python类与对象实例-以逻辑门为例
逻辑门分为 且,或,非;
且门是 a and b中a 跟 b均为1 才返回1,其他返回0;有两个阀门;
或门是 a and b中两者都为0则返回0,其他返回1;有两个阀门;
非门是 not a,如果a是1则返回0; 有一个阀门;
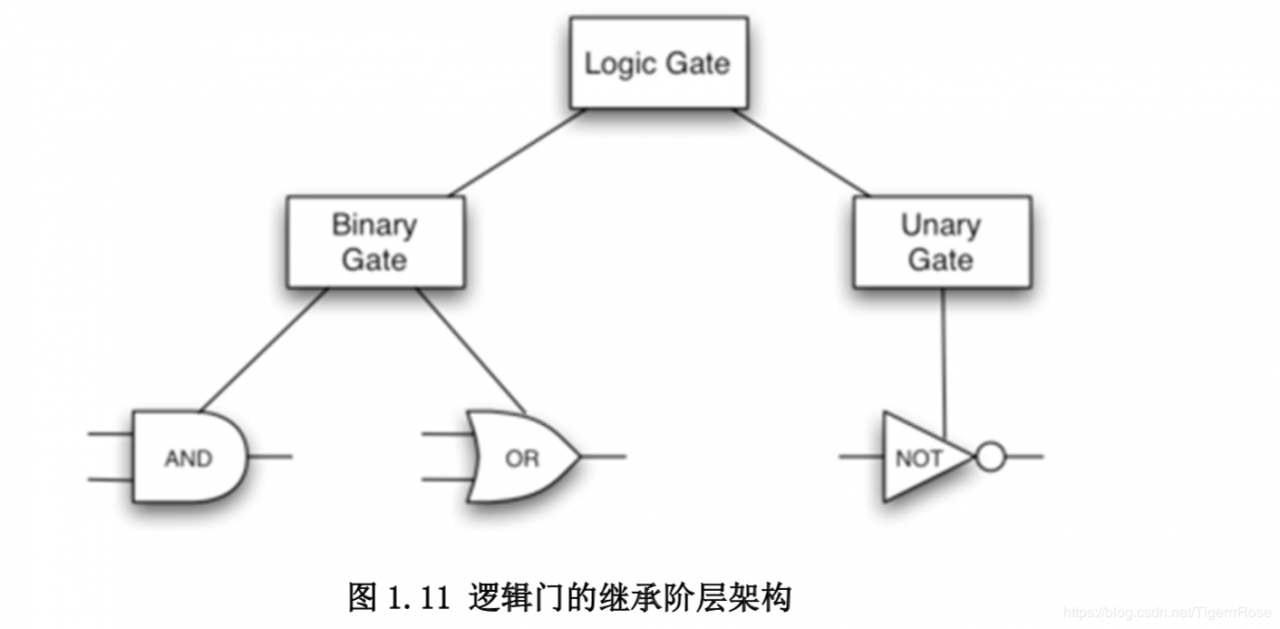
如上图我们可以创造一个大的LogicGate,进一步根据阀门为1的情况,创造类UnaryGate, 阀门为2则创造类BinaryGate. 进一步细分实现各种阀门。
LogicGate是一个父类,里面需要包含这个门的标签,比如这是第几个门?另外还需要根据之前的输入有个output的返回值(因为阀门有一有二,则将阀门输入设计在下一细分类中)。
class LogicGate:
def __init__(self,n):
self.label=n
self.output=None
def getLabel(self):
return self.label
def getOutput(self):
self.output = self.performGateLogic()
# 父类可以书写目前不存在的函数 惊!
return self.output
1.23 继承父类LogicGate
两个阀门的类 BinaryGate
思路: 继承父类LogicGate,在重新封装初始化函数__init__,并需要增加各阀门如何获取。
class BinaryGate(LogicGate):
def __init__(self,n):
LogicGate.__init__(self,n) #继承父类的属性
self.pinA=None #初始化两个阀门
self.pinB=None
def getPinA(self): #得到阀门A的值
return int(input('enter PinA input for gate'+self.getLabel()+':'))
def getPinB(self):
return int(input('enter PinB input for gate'+self.getLabel()+':'))
一个阀门的类 UnaryGate
class UnaryGate(LogicGate):
def __init__(self,n):
LogicGate.__init__(self,n) # 可替换成 super(LogicGate,self).__init__(n)
self.pinA=None
def getPin(self):
return int(input('enter pin input for gate'+self.getLabel()+':'))
注意__init___是属于类内的函数用加括号 init();
可将每个self,都理解为这个class的对象,每个对象self都具有自身的属性(调用可不用加括号)和自身的函数(调用加括号)
class AndGate(BinaryGate):
def __init__(self,n):
BinaryGate.__init__(self,n)
def performGateLogic(self):
a=self.getPinA()
b=self.getPinB()
if a==1 and b==1:
return 1
else:
return0
OR门 -从BinaryGate继承
class OrGate(BinaryGate):
def __init__(self,n):
BinaryGate.__init__(self,n)
def performGateLogic(self):
a=self.getPinA()
b=self.getPinB()
if a==1 or b==1:
return 1
else:
return 0
非门 -从UnaryGate继承
class notGate(UnaryGate):
def __init__(self,n):
UnaryGate.__init__(self,n)
def perfromGateLogic(self):
a = getPin()
return abs(a-1)
1.4 构建connector类
connector类 是独立的类,没有从以上任何类中继承
作用是 将门与门连接起来,如下图
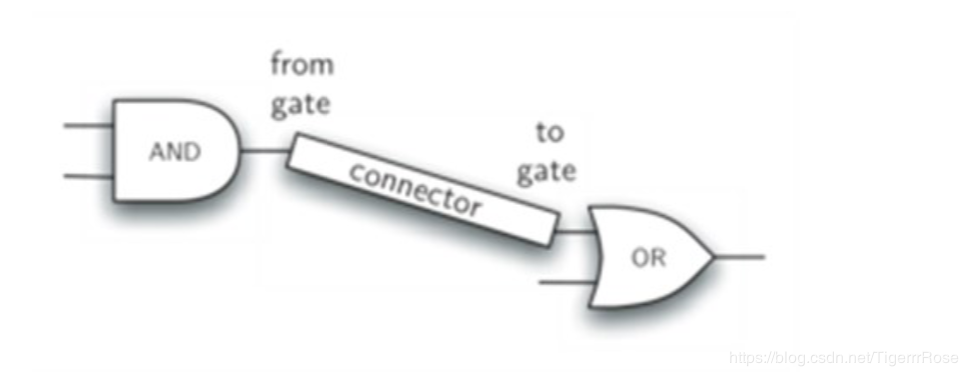
设计setNextPin思路:在BinaryGate类中,有些门有两条输入行,而连接器只能连接一条。如果两条行都是可用的,我们默认选择pinA。如果 pinA 已经被其他连接器连接了,我们便选择pinB。想要实现一个门的连接,至少要有一条可用的输入行。
class conenctor:
def __init__(self,tgate,fgate):
self.fromgate=fgate
self.togate=tgate
tgate.setNextPin(self)
def getFrom(self):
return self.fromgate
def getTo(self):
return self.togate
def setNextPin(self,source):
if self.PinA ==None:
self.PinA=source
elif self.PinB==None:
self.pinB=source
else:
raise RuntimeError('Error:NO EMPTY PINS')
现在我们可以从两个地方得到输入数据:一种就是前述的从外部用户处获取,另一种是从上一 个门的输出值中获取。
modify getPinA 跟getpinB:
如果输入线没有任何可用连接(None),便与原来一样提示用户输入数据;如果有可用连接,连接便会运行,而从 fromgate 的输出值也会被重新检索。这便相应地使门自动执行逻辑过程。这种操作一直 重复到所有的输入值都变为可用值并且最后的输出值变为问题中的门中所需要的输入值。
#modify 类binarygate中的method
def getPinA(self):
if self.pinA == None:
return int(input('enter PinA input for gate'+self.getLabel()+':'))
else:
return self.pinA.getFrom().getOutput()
同理可以取modify getPinB 跟getPin(见1.5)。
1.5完整代码class LogicGate:
def __init__(self,n):
self.label=n
self.output=None
def getLabel(self):
return self.label
def getOutput(self):
self.output = self.performGateLogic()
return self.output
class BinaryGate(LogicGate):
def __init__(self,n):
LogicGate.__init__(self,n) #继承父类的属性
self.pinA=None #初始化两个阀门
self.pinB=None
def getPinA(self):
if self.pinA == None:
return int(input('enter PinA input for gate'+self.getLabel()+':'))
else:
return self.pinA.getFrom().getOutput()
def getPinB(self):
if self.pinA == None:
return int(input('enter PinB input for gate'+self.getLabel()+':'))
else:
return self.pinB.getFrom().getOutput()
class UnaryGate(LogicGate):
def __init__(self,n):
LogicGate.__init__(self,n) # 可替换成 super(LogicGate,self).__init__(n)
self.pinA=None
def getPinA(self):
return int(input('enter pinA input for gate'+self.getLabel()+':'))
class AndGate(BinaryGate):
def __init__(self,n):
BinaryGate.__init__(self,n)
def performGateLogic(self):
a=self.getPinA()
b=self.getPinB()
if a==1 and b==1:
return 1
else:
return0
class OrGate(BinaryGate):
def __init__(self,n):
BinaryGate.__init__(self,n)
def performGateLogic(self):
a=self.getPinA()
b=self.getPinB()
if a==1 or b==1:
return 1
else:
return 0
class notGate(UnaryGate):
def __init__(self,n):
UnaryGate.__init__(self,n)
def perfromGateLogic(self):
a = getPin()
return abs(a-1)
class conenctor:
def __init__(self,tgate,fgate):
self.fromgate=fgate
self.togate=tgate
tgate.setNextPin(self)
def getFrom(self):
return self.fromgate
def getTo(self):
return self.togate
def setNextPin(self,source):
if self.PinA ==None:
self.PinA=source
elif self.PinB==None:
self.pinB=source
else:
raise RuntimeError('Error:NO EMPTY PINS')
reference:北大教程mooc 算法与数据结构
作者:TigerrrRose