java学习打卡一数组
1:java基础反转数组
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []a=new int[5];
int m=0,n=a.length-1;
int temp=0;
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) {
a[i]=(int) (Math.random() * 100);
}
System.out.print(“数组中的各个随机数是: “);
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) {
System.out.print(a[i]+”\t”);
}
while(m<n) {
temp=a[m];
a[m]=a[n];
a[n]=temp;
m++;
n–;
}
System.out.println("\n");
System.out.print(“数组中的各个随机数是: “);
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) {
System.out.print(a[i]+”\t”);
}
}
2:增强循环(foreach循环)
增强型for循环只能用来取值,却不能用来修改数组里的值
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] intary = { 1,2,3,4};
forDisplay(intary);
foreachDisplay(intary);
}
public static void forDisplay(int[] a){
System.out.println(“使用 for 循环数组”);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void foreachDisplay(int[] data){
System.out.println(“使用 foreach 循环数组”);
for (int a : data) {
System.out.print(a+ " ");
}
}
}
for(元素类型t 元素变量x : 遍历对象obj){
引用了x的java语句;
}
3:选择排序
选择法排序的思路:
把第一位和其他所有的进行比较,只要比第一位小的,就换到第一个位置来
比较完后,第一位就是最小的
然后再从第二位和剩余的其他所有进行比较,只要比第二位小,就换到第二个位置来
比较完后,第二位就是第二小的
以此类推
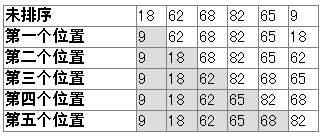
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a [] = new int[]{18,62,68,82,65,9};
//排序前,先把内容打印出来
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
//选择法排序
//第一步: 把第一位和其他所有位进行比较
//如果发现其他位置的数据比第一位小,就进行交换
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if(a[i]<a[0]){
int temp = a[0];
a[0] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
}
}
//把内容打印出来
//可以发现,最小的一个数,到了最前面
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
//第二步: 把第二位的和剩下的所有位进行比较
for (int i = 2; i < a.length; i++) {
if(a[i]<a[1]){
int temp = a[1];
a[1] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
}
}
//把内容打印出来
//可以发现,倒数第二小的数,到了第二个位置
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
//可以发现一个规律
//移动的位置是从0 逐渐增加的
//所以可以在外面套一层循环
for (int j = 0; j < a.length-1; j++) {
for (int i = j+1; i < a.length; i++) {
if(a[i]<a[j]){
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
}
}
}
//把内容打印出来
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
}
4:冒泡排序
冒泡法排序的思路:
第一步:从第一位开始,把相邻两位进行比较
如果发现前面的比后面的大,就把大的数据交换在后面,循环比较完毕后,最后一位就是最大的
第二步: 再来一次,只不过不用比较最后一位
以此类推

public static void main(String[] args) {
int a [] = new int[]{18,62,68,82,65,9};
//排序前,先把内容打印出来
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
//冒泡法排序
//第一步:从第一位开始,把相邻两位进行比较
//如果发现前面的比后面的大,就把大的数据交换在后面
for (int i = 0; i a[i+1]){
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[i+1];
a[i+1] = temp;
}
}
//把内容打印出来
//可以发现,最大的到了最后面
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
//第二步: 再来一次,只不过不用比较最后一位
for (int i = 0; i a[i+1]){
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[i+1];
a[i+1] = temp;
}
}
//把内容打印出来
//可以发现,倒数第二大的到了倒数第二个位置
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
//可以发现一个规律
//后边界在收缩
//所以可以在外面套一层循环
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i a[i+1]){
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[i+1];
a[i+1] = temp;
}
}
}
//把内容打印出来
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
}
5:复制合并数组
把一个数组的值,复制到另一个数组中
System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length)
src: 源数组
srcPos: 从源数组复制数据的起始位置
dest: 目标数组
destPos: 复制到目标数组的起始位置
length: 复制的长度
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a [] = new int[]{18,62,68,82,65,9};
int b[] = new int[3];//分配了长度是3的空间,但是没有赋值
//通过数组赋值把,a数组的前3位赋值到b数组
//方法一: for循环
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = a[i];
}
//方法二: System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length)
//src: 源数组
//srcPos: 从源数组复制数据的起始位置
//dest: 目标数组
//destPos: 复制到目标数组的启始位置
//length: 复制的长度
System.arraycopy(a, 0, b, 0, 3);
//把内容打印出来
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
System.out.print(b[i] + " ");
}
}
合并
首先准备两个数组,他俩的长度是5-10之间的随机数,并使用随机数初始化这两个数组
(向数组填充随机数的办法,参考这里)
然后准备第三个数组,第三个数组的长度是前两个的和
通过System.arraycopy 把前两个数组合并到第三个数组中
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = new int [(int) (Math.random()*5+5)];
int b[] = new int [(int) (Math.random()*5+5)];
for (int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
a[i]=(int)(Math.random()*100);
for (int i=0;i<b.length;i++)
b[i]=(int)(Math.random()*100);
System.out.println(“a数组为:”);
for(int i: a){
System.out.print(i+" “);}
System.out.println( );
System.out.println(“b数组为:”);
for(int i: b){
System.out.print(i+” “);
}
System.out.println();
int c[]= new int[a.length+b.length];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, c, 0, a.length);
System.arraycopy(b, 0, c, a.length, b.length);
System.out.println(“c数组为:”);
for(int i=0;i<a.length+b.length;i++){
System.out.print(c[i]+” ");
}
作者:糖唐qaq