Python-梯度下降法(最速下降法)求解多元函数
梯度下降法的计算过程就是沿梯度下降的方向求解极小值。在求解机器学习算法的模型参数,即无约束优化问题时,梯度下降法是最常采用的方法之一。
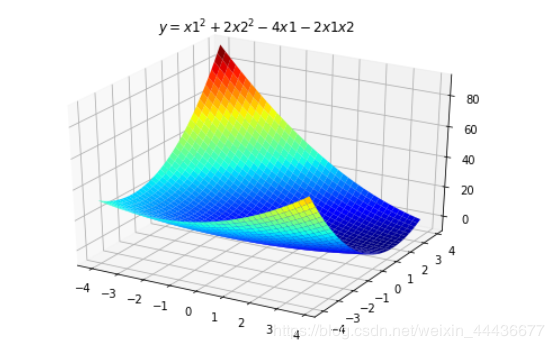
多元函数的图像显示方程为z=x1 ^2 + 2 * x2 ^2 - 4 * x1- 2 * x1 * x2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
%matplotlib inline
import math
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import warnings
def f2(x1,x2):
return x1*x1+2*x2*x2-4*x1-2*x1*x2 #方程为z=x1^2+2x2^2-4x1-2x1x2
X1 = np.arange(-4,4,0.2)
X2 = np.arange(-4,4,0.2)
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(X1, X2) # 生成xv、yv,将X1、X2变成n*m的矩阵,方便绘图
Y = np.array(list(map(lambda t : f2(t[0],t[1]),zip(X1.flatten(),X2.flatten()))))
Y.shape = X1.shape # 1600的Y图还原成原来的(40,40)
#作图
fig = plt.figure(facecolor='w')
ax = Axes3D(fig)
ax.plot_surface(X1,X2,Y,rstride=1,cstride=1,cmap=plt.cm.jet)
ax.set_title(u'$ y = x1^2+2x2^2-4x1-2x1x2 $')
plt.show()
结果如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import numpy as np
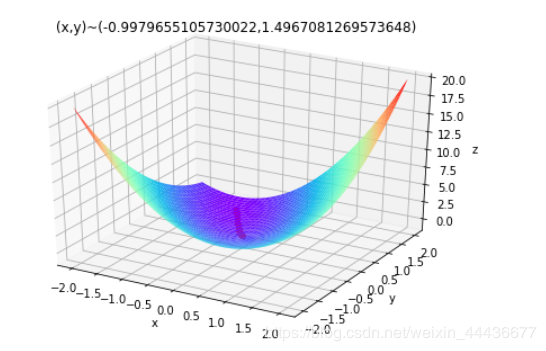
def Fun(x,y): #原函数
return x-y+2*x*x+2*x*y+y*y #方程为z=x1^2+2x2^2-4x1-2x1x2
def PxFun(x,y): #x偏导
return 1+4*x+2*y
def PyFun(x,y): #y偏导
return -1+2*x+2*y
#初始化
fig = plt.figure() #figure对象
ax = Axes3D(fig) #Axes3D对象
X,Y = np.mgrid[-2:2:40j,-2:2:40j] #取样并作满射联合
Z = Fun(X,Y) #取样点Z坐标打表
ax.plot_surface(X,Y,Z,rstride=1,cstride=1,cmap="rainbow")
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
ax.set_zlabel('z')
#梯度下降
step = 0.0008 #下降系数
x = 0
y = 0 #初始选取一个点
tag_x = [x]
tag_y = [y]
tag_z = [Fun(x,y)] #三个坐标分别打入表中,该表用于绘制点
new_x = x
new_y = y
Over = False
while Over == False:
new_x -= step*PxFun(x,y)
new_y -= step*PyFun(x,y) #分别作梯度下降
if Fun(x,y) - Fun(new_x,new_y) < 7e-9: #精度
Over = True
x = new_x
y = new_y #更新旧点
tag_x.append(x)
tag_y.append(y)
tag_z.append(Fun(x,y)) #新点三个坐标打入表中
#绘制点/输出坐标
ax.plot(tag_x,tag_y,tag_z,'r.')
plt.title('(x,y)~('+str(x)+","+str(y)+')')
plt.show()
结果如下:
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35946969/article/details/84446000
作者:君琴