机器学习之集成学习和随机森林
1 基本概念
集成学习,通过构建并结合多个学习器来完成学习任务。一般结构是:先产生一组“个体学习器”,再用某种策略将它们结合起来。结合策略主要有平均法、投票法和学习法等。
随机森林指的是利用多棵树对样本进行训练并预测的一种分类器。
 2 自己模拟的集成学习法
2 自己模拟的集成学习法
作者:何家劲
 2 自己模拟的集成学习法
2 自己模拟的集成学习法
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
X, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500, noise=0.3, random_state=42)
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1])
plt.show()
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
log_clf = LogisticRegression()
log_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
log_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
from sklearn.svm import SVC
svm_clf = SVC()
svm_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
svm_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
dt_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=666)
dt_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
dt_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
y_predict1 = log_clf.predict(X_test)
y_predict2 = svm_clf.predict(X_test)
y_predict3 = dt_clf.predict(X_test)
y_predict = np.array((y_predict1 + y_predict2 + y_predict3) >= 2, dtype='int')
y_predict[:10]
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
依据三种分类算法svc,逻辑回归,决策树三种方式投票方式来进行
3 sklearn中的集成学习1.voting classifier
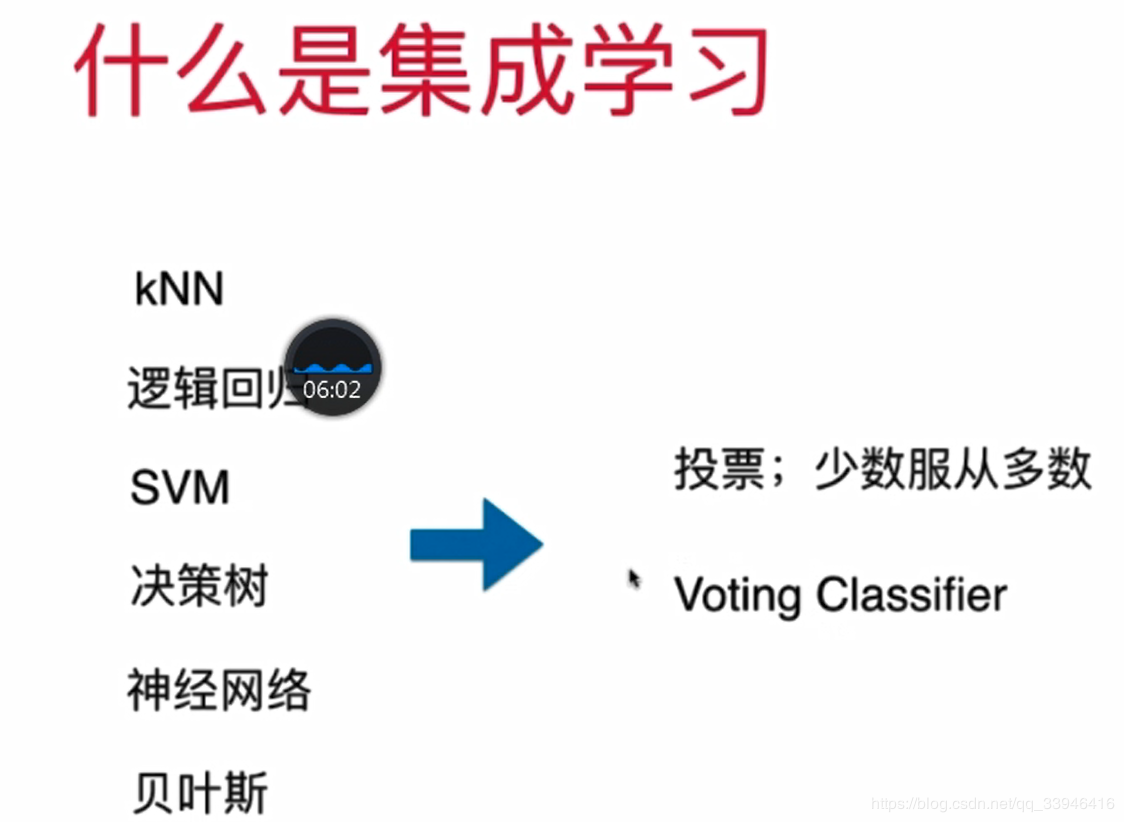

1)使用voting classifier 集成学习(少数服从多数)hard voting
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier
voting_clf = VotingClassifier(estimators=[
('log_clf', LogisticRegression()),
('svm_clf', SVC()),
('dt_clf', DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=666))],
voting='hard')
voting_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
voting_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
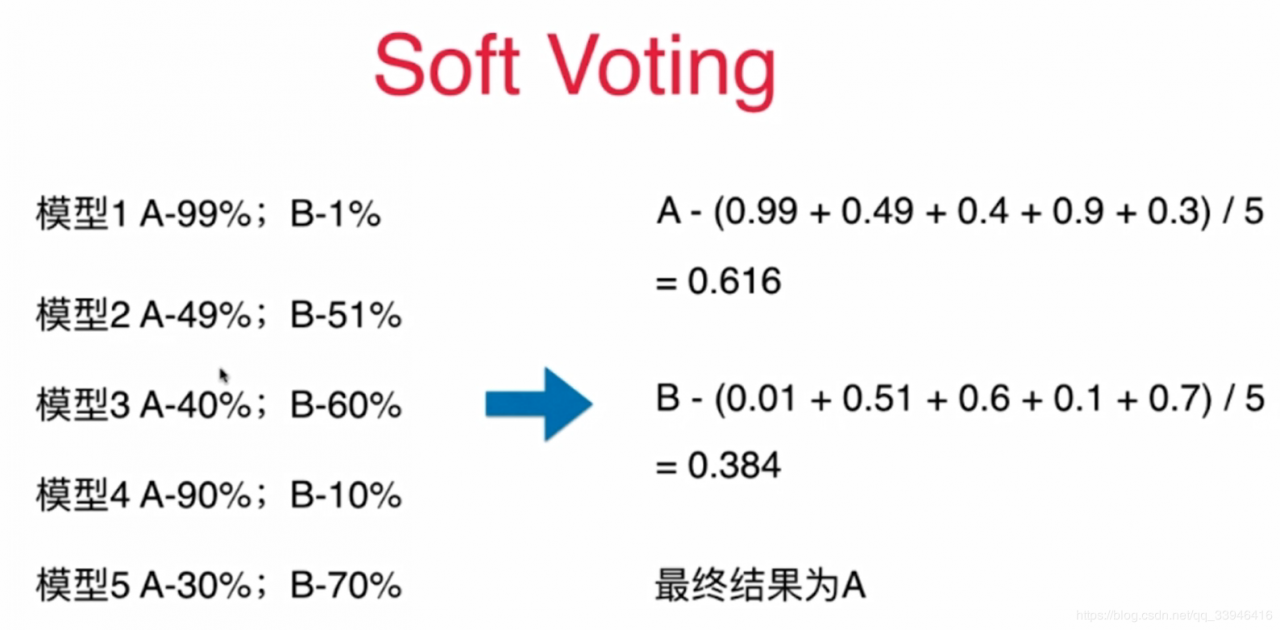
2) soft Voting 使用概率来衡量
voting_clf2 = VotingClassifier(estimators=[
('log_clf', LogisticRegression()),
('svm_clf', SVC(probability=True)),
('dt_clf', DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=666))],
voting='soft')
voting_clf2.fit(X_train, y_train)
voting_clf2.score(X_test, y_test)

3)Bagging 和 Pasting
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
bagging_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),
n_estimators=500,max_samples=100,
bootstrap=True) # 放回取样
bagging_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
bagging_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
n_estimators总样本数,max_samples每次取出的样本数

4)oob_score_
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
bagging_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),
n_estimators=500,max_samples=100,
bootstrap=True,oob_score=True,n_jobs=12) # 放回取样
bagging_clf.fit(X,y)
#不同区分训练测试集 oob将没取到的百分之37的数据自动当测试集

5)bootstrap features 放回取样是关于特征数而不是样本数
# 只对样本特征放回采样
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
random_subspaces_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),
n_estimators=500,max_samples=500,
bootstrap=True,oob_score=True,n_jobs=12,# 放回取样
max_features=1,bootstrap_features=True) #随机选一个特征,放回取样
random_subspaces_clf.fit(X,y)
#不同区分训练测试集 oob将没取到的百分之37的数据自动当测试集
random_subspaces_clf.oob_score_
# 即对样本和样本特征都进行放回采样
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
random_patches_clf = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),
n_estimators=500,max_samples=100,
bootstrap=True,oob_score=True,n_jobs=12,# 放回取样
max_features=1,bootstrap_features=True) #随机选一个特征,放回取样
random_patches_clf.fit(X,y)
#不同区分训练测试集 oob将没取到的百分之37的数据自动当测试集
random_patches_clf.oob_score_
4 随机森林
1 使用随机森林

from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
rf_clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500,random_state=666,n_jobs=-1,oob_score=True)
rf_clf.fit(X,y)
rf_clf.oob_score_
rf_clf2 = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500,max_leaf_nodes=16,random_state=666,n_jobs=-1,oob_score=True)
rf_clf2.fit(X,y)
rf_clf2.oob_score_

2 使用Extra-tree
from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier
et_clf = ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=500,random_state=666,bootstrap=True,oob_score=True)
et_clf.fit(X,y)
et_clf.oob_score_
5 集成学习解决回归问题(和分类类似)
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingRegressor
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesRegressor
6 小结
集成学习和随机森林(多棵决策树)的方法可以集成多种简单的分类回归算法进行比较好的处理分类和回归的任务。
作者:何家劲
相关文章
Quirita
2021-04-07
Iris
2021-08-03
Vesta
2021-07-19
Grace
2020-11-05
Ula
2023-05-13
Jacinda
2023-05-13
Winona
2023-05-13
Fawn
2023-05-13
Echo
2023-05-13
Maha
2023-05-13
Kande
2023-05-15
Viridis
2023-05-17
Pandora
2023-07-07
Tallulah
2023-07-17
Janna
2023-07-20
Ophelia
2023-07-20
Natalia
2023-07-20
Irma
2023-07-20