C/C++中多重继承详解及其作用介绍
目录
概述
优缺点
优点
缺点
声明多重继承的方法
格式
例子
二义性
两个基类有同名成员
基类和派生类有同名成员
两个基类从同一个基类派生
概述多重继承 (multiple inheritance): 一个派生类有两个或多个基类, 派生类从两个或多个基类中继承所需的属性. C++ 为了适应这种情况, 允许一个派生类同时继承多个基类. 这种行为称为多重继承.
自然地做到了对单继承的扩展
可以继承多个类的功能
缺点结构复杂化
优先顺序模糊
功能冲突
声明多重继承的方法 格式多重继承的格式:
派生类构造函数名(总形式参数表列):
基类1构造函数(实际参数表列),
基类2构造函数(实际参数表列),
基类3构造函数(实际参数表列)
{
派生类中新增数成员据成员初始化语句
}
例子
Teacher 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_TEACHER_H
#define PROJECT5_TEACHER_H
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Teacher {
protected:
string name;
int age;
string title;
public:
Teacher(string n, int a, string t);
void display_teacher();
};
#endif //PROJECT5_TEACHER_H
Teacher.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Teacher.h"
using namespace std;
Teacher::Teacher(string n, int a, string t) : name(n), age(a), title(t) {}
void Teacher::display_teacher() {
cout << "Teacher name: " << name << endl;
cout << "age: " << age << endl;
cout << "title: " << title << endl;
}
Student 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_STUDENT_H
#define PROJECT5_STUDENT_H
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Student {
protected:
string name;
char gender;
double score;
public:
Student(string n, char g, double s);
void display_student();
};
#endif //PROJECT5_STUDENT_H
Student.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Student.h"
using namespace std;
Student::Student(string n, char g, double s) : name(n), gender(g), score(s) {}
void Student::display_student() {
cout << "Student name: " << name << endl;
cout << "gender: " << gender << endl;
cout << "score: " << score << endl;
}
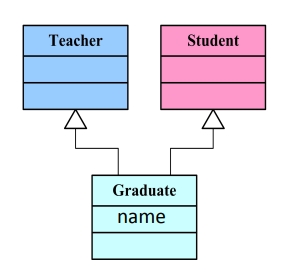
Graduate 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H
#define PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H
#include "Teacher.h"
#include "Student.h"
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Graduate : public Teacher, public Student{
private:
double wage;
public:
Graduate(string t_n, int t_a, string t_t, string s_n, char s_g, double s_s);
void display_graduate();
};
#endif //PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H
Graduate.cpp:
#include "Graduate.h"
Graduate::Graduate(string t_n, int t_a, string t_t, string s_n, char s_g, double s_s) :
Teacher(t_n, t_a, t_t),
Student(s_n, s_g, s_s) {}
void Graduate::display_graduate() {
display_teacher();
display_student();
}
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "Graduate.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Graduate graduate1("王叔叔", 18, "隔壁老王", "我是小白呀", 'f', 99);
graduate1.display_graduate();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
Teacher name: 王叔叔
age: 18
title: 隔壁老王
Student name: 我是小白呀
gender: f
score: 99
二义性
二义性 (Ambiguity) 指在多重继承中, 两个基类中的数据成员名相同.
二义性在派生类中的解决方法:
在标识符前用类名做前缀: Teacher::name 和 Student::name
基类和派生类需要有一个完整的设计, 不能随意而为
两个基类有同名成员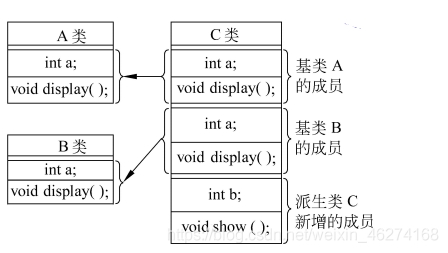
A 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_A_H
#define PROJECT5_A_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "A's num:" << num << endl;};
};
#endif //PROJECT5_A_H
B 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_B_H
#define PROJECT5_B_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class B {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "B's num:" << num << endl;};
};
#endif //PROJECT5_B_H
C 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_C_H
#define PROJECT5_C_H
#include <iostream>
#include "A.h"
#include "B.h"
using namespace std;
class C: public A, public B{
public:
int c;
void display() {cout << c << endl;};
};
#endif //PROJECT5_C_H
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "C.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
C c1;
c1.A::num = 1; // 用基类名限定
c1.B::num = 2; // 用基类名限定
c1.A::display();
c1.B::display();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
A's num:1
B's num:2
错误的写法
#include <iostream>
#include "C.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
C c1;
c1.num = 1;
c1.display();
return 0;
}
基类和派生类有同名成员
A 类:
class A {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "A's num:" << num << endl;};
};
B 类:
class B {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "B's num:" << num << endl;};
};
C 类:
class C: public A, public B{
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "C's num:" << num << endl;};
};
main:
int main() {
C c1;
c1.num = 3;
c1.A::num = 1;
c1.B::num = 2;
c1.display();
c1.A::display();
c1.B::display();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
C's num:3
A's num:1
B's num:2
同名覆盖:
基类的同名成员在派生类中被屏蔽, 成为 "不可见"的
对成员函数, 限于函数名和参数个数相同, 类型相匹配. 若只有函数名相同而参数不同, 属于函数重载
两个基类从同一个基类派生N 类:
class N {
public:
int a;
void display(){
cout << "A::a=" << a <<endl;
}
};
A 类:
class A : public N {
public:
int a1;
};
B 类:
class B : public N {
public:
int a2;
};
C 类:
class C: public A, public B{
public:
int a3;
void display() {cout << "a3=" << a3 << endl;};
};
main:
int main() {
C c1;
// 合法访问
c1.A::a = 3;
c1.A::display();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
A::a=3
到此这篇关于C/C++中多重继承详解及其作用介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++多重继承内容请搜索软件开发网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持软件开发网!