Java学习路线:day11
文章目录客户信息管理软件需求说明书软件设计结构第1步:封装CMUtility工具类第2步:Customer类的设计第3步:CustomerList类的设计第4步:CustomerView类的设计
客户信息管理软件
作者:可乐汉堡薯条?
原文:https://shimo.im/docs/9h963yQcd3QdcxyT/ 《Java项目二:客户信息管理软件》
这个项目起初书写花了4小时,一堆bug,根据相关教程步骤,最后成功,前后一共花了9小时。只是记录!!!
需求说明书 下载链接:语雀。 软件设计结构该软件由以下三个模块组成:
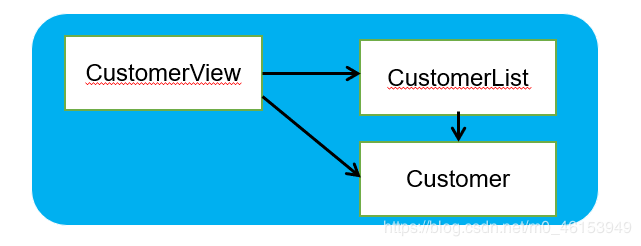
CustomerView为主模块,负责菜单的显示和处理用户操作
CustomerList为Customer对象的管理模块,内部用数组管理一组Customer对象,并提供相应的添加、修改、删除和遍历方法,供CustomerView调用
Customer为实体对象,用来封装客户信息
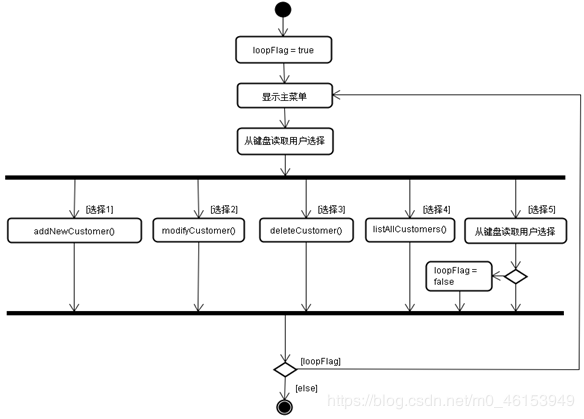
enterMainMenu()方法的活动图
该类提供了以下静态方法:
public static char readMenuSelection()
用途:该方法读取键盘,如果用户键入’1’-’5’中的任意字符,则方法返回。返回值为用户键入字符。
public static char readChar() 和 public static char readChar(char defaultValue)
用途:这两个方法功能相同,均从键盘读取一个字符,并将其作为方法的返回值。
参数: defaultValue — 如果用户不输入字符而直接回车,方法将以defaultValue 作为返回值。(提示:此方法可在修改客户时调用)
public static int readInt() 和public static int readInt(int defaultValue)
用途:这两个方法功能相同,均从键盘读取一个长度不超过2位的 整数,并将其作为方法的返回值。
参数: defaultValue — 如果用户不输入字符而直接回车,方法将以defaultValue 作为返回值。
public static String readString(int limit) 和
public static String readString(int limit, String defaultValue)
用途:这两个方法功能相同,均从键盘读取一个长度不超过limit的字符串,并将其作为方法的返回值。
参数:limit — 指定字符串的最大长度
defaultValue — 如果用户不输入字符而直接回车,方法将以defaultValue 作为返回值。
public static char readConfirmSelection()
用途:从键盘读取‘Y’或’N’,并将其作为方法的返回值。
代码
import java.util.*;
/**
CMUtility工具类:
将不同的功能封装为方法,就是可以直接通过调用方法使用它的功能,而无需考虑具体的功能实现细节。
*/
public class CMUtility {
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
/**
用于界面菜单的选择。该方法读取键盘,如果用户键入’1’-’5’中的任意字符,则方法返回。返回值为用户键入字符。
*/
public static char readMenuSelection() {
char c;
for (; ; ) {
String str = readKeyBoard(1, false);
c = str.charAt(0);
if (c != '1' && c != '2' &&
c != '3' && c != '4' && c != '5') {
System.out.print("选择错误,请重新输入:");
} else break;
}
return c;
}
/**
从键盘读取一个字符,并将其作为方法的返回值。
*/
public static char readChar() {
String str = readKeyBoard(1, false);
return str.charAt(0);
}
/**
从键盘读取一个字符,并将其作为方法的返回值。
如果用户不输入字符而直接回车,方法将以defaultValue 作为返回值。
*/
public static char readChar(char defaultValue) {
String str = readKeyBoard(1, true);
return (str.length() == 0) ? defaultValue : str.charAt(0);
}
/**
从键盘读取一个长度不超过2位的整数,并将其作为方法的返回值。
*/
public static int readInt() {
int n;
for (; ; ) {
String str = readKeyBoard(2, false);
try {
n = Integer.parseInt(str);
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.print("数字输入错误,请重新输入:");
}
}
return n;
}
/**
从键盘读取一个长度不超过2位的整数,并将其作为方法的返回值。
如果用户不输入字符而直接回车,方法将以defaultValue 作为返回值。
*/
public static int readInt(int defaultValue) {
int n;
for (; ; ) {
String str = readKeyBoard(2, true);
if (str.equals("")) {
return defaultValue;
}
try {
n = Integer.parseInt(str);
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.print("数字输入错误,请重新输入:");
}
}
return n;
}
/**
从键盘读取一个长度不超过limit的字符串,并将其作为方法的返回值。
*/
public static String readString(int limit) {
return readKeyBoard(limit, false);
}
/**
从键盘读取一个长度不超过limit的字符串,并将其作为方法的返回值。
如果用户不输入字符而直接回车,方法将以defaultValue 作为返回值。
*/
public static String readString(int limit, String defaultValue) {
String str = readKeyBoard(limit, true);
return str.equals("")? defaultValue : str;
}
/**
用于确认选择的输入。该方法从键盘读取‘Y’或’N’,并将其作为方法的返回值。
*/
public static char readConfirmSelection() {
char c;
for (; ; ) {
String str = readKeyBoard(1, false).toUpperCase();
c = str.charAt(0);
if (c == 'Y' || c == 'N') {
break;
} else {
System.out.print("选择错误,请重新输入:");
}
}
return c;
}
private static String readKeyBoard(int limit, boolean blankReturn) {
String line = "";
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
line = scanner.nextLine();
if (line.length() == 0) {
if (blankReturn) return line;
else continue;
}
if (line.length() limit) {
System.out.print("输入长度(不大于" + limit + ")错误,请重新输入:");
continue;
}
break;
}
return line;
}
}
第2步:Customer类的设计
需求说明
Customer为实体类,用来封装客户信息
该类封装客户的以下信息:
String name :客户姓名
char gender :性别
int age :年龄
String phone:电话号码
String email :电子邮箱
提供各属性的get/set方法
提供所需的构造器(可自行确定)
验证需求
在Customer 类中临时添加一个main方法中,作为单元测试方法。
在方法中创建Customer对象,并调用对象的各个方法,以测试该类是否编写正确。
代码
/**
*
* @Description 为实参构造函数
* @author subei Email:subei@163.com
* @version
* @date 2020年4月22日下午4:29:10
*
*/
public class Customer {
private String name;// 客户姓名
private char gender; // 性别
private int age; // 年龄
private String phone; // 电话号码
private String email; // 电子邮箱
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public char getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(char gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Customer() {
}
public Customer(String name, char gender, int age, String phone, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
this.phone = phone;
this.email = email;
}
}
第3步:CustomerList类的设计
需求说明
CustomerList为Customer对象的管理模块,内部使用数组管理一组Customer对象
本类封装以下信息:
Customer[] customers:用来保存客户对象的数组
int total = 0 :记录已保存客户对象的数量
该类至少提供以下构造器和方法:
public CustomerList(int totalCustomer)
public boolean addCustomer(Customer customer)
public boolean replaceCustomer(int index, Customer cust)
public boolean deleteCustomer(int index)
public Customer[] getAllCustomers()
public Customer getCustomer(int index)
public int getTotal()
相关简介:
public CustomerList(int totalCustomer)
用途:构造器,用来初始化customers数组
参数:totalCustomer:指定customers数组的最大空间
public boolean addCustomer(Customer customer)
用途:将参数customer添加到数组中最后一个客户对象记录之后
参数:customer指定要添加的客户对象
返回:添加成功返回true;false表示数组已满,无法添加
public boolean replaceCustomer(int index, Customer cust)
用途:用参数customer替换数组中由index指定的对象
参数:customer指定替换的新客户对象
index指定所替换对象在数组中的位置,从0开始
返回:替换成功返回true;false表示索引无效,无法替换
public boolean deleteCustomer(int index)
用途:从数组中删除参数index指定索引位置的客户对象记录
参数: index指定所删除对象在数组中的索引位置,从0开始
返回:删除成功返回true;false表示索引无效,无法删除
public Customer[] getAllCustomers()
用途:返回数组中记录的所有客户对象
返回: Customer[] 数组中包含了当前所有客户对象,该数组长度与对象个数相同。
public Customer getCustomer(int index)
用途:返回参数index指定索引位置的客户对象记录
参数: index指定所要获取的客户在数组中的索引位置,从0开始
返回:封装了客户信息的Customer对象
验证需求
在CustomerList类中临时添加一个main方法中,作为单元测试方法。
在方法中创建CustomerList对象(最多存放5个客户对象),然后分别用模拟数据调用以下各个方法,以测试各方法是否编写正确:
addCustomer()
replaceCustomer()
deleteCustomer()
getAllCustomers()
getCustomer()
getTotal()
进一步测试以下情况,以验证该类是否编写正确:
调用addCustomer方法,添加至少5个以上客户对象时
当数组中客户对象数量为0时,仍然调用replaceCustomer方法替换对象
当数组中客户对象数量为0时,仍然调用deleteCustomer方法删除对象
对于replaceCustomer、 deleteCustomer和getCustomer的调用,当参数index的值无效时(例如-1或6)
getAllCustomers方法返回的数组长度是否与实际的客户对象数量一致
代码
public class CustomerList {
private Customer[] customers; //用来保存客户对象的数组
private int total = 0; //记录已保存客户对象的数量
/**
* 用来初始化customers数组的构造器
* @param totalCustomer:指定数组的长度
*/
public CustomerList(int totalCustomer){
customers = new Customer[totalCustomer];
}
/*
* 将参数customer添加到数组中最后一个客户对象记录之后
*/
public boolean addCustomer(Customer customer){
if(total >= customers.length){
return false;
}
// customers[total] = customer;
// total++;
// 或
customers[total++] = customer;
return true;
}
/*
* 用参数customer替换数组中由index指定的
*/
public boolean replaceCustomer(int index, Customer cust){
if(index >= total || index = total || index < 0){
return false;
}
for(int i = index;i < total - 1;i++){
customers[i] = customers[i+1];
}
//最后有数据的元素需要置空
// customers[total -1] = null;
// total --;
//或
customers[--total] = null;
return true;
}
/*
* 返回数组中记录的所有客户对象
*/
public Customer[] getAllCustomers(){
Customer[] custs = new Customer[total];
for(int i = 0;i < total;i++){
custs[i] = customers[i];
}
return custs;
}
/*
* 返回参数index指定索引位置的客户对象记录
*/
public Customer getCustomer(int index){
if(index = total){
return null;
}
return customers[index];
}
/*
* 获取客户的数量
*/
public int getTotal(){
return total;
}
}
第4步:CustomerView类的设计
需求说明
CustomerView为主模块,负责菜单的显示和处理用户操作
本类封装以下信息:
CustomerList customerList = new CustomerList(10);
创建最大包含10个客户对象的CustomerList 对象,供以下各成员方法使用。
该类至少提供以下方法:
public void enterMainMenu()
private void addNewCustomer()
private void modifyCustomer()
private void deleteCustomer()
private void listAllCustomers()
public static void main(String[] args)
public void enterMainMenu()
用途:显示主菜单,响应用户输入,根据用户操作分别调用其他相应的成员方法(如addNewCustomer),以完成客户信息处理。
private void addNewCustomer()
private void modifyCustomer()
private void deleteCustomer()
private void listAllCustomers()
用途:这四个方法分别完成“添加客户”、“修改客户”、“删除客户”和“客户列表”等各菜单功能。
这四个方法仅供enterMainMenu()方法调用。
public static void main(String[] args)
用途:创建CustomerView实例,并调用 enterMainMenu()方法以执行程序。
验证需求
执行main方法中,测试以下功能:
主菜单显示及操作是否正确
“添加客户”操作是否正确,给用户的提示是否明确合理;测试当添加的客户总数超过10时,运行是否正确
“修改客户”操作是否正确,给用户的提示是否明确合理;
“删除客户”操作是否正确,给用户的提示是否明确合理;
“客户列表”操作是否正确,表格是否规整;
代码
public class CustomerView {
private CustomerList customerList = new CustomerList(10);
public CustomerView(){
Customer customer = new Customer("张三", '男', 30, "010-56253825",
"abc@email.com");
customerList.addCustomer(customer);
}
/*
* 显示主菜单,响应用户输入,根据用户操作分别调用其他相应的成员方法(如addNewCustomer),以完成客户信息处理。
*/
public void enterMainMenu(){
boolean loopFlag = true;
do {
System.out
.println("\n-----------------客户信息管理软件-----------------\n");
System.out.println(" 1 添 加 客 户");
System.out.println(" 2 修 改 客 户");
System.out.println(" 3 删 除 客 户");
System.out.println(" 4 客 户 列 表");
System.out.println(" 5 退 出\n");
System.out.print(" 请选择(1-5):");
char menu = CMUtility.readMenuSelection();
switch(menu){
case '1':
addNewCustomer();
break;
case '2':
modifyCustomer();
break;
case '3':
deleteCustomer();
break;
case '4':
listAllCustomers();
break;
case '5':
System.out.print("确认是否退出(Y/N):");
char isExit = CMUtility.readConfirmSelection();
if(isExit == 'Y')
loopFlag = false;
break;
}
} while (loopFlag);
}
/*
* 添加客户的操作
*/
private void addNewCustomer(){
System.out.println("---------------------添加客户---------------------");
System.out.print("姓名:");
String name = CMUtility.readString(10);
System.out.print("性别:");
char gender = CMUtility.readChar();
System.out.print("年龄:");
int age = CMUtility.readInt();
System.out.print("电话:");
String phone = CMUtility.readString(13);
System.out.print("邮箱:");
String email = CMUtility.readString(30);
//将上述类封装到对象中
Customer customer = new Customer(name,gender,age,phone,email);
boolean isCustomer = customerList.addCustomer(customer);
if(isCustomer){
System.out.println("---------------------添加完成---------------------");
}else{
System.out.println("----------------记录已满,无法添加-----------------");
}
}
/*
* 修改客户的操作
*/
private void modifyCustomer(){
System.out.println("---------------------修改客户---------------------");
Customer cust ;
int number = 0;
for(;;){
System.out.print("请选择待修改客户的编号(-1退出):");
number = CMUtility.readInt();
if(number == -1){
return;
}
cust = customerList.getCustomer(number - 1);
if(cust == null){
System.out.println("无法找到指定用户");
}else{//找到了相应用户
break;
}
}
//修改客户信息
System.out.print("姓名(" + cust.getName() + "):");
String name = CMUtility.readString(10,cust.getName());
System.out.print("性别(" + cust.getGender() + "):");
char gender = CMUtility.readChar(cust.getGender());
System.out.print("年龄(" + cust.getAge() + "):");
int age = CMUtility.readInt(cust.getAge());
System.out.print("电话(" + cust.getPhone() + "):");
String phone = CMUtility.readString(13,cust.getPhone());
System.out.print("邮箱(" + cust.getEmail() + "):");
String email = CMUtility.readString(30, cust.getEmail());
Customer newCust = new Customer(name, gender, age, phone, email);
boolean isRepalce = customerList.replaceCustomer(number - 1, newCust);
if (isRepalce) {
System.out
.println("---------------------修改完成---------------------");
} else {
System.out.println("----------无法找到指定客户,修改失败--------------");
}
}
/*
* 删除客户的操作
*/
private void deleteCustomer(){
System.out.println("---------------------删除客户---------------------");
for(;;){
System.out.println("请选择待删除客户编号(-1退出):");
int number = CMUtility.readInt();
if(number == -1){
return;
}
Customer customer = customerList.getCustomer(number - 1);
if(customer == null){
System.out.println("无法找到指定客户");
}else{
break;
}
//找到了指定用户
System.out.println("确认是否删除(Y/N):");
char isDelete = CMUtility.readConfirmSelection();
if(isDelete == 'Y'){
boolean deletesuccess = customerList.deleteCustomer(number - 1);
if (deletesuccess) {
System.out.println("---------------------删除完成---------------------");
} else {
System.out.println("----------无法找到指定客户,删除失败--------------");
}
}else{
return;
}
}
}
/*
* 客户列表查询的操作
*/
private void listAllCustomers(){
System.out.println( "---------------------------客户列表---------------------------");
int total = customerList.getTotal();
if(total == 0){
System.out.println("没有客户记录!");
}else{
System.out.println("编号\t姓名\t性别\t年龄\t\t电话\t\t邮箱");
Customer[] custs = customerList.getAllCustomers();
for(int i = 0;i < custs.length;i++){
System.out.println(i + 1 + "\t" + custs[i].getName() + "\t" + custs[i].getGender() + "\t" + custs[i].getAge() + "\t\t" + custs[i].getPhone() + "\t" + custs[i].getEmail());
}
}
System.out.println("-------------------------客户列表完成-------------------------");
}
/*
* 主函数
*/
public static void main(String[] args){
CustomerView view = new CustomerView();
view.enterMainMenu();
}
}
这个项目是对初学者的前10天内容,而由于这个项目只用了四个类,所以都放在了一个包下,如果放在不同包下,甚至不同项目中,代码出现报错,需要使用调用语句import,代码需要慢慢研究,只是做出来了,还需详细分析。
整个Java全栈系列都是笔者自己敲的笔记。写作不易,如果可以,点个赞呗!✌
作者:可乐汉堡薯条?