Java - 并发编程 - 线程池
前言
常用线程池
作者:全栈-民
做的学习笔记,并加入了自己的理解,谢谢
使用线程池的原因我们创建的线程在运行结束后都会被虚拟机销毁,如果线程数量多的话,频繁的创建和销毁线程会大大浪费时间和效率,更重要的是浪费内存,线程池可以让线程运行后不立刻销毁,而是让线程重复使用,继续执行其他任务
线程池的优化 降低资源消耗 提高响应速度 提高线程的可管理性 流程图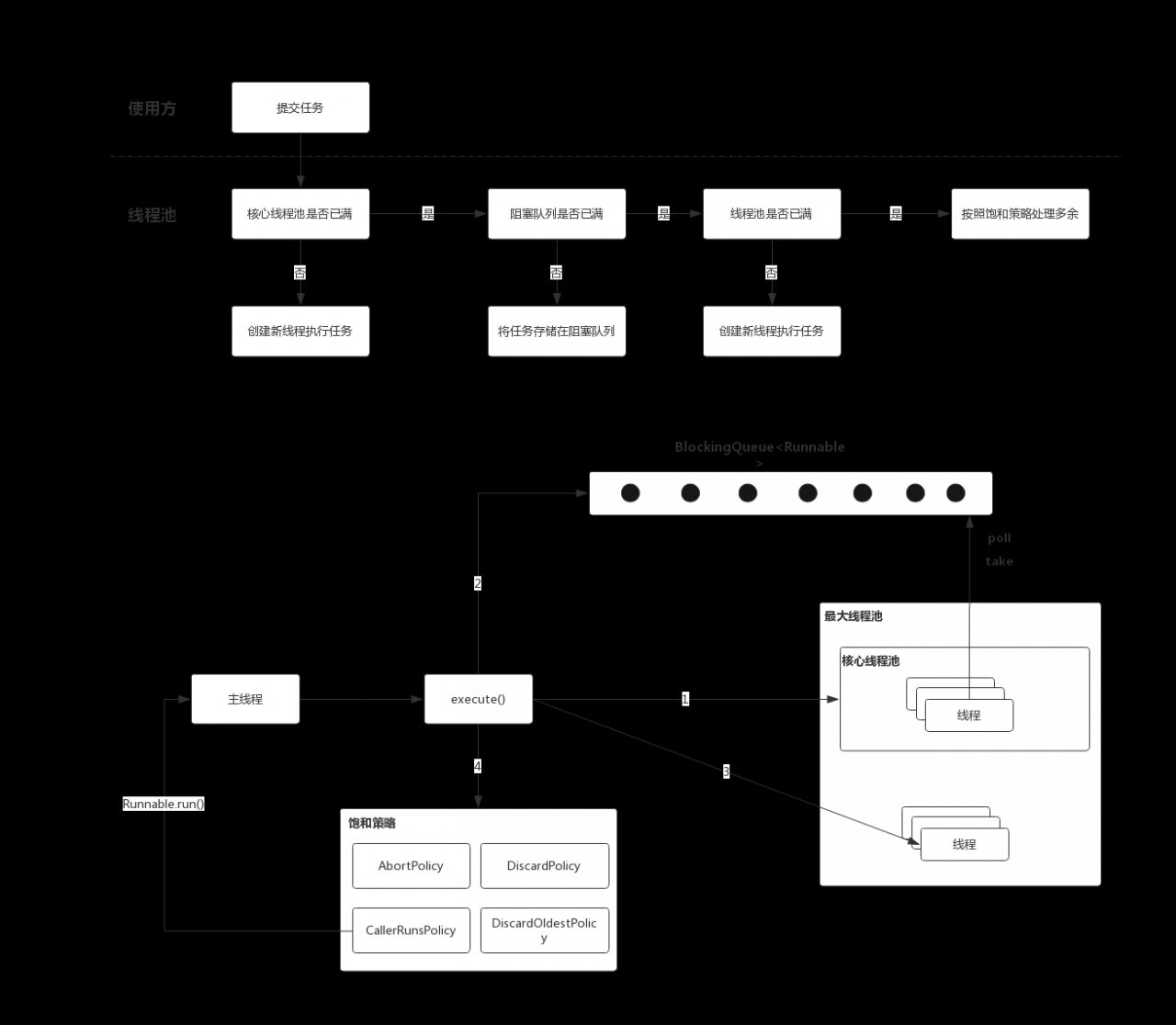
/**
* 线程核心参数
* @param corePoolSize 核心线程数量
* @param maximumPoolSize 最大线程数量
* @param keepAliveTime 线程空间后的存活时间
* @param unit 时间单位
* @param workQueue 用于存放任务的阻塞队列
* @param threadFactory 线程工厂类
* @param handler 当队列和最大线程池都满了之后的饱和策略
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
线程池可选择的阻塞队列
无界队列
有界队列 如果超出界定值,将阻塞 put 方法
同步移交队列 也就是队列不存储元素,每个插入操作都要等待另一个线程调用移出操作,否则插入操作一直处于阻塞
无界队列
ArrayBlockingQueue queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
queue.put(i);
System.out.println("向队列中添加值:" + i);
}
LinkedBlockingQueue queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
queue.put(i);
System.out.println("向队列中添加值:" + i);
}
有界队列
ArrayBlockingQueue queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
queue.put(i);
System.out.println("向队列中添加值:" + i);
}
LinkedBlockingQueue queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
queue.put(i);
System.out.println("向队列中添加值:" + i);
}
同步移交队列
SynchronousQueue queue = new SynchronousQueue();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 阻塞在这里
queue.put(i);
System.out.println("向队列中添加值:" + i);
}
SynchronousQueue queue = new SynchronousQueue();
// 插入值
new Thread(() -> {
try {
queue.put(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
// 取值
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Integer value = queue.take();
System.out.println("取到值:" + value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
线程池可选择的饱和策略
| 类 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| AbortPolicy | 丢弃任务并抛出RejectedExecutionException异常 《默认》 |
| DiscardPolicy | 抛弃策略,但是不抛出异常 |
| DiscardOldestPolicy | 丢弃队列最前面的任务(旧任务),然后重新尝试执行任务 |
| CallerRunsPolicy | 由调用线程处理该任务 |
线程数量无限的线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
public class Executors {
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue());
}
}
线程数量固定线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue());
}
单一线程线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue()));
}
提交任务
submit,获取结果
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 提交任务,并获取结构
Future future = threadPool.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
return 2 * 5;
});
// 阻塞获取结果
Integer value = future.get();
System.out.println("执行结果:" + value);
execute,没有结果
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 计算结果
Integer num = 2 * 3;
System.out.println("执行结果:" + num);
});
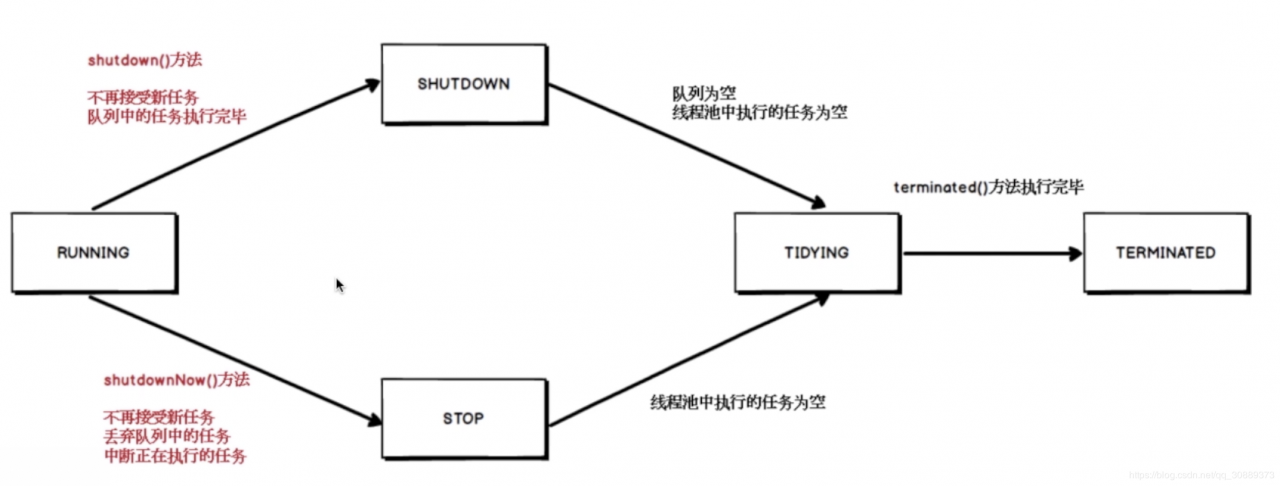
线程池的状态
作者:全栈-民