// pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom sig(cloud, 0, 255, 0);
// viewer.addPointCloud(cloud, sig, "cloud");
// while (!viewer.wasStopped())
// {
// viewer.spinOnce();
// }
// 保存点云
// pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(work_dir + "result/" + std::to_string(i) + "" + ".pcd", *cloud);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// arg1:mod arg2:file_path
// 加载点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile(argv[2], *cloud);
// 下采样
down_sample(cloud);
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
if (strcmp(argv[1], "0") == 0)
{
get_faces(cloud, true);
}
else if (strcmp(argv[1], "1") == 0)
{
get_faces(cloud, false);
}
else if (strcmp(argv[1], "2") == 0)
{
match(cloud);
}
return 0;
}
tools.h
#ifndef TOOLS_H_
#define TOOLS_H_
int ransac();
void down_sample(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud);
void outliner(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud);
void gauss_filter(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud);
void msl(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud);
void segment(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr input_cloud, vector<pcl::PointCloud::Ptr>& seg_clouds,
vector& seg_coefficients, int faces);
void visual_clouds(vector<pcl::PointCloud::Ptr> clouds);
void save_clouds(vector<pcl::PointCloud::Ptr> clouds, string name = "cloud");
vector split(const std::string& s, char delimiter);
vector in_range(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud, pcl::PointCloud &points, double radius);
#endif
tools.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include "main.h"
int *rand_rgb() {//随机产生颜色
int *rgb = new int[3];
rgb[0] = rand() % 255;
rgb[1] = rand() % 255;
rgb[2] = rand() % 255;
return rgb;
}
// 下采样
void down_sample(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud)
{
cout << "正在进行下采样" << endl;
pcl::VoxelGrid voxel;
voxel.setInputCloud(cloud);
voxel.setLeafSize(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f);// 设置体素大小
voxel.filter(*cloud);
}
// 统计滤波
void outliner(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud)
{
cout << "正在剔除离群点" << endl;
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval sor;
sor.setInputCloud(cloud);
sor.setMeanK(50); // 设置临近点个数
sor.setStddevMulThresh(1.0); // 设置阈值,判断是否为离群点
sor.filter(*cloud);
}
// 高斯卷积(效果很奇怪)
void gauss_filter(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud)
{
// 高斯核
pcl::filters::GaussianKernel::Ptr kernel(new pcl::filters::GaussianKernel);
(*kernel).setSigma(3);// 方差
(*kernel).setThresholdRelativeToSigma(5);// 阈值
// Kd树
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr kdtree(new pcl::search::KdTree);
(*kdtree).setInputCloud(cloud);
// 卷积
pcl::filters::Convolution3D<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::filters::GaussianKernel> convolution;
convolution.setKernel(*kernel);
convolution.setInputCloud(cloud);
convolution.setSearchMethod(kdtree);
convolution.setRadiusSearch(10);// 查找半径
std::cout << "开始卷积" << std::endl;
convolution.convolve(*cloud);
}
// 最小二乘平滑
void msl(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud)
{
std::cout << "开始最小二乘平滑处理" << std::endl;
// kd树
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr kdtree(new pcl::search::KdTree);
// 法线
pcl::PointCloud mls_points;
// 最小二乘
pcl::MovingLeastSquares mls;
mls.setComputeNormals(true);// 在最小二乘计算时进行法线估计
mls.setPolynomialFit(true);// 采用多项式拟合来提升精度
mls.setInputCloud(cloud);
mls.setSearchMethod(kdtree);
mls.setSearchRadius(.3);
mls.process(mls_points);
// 将重采样的法线转化为点云
pcl::copyPointCloud(mls_points, *cloud);
return;
}
// 提取表面
void segment(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr input_cloud, vector<pcl::PointCloud::Ptr>& seg_clouds,
vector& seg_coefficients, int faces)
{
cout << "正在准备表面提取" << endl;
// 复制点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*input_cloud, *cloud);
// 提取表面
pcl::SACSegmentation seg;
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);
// 参数
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
// 可选参数
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);//所提取目标模型的属性(平面、球、圆柱等等)
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);//采样方法(RANSAC、LMedS等)
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.1);//查询点到目标模型的距离阈值(如果大于此阈值,则查询点不在目标模型上,默认值为0)。
seg.setMaxIterations(100);//最大迭代次数(默认值为50)
// seg.setProbability(.99);//至少一个样本不包含离群点的概率(默认值为0.99)
// 提取索引
pcl::ExtractIndices extract;
seg_clouds.clear();
seg_coefficients.clear();
for (int i = 0;i < faces;i++)
{
// cout << "正在提取第" << i + 1 << "个表面" << endl;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
seg.setInputCloud(cloud);
seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients);
extract.setInputCloud(cloud);
extract.setIndices(inliers);// 设置分割后的内点为需要提取的点集
extract.setNegative(false);// 设置提取内点
extract.filter(*cloud_filtered);// 提取并保存
extract.setNegative(true);
extract.filter(*cloud);
seg_clouds.push_back(cloud_filtered);
seg_coefficients.push_back(coefficients);
}
seg_clouds.push_back(cloud);
cout << "表面提取完成" << endl;
return;
}
// 可视化点云集合
void visual_clouds(vector<pcl::PointCloud::Ptr> clouds)
{
cout << "开始可视化点云集合" << endl;
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("pointcloud viewer");
for (int i = 0;i < clouds.size();i++)
{
int *rgb = rand_rgb();//随机生成0-255的颜色值
// 最后一组点云设置为白色
if (i == clouds.size() - 1)
{
rgb[0] = 255;
rgb[1] = 255;
rgb[2] = 255;
}
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom sig(clouds[i], rgb[0], rgb[1], rgb[2]);
viewer.addPointCloud(clouds[i], sig, "cloud" + std::to_string(i));
}
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
viewer.spinOnce();
}
}
// 保存点云集合
void save_clouds(vector<pcl::PointCloud::Ptr> clouds, string path="cloud")
{
cout << "正在储存点云集合到" << path << "_?.pcd" << endl;
for (int i = 0;i < clouds.size();i++)
{
pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary(path + "_" + std::to_string(i) + ".pcd", *clouds[i]);
}
cout << "点云储存完毕" << endl;
}
int ransac()
{
// 输入参数
int faces;
double threshold;
int maxiter;
double probability;
int meank;
double std;
fflush(stdin);
cout << "-----------------------" << endl;
cout <> faces;
cout <> threshold;
cout <> maxiter;
cout <> probability;
// 载入点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("C:/Users/78753/Desktop/室内扫描/pcd/7.pcd", *cloud);
// 提取表面
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);
pcl::SACSegmentation seg;
// 参数
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
// 可选参数
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);//所提取目标模型的属性(平面、球、圆柱等等)
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);//采样方法(RANSAC、LMedS等)
seg.setDistanceThreshold(threshold);//查询点到目标模型的距离阈值(如果大于此阈值,则查询点不在目标模型上,默认值为0)。
seg.setMaxIterations(maxiter);//最大迭代次数(默认值为50)
seg.setProbability(probability);//至少一个样本不包含离群点的概率(默认值为0.99)
pcl::ExtractIndices extract;
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("pointcloud viewer");
for (int i = 0;i < faces;i++)
{
seg.setInputCloud(cloud);
seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients);
extract.setInputCloud(cloud);
extract.setIndices(inliers);
extract.setNegative(false);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
extract.filter(*cloud_filtered);
extract.setNegative(true);
extract.filter(*cloud);
int *rgb = rand_rgb();//随机生成0-255的颜色值
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom sig(cloud_filtered, rgb[0], rgb[1], rgb[2]);
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_filtered, sig, "cloud" + std::to_string(i));
}
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom sig(cloud, 255, 0, 0);
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud, sig, "cloud");
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
viewer.spinOnce();
}
return (0);
}
// 字符串分割
vector split(const std::string& s, char delimiter)
{
std::vector tokens;
std::string token;
std::istringstream tokenStream(s);
while (std::getline(tokenStream, token, delimiter))
{
tokens.push_back(token);
}
return tokens;
}
// 判断特定点附近的点云数量
vector in_range(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud, pcl::PointCloud &points, double radius)
{
pcl::KdTreeFLANN kdtree;
kdtree.setInputCloud(cloud);
std::vector pointIdxRadiusSearch;
std::vector pointRadiusSquaredDistance;
vector match;
for (size_t i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
match.push_back(kdtree.radiusSearch(points[i], radius, pointIdxRadiusSearch, pointRadiusSquaredDistance));
}
return match;
}
作者:3D_DLW