python基础教程:python实现树的深度优先遍历与广度优先遍历详解
@本文来源于公众号:csdn2299,喜欢可以关注公众号 程序员学府
本文实例讲述了python实现树的深度优先遍历与广度优先遍历。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
广度优先(层次遍历)
从树的root开始,从上到下从左到右遍历整个树的节点
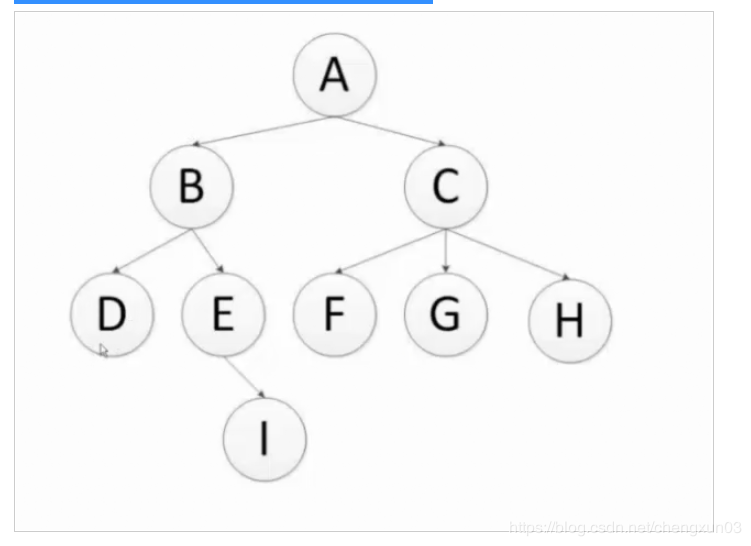
数和二叉树的区别就是,二叉树只有左右两个节点
广度优先 顺序:A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I
代码实现
def breadth_travel(self, root):
"""利用队列实现树的层次遍历"""
if root == None:
return
queue = []
queue.append(root)
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
print node.elem,
if node.lchild != None:
queue.append(node.lchild)
if node.rchild != None:
queue.append(node.rchild)
深度优先
深度优先有三种算法:前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历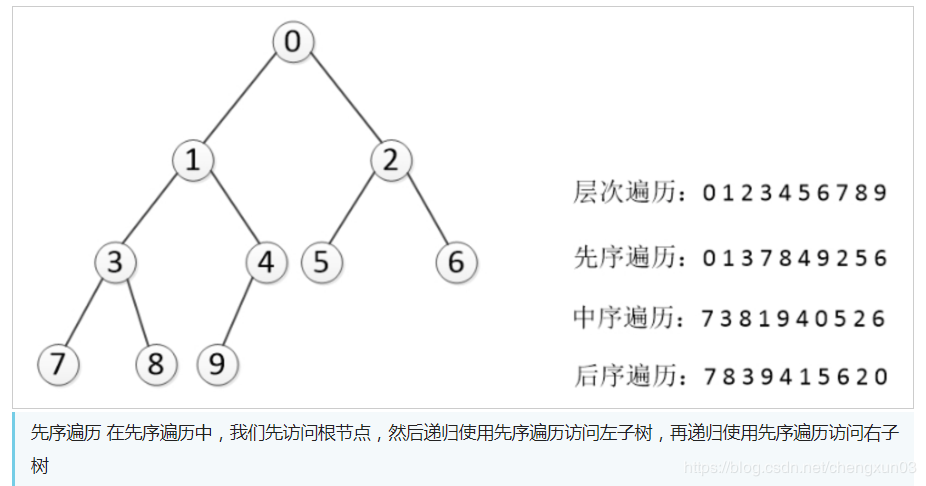
根节点->左子树->右子树
#实现 1
def preorder(self, root):
"""递归实现先序遍历"""
if root == None:
return
print root.elem
self.preorder(root.lchild)
self.preorder(root.rchild)
#实现 2
def depth_tree(tree_node):
if tree_node is not None:
print (tree_node._data)
if tree_node._left is noe None:
return depth_tree(tree_node._left)
if tree_node._right is not None:
return depth_tree(tree_node._right)
中序遍历 在中序遍历中,我们递归使用中序遍历访问左子树,然后访问根节点,最后再递归使用中序遍历访问右子树
左子树->根节点->右子树
def inorder(self, root):
"""递归实现中序遍历"""
if root == None:
return
self.inorder(root.lchild)
print root.elem
self.inorder(root.rchild)
后序遍历 在后序遍历中,我们先递归使用后序遍历访问左子树和右子树,最后访问根节点
左子树->右子树->根节点
def postorder(self, root):
"""递归实现后续遍历"""
if root == None:
return
self.postorder(root.lchild)
self.postorder(root.rchild)
print root.elem
非常感谢你的阅读
大学的时候选择了自学python,工作了发现吃了计算机基础不好的亏,学历不行这是
没办法的事,只能后天弥补,于是在编码之外开启了自己的逆袭之路,不断的学习python核心知识,深入的研习计算机基础知识,整理好了,如果你也不甘平庸,那就与我一起在编码之外,不断成长吧!
其实这里不仅有技术,更有那些技术之外的东西,比如,如何做一个精致的程序员,而不是“屌丝”,程序员本身就是高贵的一种存在啊,难道不是吗?[点击加入]想做你自己想成为高尚人,加油!
作者:程序员牡蛎