Task05:卷积神经网络基础+LeNet
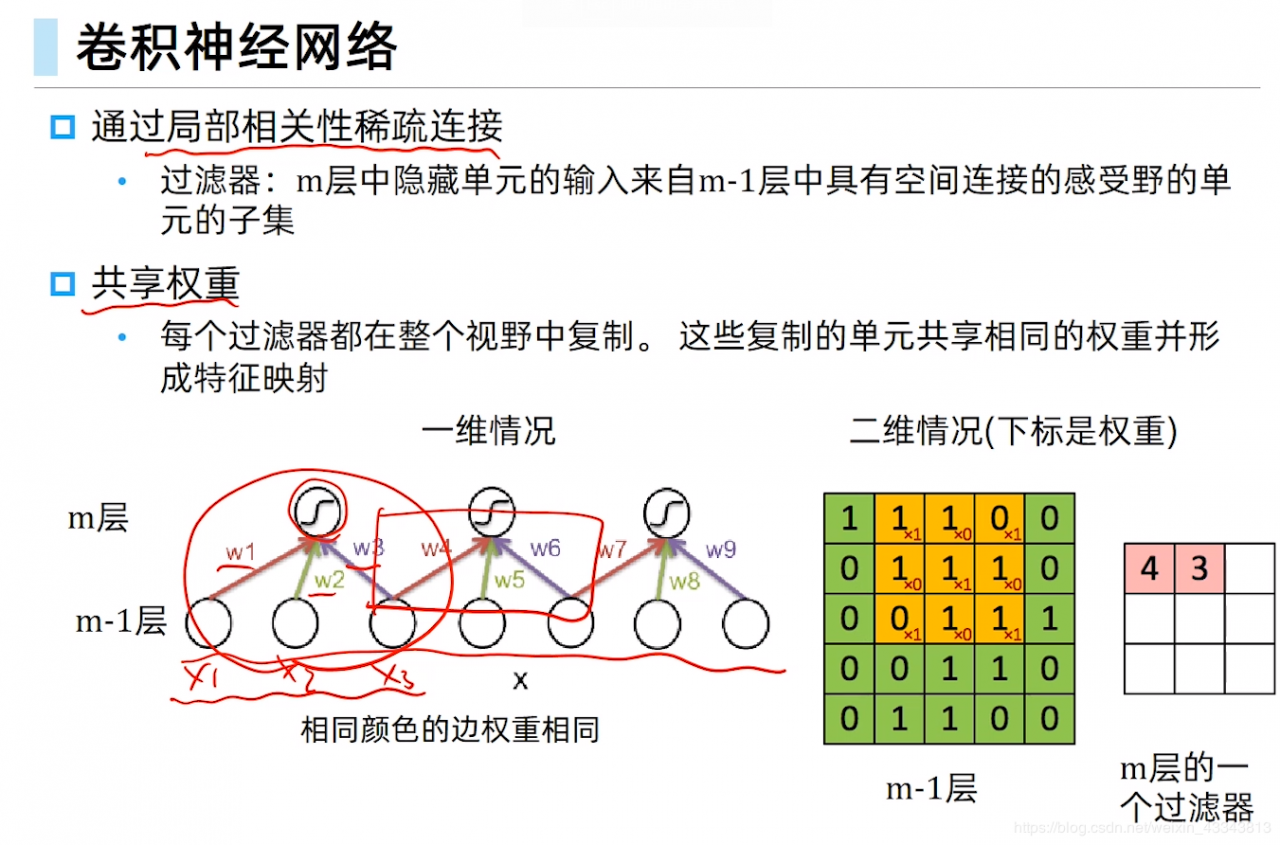
卷积神经网络
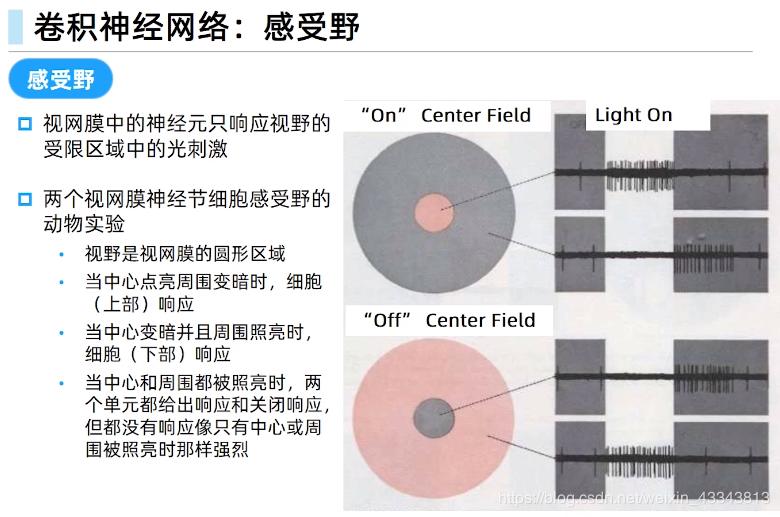
感受野
作者:like alone
互相关运算与卷积运算
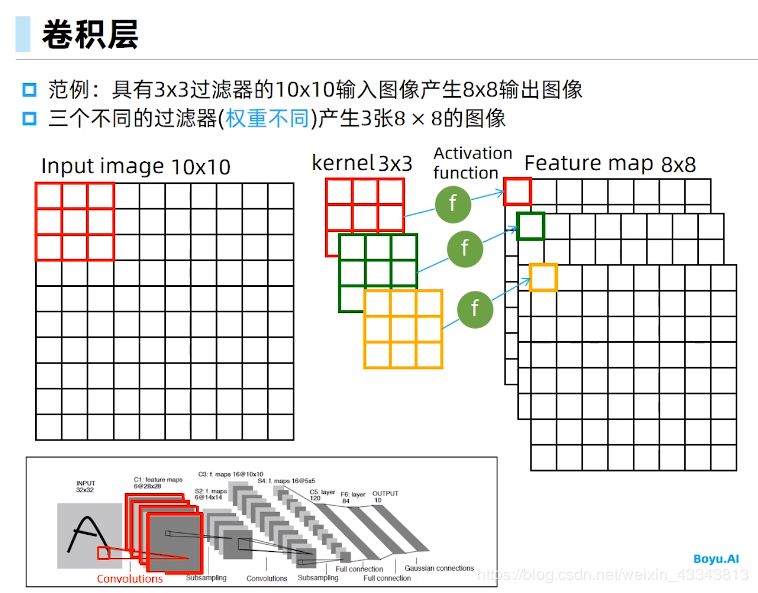
卷积层得名于卷积运算,但卷积层中用到的并非卷积运算而是互相关运算。我们将核数组上下翻转、左右翻转,再与输入数组做互相关运算,这一过程就是卷积运算。由于卷积层的核数组是可学习的,所以使用互相关运算与使用卷积运算并无本质区别。
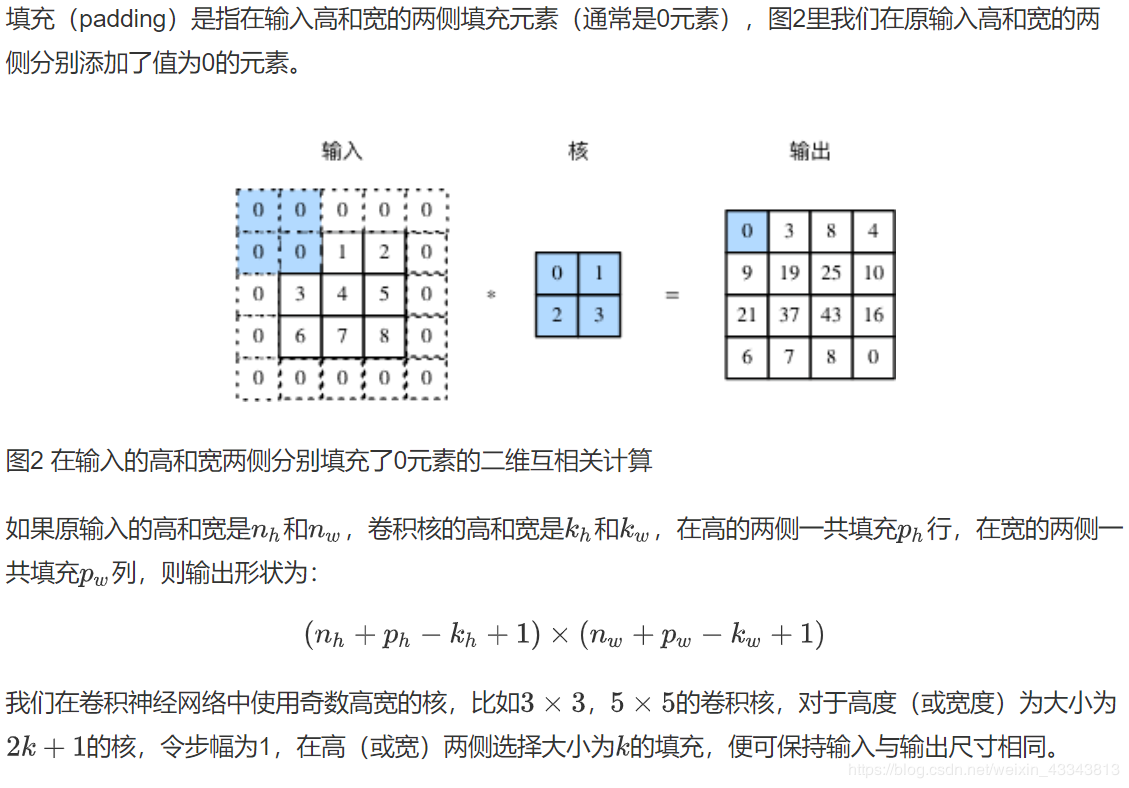
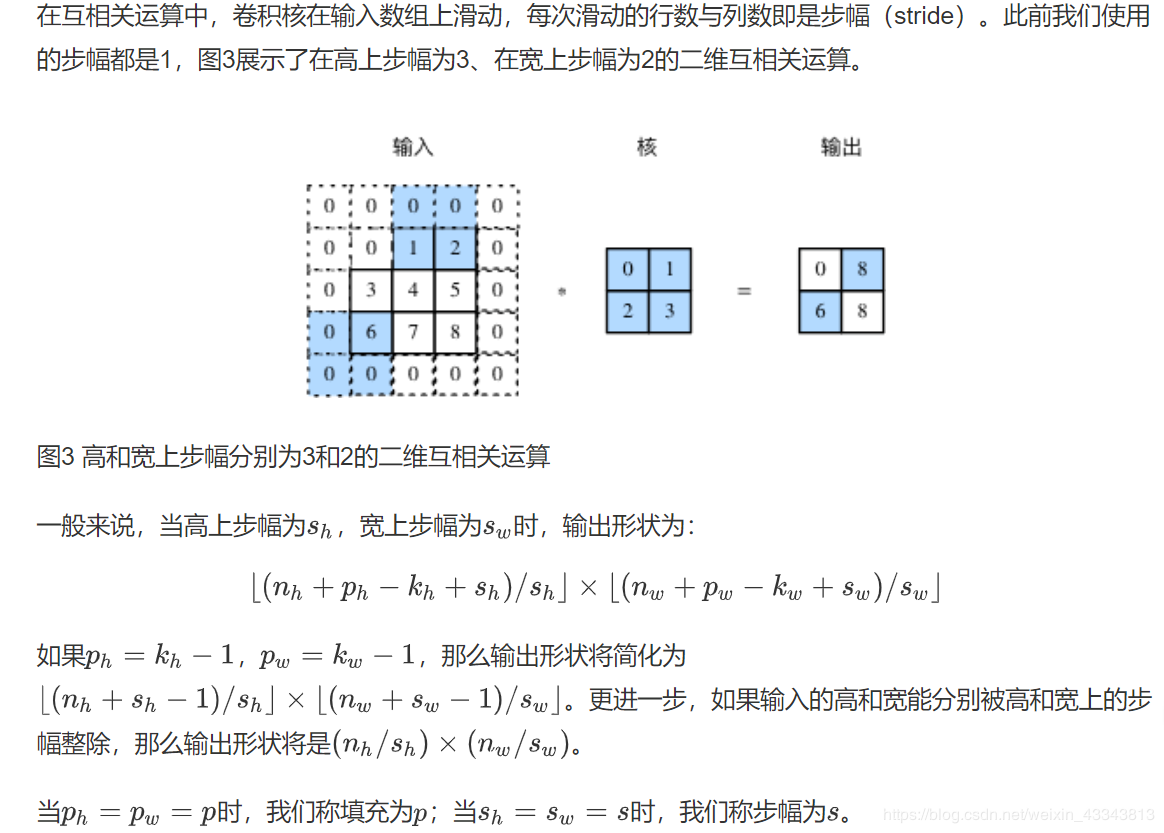

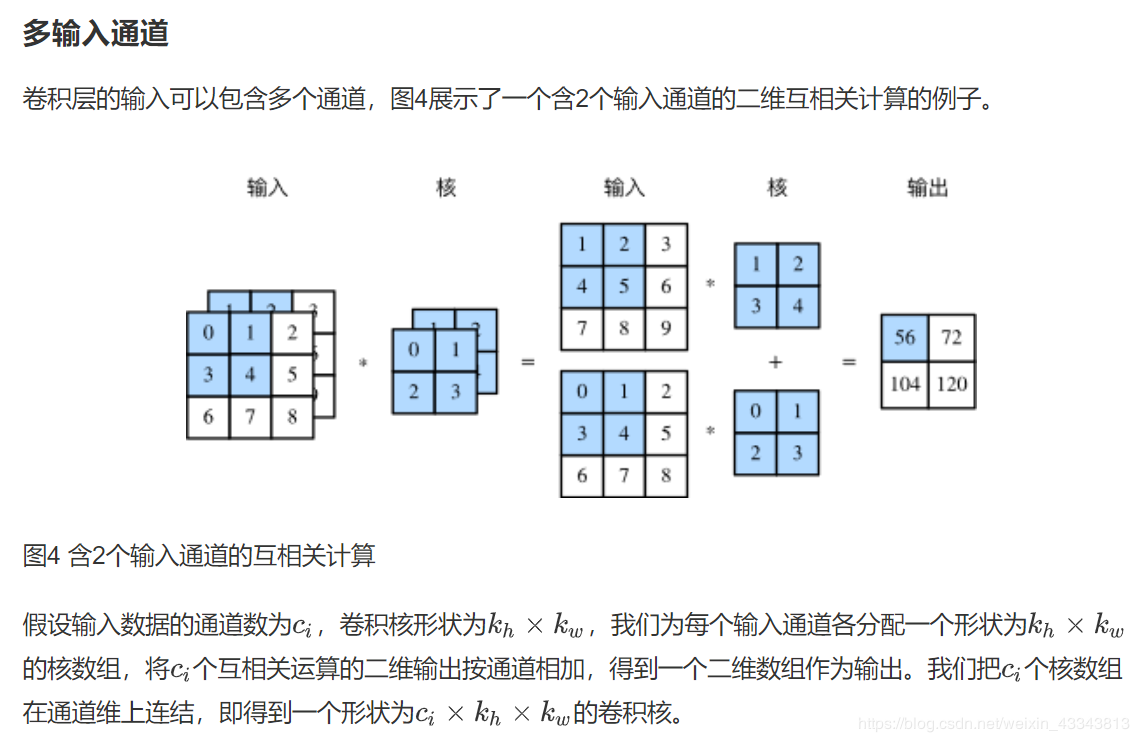



X = torch.rand(4, 2, 3, 5)
print(X.shape)
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=2, out_channels=3, kernel_size=(3, 5), stride=1, padding=(1, 2))
Y = conv2d(X)
print('Y.shape: ', Y.shape)
print('weight.shape: ', conv2d.weight.shape)
print('bias.shape: ', conv2d.bias.shape)
池化层
在区域里进行降采样
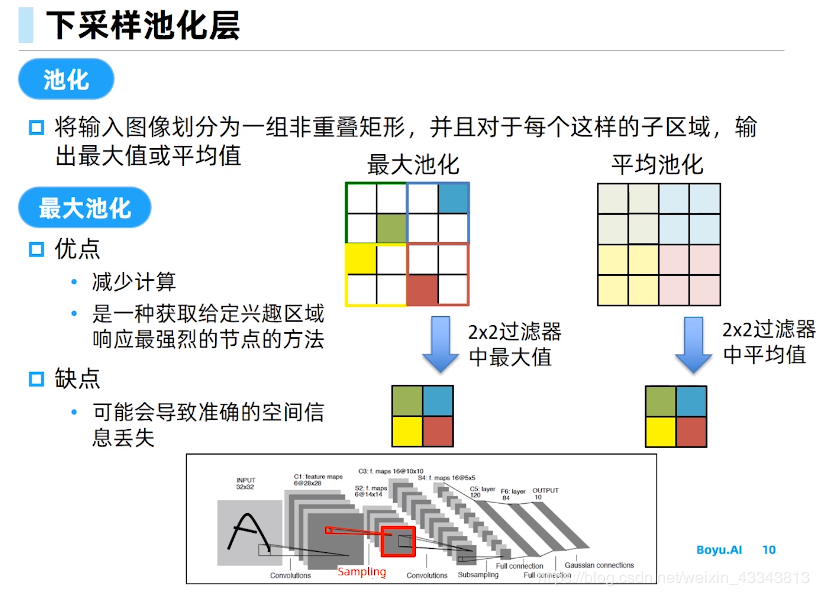

X = torch.arange(32, dtype=torch.float32).view(1, 2, 4, 4)
pool2d = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=(2, 1))
Y = pool2d(X)
# 平均池化层使用的是nn.AvgPool2d,使用方法与nn.MaxPool2d相同。

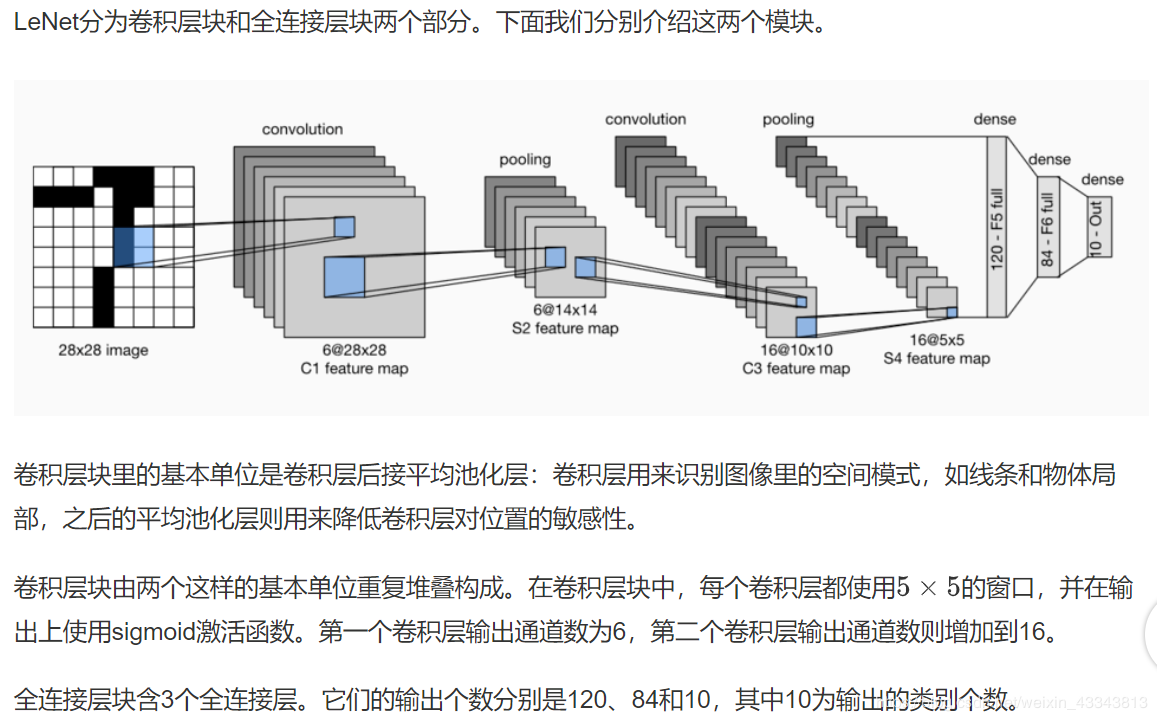
#下面我们通过Sequential类来实现LeNet模型。
import sys
sys.path.append("/home/kesci/input")
import d2lzh1981 as d2l
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import time
#net
class Flatten(torch.nn.Module): #展平操作
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
class Reshape(torch.nn.Module): #将图像大小重定型
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(-1,1,28,28) #(B x C x H x W)
net = torch.nn.Sequential( #Lelet
Reshape(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=6, kernel_size=5, padding=2), #b*1*28*28 =>b*6*28*28
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), #b*6*28*28 =>b*6*14*14
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=6, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5), #b*6*14*14 =>b*16*10*10
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), #b*16*10*10 => b*16*5*5
Flatten(), #b*16*5*5 => b*400
nn.Linear(in_features=16*5*5, out_features=120),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(84, 10)
)
#接下来我们构造一个高和宽均为28的单通道数据样本,并逐层进行前向计算来查看每个层的输出形状。
X = torch.randn(size=(1,1,28,28), dtype = torch.float32)
for layer in net:
X = layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape: \t',X.shape)

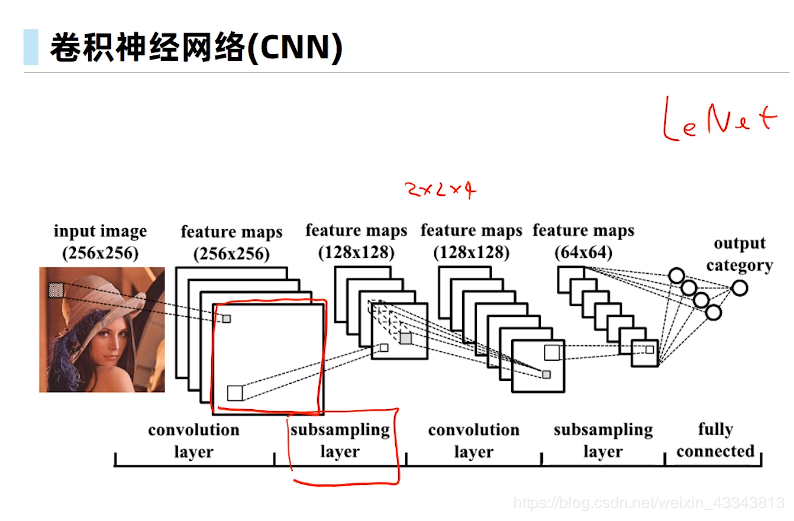
可以看到,在卷积层块中输入的高和宽在逐层减小。卷积层由于使用高和宽均为5的卷积核,从而将高和宽分别减小4,而池化层则将高和宽减半,但通道数则从1增加到16。全连接层则逐层减少输出个数,直到变成图像的类别数10。
#训练函数
def train_ch5(net, train_iter, test_iter,criterion, num_epochs, batch_size, device,lr=None):
"""Train and evaluate a model with CPU or GPU."""
print('training on', device)
net.to(device)
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_l_sum = torch.tensor([0.0],dtype=torch.float32,device=device)
train_acc_sum = torch.tensor([0.0],dtype=torch.float32,device=device)
n, start = 0, time.time()
for X, y in train_iter:
net.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
X,y = X.to(device),y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
loss = criterion(y_hat, y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
with torch.no_grad():
y = y.long()
train_l_sum += loss.float()
train_acc_sum += (torch.sum((torch.argmax(y_hat, dim=1) == y))).float()
n += y.shape[0]
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(test_iter, net,device)
print('epoch %d, loss %.4f, train acc %.3f, test acc %.3f, '
'time %.1f sec'
% (epoch + 1, train_l_sum/n, train_acc_sum/n, test_acc,
time.time() - start))
作者:like alone