Android 进阶——高级UI必知必会之CoordinatorLayout源码解析及Behavior解耦思想分享(九)
前面一篇文章Android进阶——Material Design新控件之利用CoordinatorLayout协同多控件交互(七)介绍了下CoordinatorLayout 的简单应用,在使用的时候,你是否有想过为何CoordinatorLayout比其他ViewGroup具有可以让直接子View交互的功能?相关系列文章链接如下:
Android进阶——高级UI必知必会之2D绘制与Paint的基础应用(一) Android进阶——高级UI必知必会之2D绘制与使用Paint对图形进行渲染和滤镜混合处理(二) Android进阶——高级UI必知必会之Android坐标系与Canvas小结(三) Android 进阶——高级UI必知必会之统一可绘制概念Drawable详解(四) Android 进阶——高级UI必知必会之Path和贝塞尔曲线(五) Android 进阶——高级UI必知必会之借助PathMeasure打造酷炫Path特效(六) Android 进阶——高级UI必知必会之常用的屏幕适配完全攻略详解(七) Android 进阶——高级UI必知必会之常用的自定义ViewGroup进行屏幕适配核心思想分享(八) Android 进阶——高级UI必知必会之常用的自定义ViewGroup进行屏幕适配核心思想分享(九) 一、CoordinatorLayout核心角色CoordinatorLayout直接继承自ViewGroup并且实现了NestedScrollingParent2接口,核心参与角色主要有:CoordinatorLayout.CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams、CoordinatorLayout.Behavior两个内部类。
NestedScrollingParent2接口主要是用于处理嵌套滑动事件的,本质上也没有什么特别的逻辑,和Behavior一样是预约定好的接口API,区别在于Behavior是由CoordinatorLayout赋能,而NestedScrollingParent2是由实现此接口的View进行赋能。
1、CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParamsCoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams是CoordinatorLayout的内部类,和其他ViewGroup功能类似,在CoordinatorLayout的generateLayoutParams方法中直接调用构造方法进行初始化且在CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams构造方法内部调用CoordinatorLayout的parseBehavior根据配置的Behavior的类名反射创建Behavior并赋值到mBehavior字段,然后再通过Behavior的onAttachedToLayoutParams方法Called when the Behavior has been attached to a LayoutParams instance.,所以除了保存CoordinatorLayout内的子控件的布局信息之外,还保存着对应的Behavior对象引用 mBehavior。
public class CoordinatorLayout extends ViewGroup implements NestedScrollingParent2 {
...
public static class LayoutParams extends MarginLayoutParams {
...
Behavior mBehavior;
LayoutParams(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout);
this.gravity = a.getInteger(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_android_layout_gravity,Gravity.NO_GRAVITY);
mAnchorId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_anchor,View.NO_ID);
this.anchorGravity = a.getInteger(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_anchorGravity,Gravity.NO_GRAVITY);
this.keyline = a.getInteger(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_keyline,-1);
insetEdge = a.getInt(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_insetEdge, 0);
dodgeInsetEdges = a.getInt(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_dodgeInsetEdges, 0);
mBehaviorResolved = a.hasValue(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_behavior);
if (mBehaviorResolved) {
mBehavior = parseBehavior(context, attrs, a.getString(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_behavior));
}
a.recycle();
if (mBehavior != null) {
// If we have a Behavior, dispatch that it has been attached
mBehavior.onAttachedToLayoutParams(this);
}
}
}
...
}
这个类设计的原因是在于我们要在XML中通过自定义的属性给主题View绑定对应的Behavior,所以需要重写generateLayoutParams方法传入自定义的属性。
2、CoordinatorLayout.BehaviorCoordinatorLayout.Behavior是CoordinatorLayout的抽象泛型内部类,Behvaior 本身并不具备具体的业务功能,本质上就只是为了进行解耦的而封装的一个交互接口集合类,而CoordinatorLayout可以借助Behavior使得独立的子View可以产生交互,是因为CoordinatorLayout内部把事件分发至Behavior,让Behavior具有可以控制其他子View的效果了,也是CoordinatorLayout中核心的设计,也正是因为这个CoordinatorLayout.Behavior使得CoordinatorLayout中的直接子控件间可以产生联系,CoordinatorLayout.Behavior可以理解为事件分发的传送渠道(并不负责具体的任务),只是负责调用对应子View的相关方法,parseBehavior方法根据配置的Behavior的类名反射创建Behavior并赋值到mBehavior字段,这是继承Behavior时必须要重写两个参数的构造方法的原因。通俗来说,Behavior 设置在谁身上,就可以通过Behavior来改变它对应的状态,观察者改变时,主题也跟着改变。
2、CoordinatorLayout.Behavior核心方法CoordinatorLayout.Behavior中最核心的方法只有三个:layoutDependsOn方法、onDependentViewChanged方法和onDependentViewRemoved方法,通过这三个方法就可以实现直接子View之间的交互,至于其他方法是处理到其他业务情况的时候,比如说嵌套滑动、重新布局等等。
2.1、layoutDependsOn方法当进行Layout请求的时候就会触发执行,给CoordinatorLayout中的直接子控件设置了对应的Behavior之后,绘制时至少会执行一次,表示是否给配置了Behavior 的CoordinatorLayout直接子View 指定一个作为观察者角色的子View,返回true则表示主题角色child view的观察者是dependency view, 当观察者角色View状态(大小、位置)发生变化时,不管被观察View 的顺序怎样,被观察的View也可监听到并回调对应的方法;反之则两者之间没有建立联系。简而言之,这个方法的作用是配置了Behavior的主题子控件被符合哪些条件逻辑的子控件观察的(即作为主题的观察者之一)(Determine whether the supplied child view has another specific sibling view as a layout dependency)。
@Override
public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent, View child, View dependency) {
//TODO 在这里自己去实现依赖联系成立的逻辑,允许建立则返回true,完全不依赖CoordinatorLayout,实现解耦
if(dependency instanceof Button){
return true;
}
return super.layoutDependsOn(parent, child, dependency);
}
2.2、onDependentViewChanged方法
当且仅当Dependency View 状态(位置、大小等)改变时就会触发,返回true则表示Behavior改变了主题的状态,可能会执行多次,当然第一次绘制到布局上也算是状态改变时,所以自然也会触发,至于当监听到改变之后,如何去实现什么样的效果则由我们自己去开发实现。
/**
* 当被观察者的View 状态(如:位置、大小)发生变化时就会触发执行
* @return true if the Behavior changed the child view's size or position, false otherwise
*/
@Override
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, View child, View dependency) {
//TODO 根据具体的业务需求定义我们的结果
return super.onDependentViewChanged(parent, child, dependency);
}
2.3、onDependentViewRemoved方法
当依赖的Dependency View被移除时触发回调(Respond to a child’s dependent view being removed.)
/**
* Respond to a child's dependent view being removed.
* @param parent the parent view of the given child
* @param child the child view to manipulate
* @param dependency the dependent view that has been removed
*/
public void onDependentViewRemoved(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child,
@NonNull View dependency) {
}
2.4、onInterceptTouchEvent方法设置是否拦截触摸事件
设置是否拦截触摸事件,返回true则表示当前Behavior会拦截触摸事件,不会分发到CoordinatorLayout内的子View下了。
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child,
@NonNull MotionEvent ev) {
return false;
}
2.5、onTouchEvent方法处理触摸事件
public boolean onTouchEvent(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child,
@NonNull MotionEvent ev) {
return false;
}
2.6、onMeasureChild方法测量使用Behavior的View尺寸
/**
* Called when the parent CoordinatorLayout is about to measure the given child view.
* @param child the child to measure
* @return true if the Behavior measured the child view, false if the CoordinatorLayout
* should perform its default measurement
*/
public boolean onMeasureChild(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
return false;
}
2.7、onLayoutChild方法重新布局使用Behavior的View
/**
* Called when the parent CoordinatorLayout is about the lay out the given child view.
* @return true if the Behavior performed layout of the child view, false to request default layout behavior
*/
public boolean onLayoutChild(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child,
int layoutDirection) {
return false;
}
xxNestedxxScrollxx方法是用于监听嵌套滑动的事件,对应的是NestedScrollingParent2接口里的相关方法。
2.8、onStartNestedScroll方法当CoordinatorLayout 的子View试图开始进行嵌套滑动的时候触发,返回true时表示CoordinatorLayout充当nested scroll parent 处理这次滑动,当且仅当返回true时,当前Behavior才能收到后面的一些nested scroll事件回调(如:onNestedPreScroll、onNestedScroll等)。
/**
* @param coordinatorLayout 和Behavior 绑定的View的父CoordinatorLayout
* @param child 和Behavior 绑定的View 观察者
* @param directTargetChild
* @param target
* @param nestedScrollAxes 嵌套滑动滑动方向
* @param type the type of input which cause this scroll event
* @return true if the Behavior wishes to accept this nested scroll
*/
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, View child, View directTargetChild,
View target, int nestedScrollAxes, int type) {
return super.onStartNestedScroll(coordinatorLayout, child, directTargetChild, target, nestedScrollAxes,type);
}
2.9、onNestedScroll方法
在嵌套滑动进行中且onStartNestedScroll方法返回true时回调,当子View调用dispatchNestedPreScroll方法时会调用该方法。
/**
* 进行嵌套滚动时被调用
* @param coordinatorLayout
* @param child
* @param target
* @param dxConsumed target 已经消费的x方向的距离
* @param dyConsumed target 已经消费的y方向的距离
* @param dxUnconsumed x 方向剩下的滚动距离
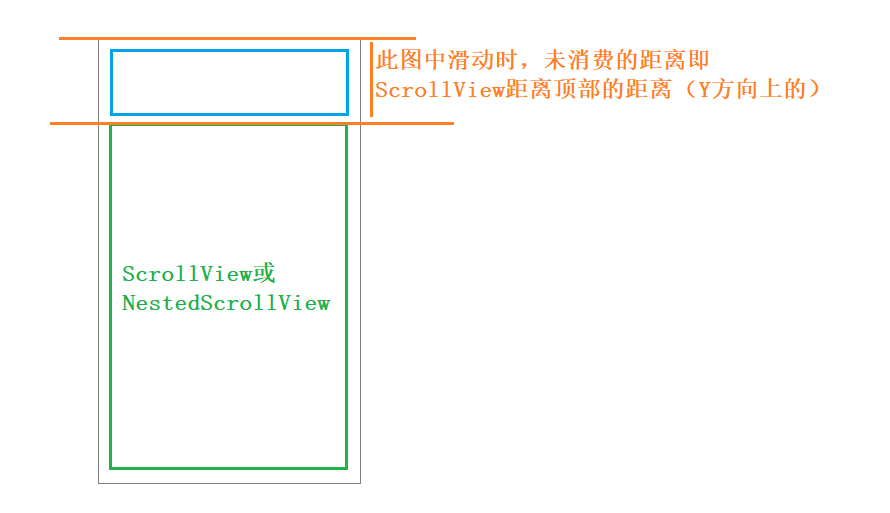
* @param dyUnconsumed y 方向剩下的滚动距离即未消费的距离
*/
@Override
public void onNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, View child, View target, int dxConsumed,
int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, int type) {
super.onNestedScroll(coordinatorLayout, child, target, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed,type);
}
 原创文章 252获赞 149访问量 58万+
关注
他的留言板
关注博主即可阅读全文
原创文章 252获赞 149访问量 58万+
关注
他的留言板
关注博主即可阅读全文
作者:CrazyMo_