Binder通信机制与AIDL的使用
Android进程间通信(Inter-Process Communication, IPC)采用Binder通信机制,是一种client/server结构。
AIDL(Android Interface Define Language):Android接口定义语言,帮助开发者自动生成实现Binder通信机制所需的相关模板代码。(如果你够牛逼的话,也可以不用AIDL生成代码,自己直接写相关java代码,当然也可以复制一份AIDL生成的代码到java目录下,用于分析Binder通信机制)。
下面通过一个实例讲解Binder机制以及AIDL的使用。
实例说明:Client进程传两个整数a和b给Server进程,Server进程进行加法运算,然后把相加后的结果返回给Client进程。
步骤1:创建Client工程和Server工程,两个工程都创建IAdd.aidl文件,IAdd.aidl文件内容:
interface IAdd {
int add(int a, int b);
}
Client工程的目录结构:
Server工程的目录结构:
Client工程和Server工程中的aidl文件的名字,内容,以及所在的包名都要一模一样,最好就是在Client工程中写好了aidl文件后直接把整个aidl文件夹拷贝一份到Server的相同目录下即可,具体见上图。
aidl文件写好后,进行编译,编译后会自动生成IAdd类的源码:
public interface IAdd extends android.os.IInterface {
/**
* Local-side IPC implementation stub class.
*/
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.binder.aidl.IAdd {
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.binder.aidl.IAdd";
/**
* Construct the stub at attach it to the interface.
*/
public Stub() {
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.binder.aidl.IAdd interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.binder.aidl.IAdd asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.binder.aidl.IAdd))) {
return ((com.binder.aidl.IAdd) iin);
}
return new com.binder.aidl.IAdd.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_add: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
int _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readInt();
int _arg1;
_arg1 = data.readInt();
int _result = this.add(_arg0, _arg1);
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(_result);
return true;
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
private static class Proxy implements com.binder.aidl.IAdd {
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() {
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
int _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(a);
_data.writeInt(b);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_add, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readInt();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
}
static final int TRANSACTION_add = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
}
public int add(int a, int b) throws android.os.RemoteException;
}
步骤2. Client工程的MainActivity代码如下:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button btnPay;
private IBinder binder;
private IAdd iAdd;
ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
binder = iBinder;
iAdd = IAdd.Stub.asInterface(iBinder);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.binder.server.MyService");
/*android5.0之后,如果service不在同一个App的包中,
需要设置service所在程序的包名,(包名可以到App的清单文件AndroidManifest中查看)*/
intent.setPackage("com.binder.server");
bindService(intent, serviceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);//开启Service
btnPay = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnPay);
btnPay.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
try {
int result = iAdd.add(1, 2);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "result=" + result, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
//因为是跨程序调用服务,可能会出现远程异常
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
Server工程的MyService的代码如下:
public class MyService extends Service {
private String TAG = "MyService";
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.i(TAG, "onBind()");
iBinder = new MyBinder();
Log.i(TAG, "onBind(), iBinder=" + iBinder);
return iBinder;//return MyBinder, 从而通过ServiceConnection在activity中拿到MyBinder
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
public int addFunction(int a, int b) {
Log.i(TAG, "(), a=" + a + " ,b=" + b );
int result = a + b;
return result;
}
private IBinder iBinder;
class MyBinder extends IAdd.Stub {
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) throws RemoteException {
int result = addFunction(a, b);
return result;
} //通过Binder实例将service中的方法暴露出去
}
}
源码分析
Client端调用iAdd.add(1, 2);最终是如何调用Server端的addFunction()方法的
客户端Client通过ServiceConnectio获得Server的IBinder对象
ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
binder = iBinder;
iAdd = IAdd.Stub.asInterface(iBinder);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
}
};
这里的onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder)方法返回的并不是Server的MyService中创建的MyBinder对象本身,而是一个代理对象BinderProxy。(如果没有跨进程,则该方法返回的就是MyService中创建的MyBinder对象)。
iAdd是什么对象呢,看下IAdd.Stub.asInterface()方法:
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.binder.aidl.IAdd interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.binder.aidl.IAdd asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.binder.aidl.IAdd))) {
return ((com.binder.aidl.IAdd) iin);
}
return new com.binder.aidl.IAdd.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
最终执行的是
return new com.binder.aidl.IAdd.Stub.Proxy(obj);
所以iAdd其实是一个Proxy对象:
private static class Proxy implements com.binder.aidl.IAdd {
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() {
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
int _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(a);
_data.writeInt(b);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_add, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readInt();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
}
所以当点击按钮,执行 result = iAdd.add(1, 2); 这句代码时,调用的是上面Proxy对象的add()方法:
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
int _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(a);
_data.writeInt(b);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_add, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readInt();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
关键的代码是这句:
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_add, _data, _reply, 0);
而这个mRemote对象就是上面onServiceConnected()方法返回的BinderProxy对象,BinderProxy类在Binder.java文件中,看下该类的transact()方法:
public boolean transact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags) throws RemoteException {
Binder.checkParcel(this, code, data, "Unreasonably large binder buffer");
if (mWarnOnBlocking && ((flags & FLAG_ONEWAY) == 0)) {
// For now, avoid spamming the log by disabling after we've logged
// about this interface at least once
mWarnOnBlocking = false;
Log.w(Binder.TAG, "Outgoing transactions from this process must be FLAG_ONEWAY",
new Throwable());
}
final boolean tracingEnabled = Binder.isTracingEnabled();
if (tracingEnabled) {
final Throwable tr = new Throwable();
Binder.getTransactionTracker().addTrace(tr);
StackTraceElement stackTraceElement = tr.getStackTrace()[1];
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ALWAYS,
stackTraceElement.getClassName() + "." + stackTraceElement.getMethodName());
}
try {
return transactNative(code, data, reply, flags);
} finally {
if (tracingEnabled) {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ALWAYS);
}
}
}
这里关键的就是调用了transactNative()方法,看下该方法
public native boolean transactNative(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply,
int flags) throws RemoteException;
可以看到,这个方法是native方法,这个方法其实是进行底层Binder驱动(C++层代码)发送消息的相关过程。
底层Binder驱动(C++层代码)最终会调用Binder的execTransact()方法
// Entry point from android_util_Binder.cpp's onTransact
private boolean execTransact(int code, long dataObj, long replyObj,
int flags) {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain(dataObj);
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain(replyObj);
// theoretically, we should call transact, which will call onTransact,
// but all that does is rewind it, and we just got these from an IPC,
// so we'll just call it directly.
boolean res;
// Log any exceptions as warnings, don't silently suppress them.
// If the call was FLAG_ONEWAY then these exceptions disappear into the ether.
final boolean tracingEnabled = Binder.isTracingEnabled();
try {
if (tracingEnabled) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ALWAYS, getClass().getName() + ":" + code);
}
res = onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
} catch (RemoteException|RuntimeException e) {
if (LOG_RUNTIME_EXCEPTION) {
Log.w(TAG, "Caught a RuntimeException from the binder stub implementation.", e);
}
if ((flags & FLAG_ONEWAY) != 0) {
if (e instanceof RemoteException) {
Log.w(TAG, "Binder call failed.", e);
} else {
Log.w(TAG, "Caught a RuntimeException from the binder stub implementation.", e);
}
} else {
reply.setDataPosition(0);
reply.writeException(e);
}
res = true;
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
// Unconditionally log this, since this is generally unrecoverable.
Log.e(TAG, "Caught an OutOfMemoryError from the binder stub implementation.", e);
RuntimeException re = new RuntimeException("Out of memory", e);
reply.setDataPosition(0);
reply.writeException(re);
res = true;
} finally {
if (tracingEnabled) {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ALWAYS);
}
}
checkParcel(this, code, reply, "Unreasonably large binder reply buffer");
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
// Just in case -- we are done with the IPC, so there should be no more strict
// mode violations that have gathered for this thread. Either they have been
// parceled and are now in transport off to the caller, or we are returning back
// to the main transaction loop to wait for another incoming transaction. Either
// way, strict mode begone!
StrictMode.clearGatheredViolations();
return res;
}
上面最关键的是调用了Binder的onTransact()方法,而Stub类重写了onTransact()方法,看下Stub类的onTransact()方法:
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_add: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
int _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readInt();
int _arg1;
_arg1 = data.readInt();
int _result = this.add(_arg0, _arg1);
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(_result);
return true;
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
可以看到调用了Stub类的add()方法,而MyBinder重写了Stub类的add()方法:
class MyBinder extends IAdd.Stub {
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) throws RemoteException {
int result = addFunction(a, b);
return result;
}
}
add()方法里调用了addFunction()方法,到这里就完成了Server端的addFunction()方法的完整调用过程。
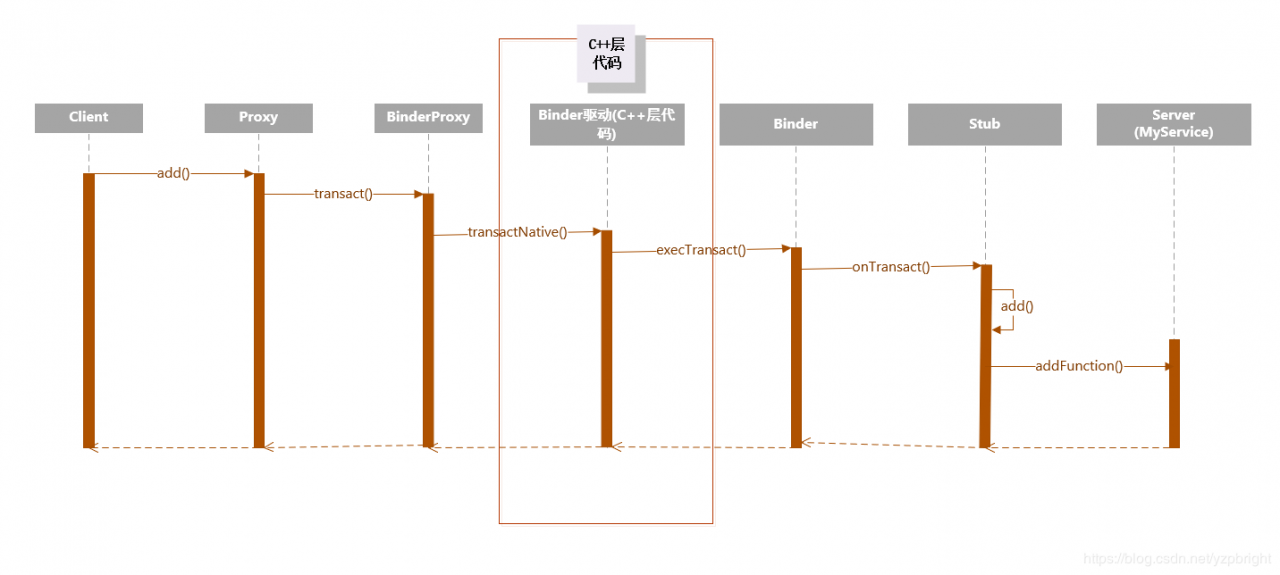
上述过程时序图:
总结:
Proxy是client端创建的用于向server端发送消息的代理(Proxy对象实现了IAdd接口,并且维护着一个Server端返回的BinderProxy对象),而Stub对象(也实现了IAdd接口)是server端用于接收消息的。client端通过BinderProxy对象的transact()方法将消息发送给底层Binder驱动,底层Binder驱动最终会将消息传递给Server端的Stub对象的onTransact()方法。
参考:
Android AIDL与proxy,stub
Android跨进程通信IPC之10——Binder之Framework层Java篇
Android Framework:Binder(6)-Java层Service的注册及跨进程调用
腾讯面试题——谈一谈Binder的原理和实现一次拷贝的流程
https://www.androidos.net.cn/android/9.0.0_r8/xref/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Binder.java
https://www.androidos.net.cn/android/9.0.0_r8/xref/frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
https://www.androidos.net.cn/android/9.0.0_r8/xref/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_util_Binder.cpp
作者:yzpyzp