c# Task.Wait()与awaiat Task异常处理的区别说明
Task.Wait()与awaiat Task异常处理区别
Task异常处理
Task.WaitAll()注意事项
先上代码
Task.Wait()与awaiat Task异常处理区别 Task异常处理下面有两个例子代码,可以直接复制粘贴到.net core中运行。两个代码要实现的功能完全一样,但是内核却又很大差异。
先看下面用await的例子与输出:
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class Program
{
static async Task Main()
{
System.Console.WriteLine($"Main Task ID:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}");
var task = Task.Run(() =>
{
System.Console.WriteLine($"In Task.Run(), Task ID:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}");
int[] vary=new int[5];
while (true)
{
Thread.Sleep(3000);
int d = vary[6];
}
});
// Just continue on this thread, or await with try-catch:
try
{
await task;
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException ex)
{
System.Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
System.Console.WriteLine($"After Wait(), Task ID:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}");
}
catch(AggregateException ex)
{
System.Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
System.Console.WriteLine($"After Wait(), Task ID:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}");
}
finally
{
//...
}
System.Console.WriteLine("Reach end.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
/*
Main Task ID:1
In Task.Run(), Task ID:4
Index was outside the bounds of the array.
Catch System.IndexOutOfRangeException
After Wait(), Task ID:4
Reach end.
*/
再看Task.Wait()方法下的异常处理与输出:
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
System.Console.WriteLine($"Main Task ID:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}");
var task = Task.Run(() =>
{
System.Console.WriteLine($"In Task.Run(), Task ID:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}");
int[] vary=new int[5];
while (true)
{
Thread.Sleep(3000);
int d = vary[6];
}
});
// Just continue on this thread, or await with try-catch:
try
{
task.Wait();
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException ex)
{
System.Console.WriteLine($"Catch {ex.GetType()}");
System.Console.WriteLine($"After Wait(), Task ID:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}");
}
catch(AggregateException ex)
{
System.Console.WriteLine($"Catch {ex.GetType()}");
System.Console.WriteLine($"After Wait(), Task ID:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}");
}
finally
{
//...
}
System.Console.WriteLine("Reach end.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
/*
Main Task ID:1
In Task.Run(), Task ID:4
Catch System.AggregateException
One or more errors occurred. (Index was outside the bounds of the array.)
After Wait(), Task ID:1
Reach end.
*/
从例子中可以看出,await之后的代码其实都是在新的线程(4线程)中执行,而Task.Wait()方法后的线程则是在主线程中执行。
因此,await之后的代码完全以传统方式处理异常;而Task.Wait()抛出的异常则由于是从新线程往外部线程抛出,所以它是被重新封装为AggregateException异常抛出。
Task.WaitAll()注意事项使用Task.WaitAll() 等待多任务执行完毕的时候发现,等待的任务还没结束,Task.WaitAll() 就先结束了,于是就写了一段测试代码进行验证。
先上代码 static void Main(string[] args)
{
//建立两个任务
Task t1 = new Task(async () => await T1());
Task t2 = new Task(async () => await T2());
//启动任务
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
//等待任务完成
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
Print("WaitAll Done");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static async Task T1()
{
Print("T1 Start");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Print("T1 await");
await Task.Delay(1000);
Print("T1 Done");
}
static async Task T2()
{
Print("T2 Start");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Print("T2 await");
await Task.Delay(1000);
Print("T2 Done");
}
static void Print(string msg)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.ffffff")}: {msg}");
}
再上结果,注意看T1、T2 Done 和 WaitAll Done的打印时间:
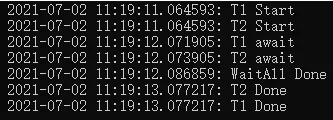
果然,坑!
Task.WaitAll() 尽然比等待的Task先结束。
总结:(不推荐,请看补充内容)
new Task().Start() 中一旦使用 await ,会立马返回结束状态。
所以,在使用 Task.WaitAll() 或其接续任务的时候,可以考虑使用 Thead.sleep() 替代 await Task.Delay() 。
2022-04-25 补充:
经过【32号就放假】提醒,测试了Task.Run() 和 Task.Factory.StartNew()两个方法,得出结论:
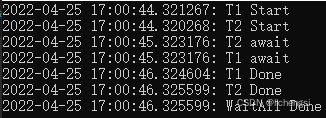
1、 在Task.Run()启动任务中,await会正常运行;(推荐使用)
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//建立两个任务
Task t1 = Task.Run(T1);
Task t2 = Task.Run(T2);
//等待任务完成
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
Print("WaitAll Done");
Console.ReadLine();
}
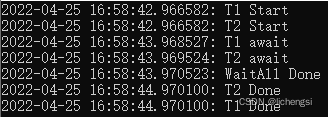
2、在Task.Factory.StartNew() 启动任务中,会立马返回结束状态。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//建立两个任务
Task t1 = Task.Factory.StartNew(T1);
Task t2 = Task.Factory.StartNew(T2);
//等待任务完成
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
Print("WaitAll Done");
Console.ReadLine();
}
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持软件开发网。