Android AsyncTask 完美解析 看不懂源码你就输了
android.os.AsyncTask,一个执行异步操作的类,我们可以使用它来处理后台任务,并且在UI线程中处理结果,而无需关心线程的问题。
AsyncTask 内部是使用 {@link Thread}和{@link Handler}来实现的。理想情况下,应将AsyncTasks用于短操作(最多几秒钟)。如果需要长时间保持线程运行,建议使用 java.util.concurrent 包提供的各种API。 例如{@link Executor},{@ link ThreadPoolExecutor}和{@link FutureTask}。
2.基本使用 2.1 关键APIandroid.os.AsyncTask#execute(Params…)
使用指定的参数执行任务。 任务返回自身(this),以便调用者可以保留对其的引用。这个方法必须在UI 线程上调用。
android.os.AsyncTask#onPreExecute
在后台任务执行之前执行,同样是运行在UI 线程。
android.os.AsyncTask#doInBackground
后台任务,用于处理一些异步操作。该方法由AsyncTask 内置的调度者执行,在使用中需要复写该方法来完成异步处理。在此方法中可以调用android.os.AsyncTask#publishProgress 函数来更新进度,通知UI 线程来显示。
android.os.AsyncTask#onProgressUpdate
更新进度。该方法是经 android.os.AsyncTask#publishProgress 函数执行后由android.os.AsyncTask 内部的Handler 进行消息分发,然后在UI 线程执行。
android.os.AsyncTask#onPostExecute
后台任务执行完毕后,通过内部的handler 将返回结果发送至UI 线程,入参是{@link #doInBackground}函数的返回值,可在该方法处理执行结果。
2.2.1 继承 AsyncTask,复写方法
class DownloadAsyncTask extends AsyncTask{
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
super.onPreExecute();
// todo 在 doInBackground() 函数之前执行,运行在UI线程
}
@Override
protected Result doInBackground(Params... params) {
// todo 处理异步任务,运行在后台(work)线程
// todo 可以调用此方法来更新进度
onProgressUpdate();
return null;
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Result result) {
super.onPostExecute(result);
// todo 在 doInBackground() 函数之后执行,可以在这里处理运行结果。运行在UI线程
}
}
2.2.2 调用执行
DownloadAsyncTask asyncTask = new DownloadAsyncTask();
asyncTask.execute();
2.2.3 小心内存泄漏
因为AsyncTask 是执行的异步操作,所以在使用的时候一定要注意内存泄露的问题,切记切记!!!
源码版本:SDK 28
3.1 构造函数 /**
* Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.
*/
public AsyncTask() {
this((Looper) null);
}
/**
* Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.
*
* @hide
*/
public AsyncTask(@Nullable Looper callbackLooper) {
mHandler = callbackLooper == null || callbackLooper == Looper.getMainLooper()
? getMainHandler()
: new Handler(callbackLooper);
mWorker = new WorkerRunnable() {
public Result call() throws Exception {
mTaskInvoked.set(true);
Result result = null;
try {
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
//noinspection unchecked
result = doInBackground(mParams);
Binder.flushPendingCommands();
} catch (Throwable tr) {
mCancelled.set(true);
throw tr;
} finally {
postResult(result);
}
return result;
}
};
mFuture = new FutureTask(mWorker) {
@Override
protected void done() {
try {
postResultIfNotInvoked(get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("An error occurred while executing doInBackground()",
e.getCause());
} catch (CancellationException e) {
postResultIfNotInvoked(null);
}
}
};
}
在构造函数里做了三件事,初始化Handler 的实例mHandler,WorkerRunnable 的实例mWorker 以及 FutureTask 的实例 mFuture。
mHandler:用于连接后台线程和UI 线程,做消息分发的。
mWorker:本质上是一个Callable,查看 WorkerRunnable 发现是实现的 java.util.concurrent.Callable 接口,而 Callable 是一个可以携带返回结果的任务。
private static abstract class WorkerRunnable implements Callable {
Params[] mParams;
}
在mWorker 的 call() 方法中执行 doInBackground 函数来获取返回结果
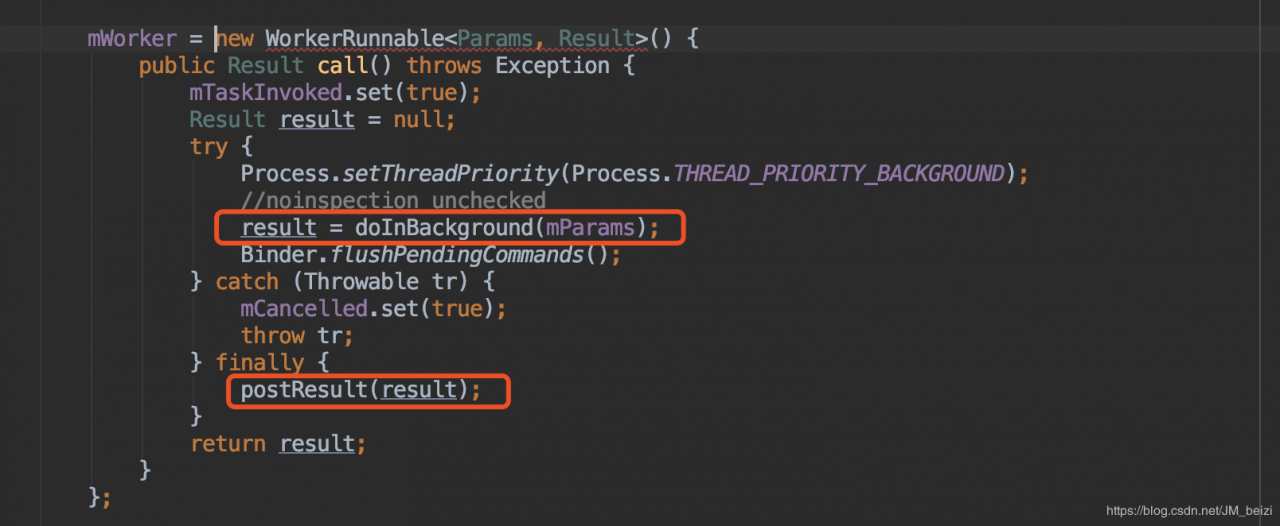
而后在finally 中执行了 android.os.AsyncTask#postResult 方法,此方法是发送一个message,其中携带的数据就是doInBackground 方法返回的数据。
private Result postResult(Result result) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Message message = getHandler().obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_RESULT,
new AsyncTaskResult(this, result));
message.sendToTarget();
return result;
}
mFuture:用来处理异步请求,配合 java.util.concurrent.Callable 接口可以实现在工作线程获取返回结果。在这里 mWorker 表示的也就是 mFuture 要执行的任务。另外,还复写 java.util.concurrent.FutureTask#done 的方法,该方法在任务执行完毕时被调用,这里做了个安全校验,当没有执行task 时仍会调用 postResult 方法,执行到UI线程上。
mFuture = new FutureTask(mWorker) {
@Override
protected void done() {
try {
postResultIfNotInvoked(get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("An error occurred while executing doInBackground()",
e.getCause());
} catch (CancellationException e) {
postResultIfNotInvoked(null);
}
}
};
private void postResultIfNotInvoked(Result result) {
final boolean wasTaskInvoked = mTaskInvoked.get();
if (!wasTaskInvoked) {
postResult(result);
}
}
mTaskInvoked 是个原子操作(AtomicBoolean),在mWorker 的run 方法中设置为true。
private final AtomicBoolean mTaskInvoked = new AtomicBoolean();
3.2 android.os.AsyncTask#execute(Params…)
android.os.AsyncTask#execute(Params…) 内部会执行 android.os.AsyncTask#executeOnExecutor 方法,传入sDefaultExecutor
@MainThread
public final AsyncTask execute(Params... params) {
return executeOnExecutor(sDefaultExecutor, params);
}
@MainThread
public final AsyncTask executeOnExecutor(Executor exec,
Params... params) {
if (mStatus != Status.PENDING) {
switch (mStatus) {
case RUNNING:
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
+ " the task is already running.");
case FINISHED:
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
+ " the task has already been executed "
+ "(a task can be executed only once)");
}
}
mStatus = Status.RUNNING;
onPreExecute();// 1.
mWorker.mParams = params;
exec.execute(mFuture);// exec 为 sDefaultExecutor
return this;
}
在方法内部调用了android.os.AsyncTask#onPreExecute 函数,到这里目前还是运行在UI 线程。其次执行 exec.execute(mFuture),而入参 exec 为 sDefaultExecutor。那sDefaultExecutor 是啥呢?
/**
* An {@link Executor} that executes tasks one at a time in serial
* order. This serialization is global to a particular process.
*/
public static final Executor SERIAL_EXECUTOR = new SerialExecutor();
private static volatile Executor sDefaultExecutor = SERIAL_EXECUTOR;
这里 sDefaultExecutor 指向了 SERIAL_EXECUTOR,这是一个串行的任务调度器,将进入的任务按顺序取出执行。
private static class SerialExecutor implements Executor {
// 这是一个双端队列,符合先进先出的原则。
final ArrayDeque mTasks = new ArrayDeque();
// 当前执行的任务
Runnable mActive;
public synchronized void execute(final Runnable r) {
// 1.把传递进去来的runnable 打包成一个新的Runnable对象,然后入队。
mTasks.offer(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
// 4.执行传入进来的runnable 任务,即 FutureTask -> WorkerRunnable -> doInBackground
r.run();
} finally {
// 5.执行完毕后,继续执行下一个任务。
scheduleNext();
}
}
});
// 2.当 mActive 为 null 时,从队列中取出任务并执行
if (mActive == null) {
scheduleNext();
}
}
protected synchronized void scheduleNext() {
// 3.从队头取出一个任务,如果不为null,则通过线程池获取一个子线程来执行该任务
if ((mActive = mTasks.poll()) != null) {
THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR.execute(mActive);
}
}
}
当一个新的任务(FutureTask)进来时
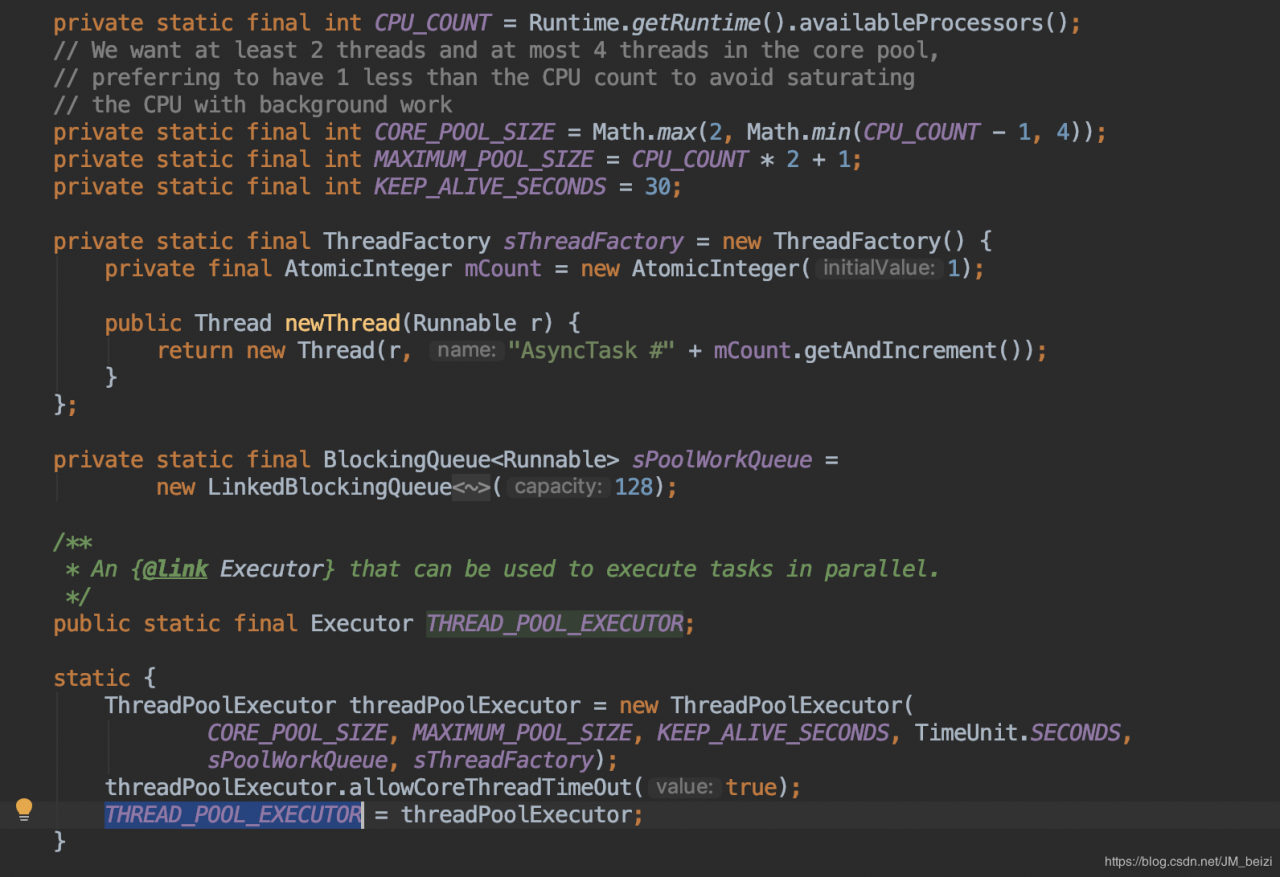
把传递进来的任务 打包成一个新的Runnable 对象,然后按先进先出的顺序执行入队(offer)操作。 检查当前是否有正在执行的任务,如果没有,则获取任务执行。 从队头取出一个任务,如果不为null,则通过线程池获取一个子线程来执行该任务 (AsyncTask 内包装了一个特有的线程池)。 执行传入进来的runnable 任务,即 可获取返回值的task ,该任务中执行 doInBackground 方法,还有执行结果的消息分发。 继续执行下一个任务,重复 3-4-5,直到任务队列中没有需要执行的任务。THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR 指向了一个线程池的对象,当有Runnbale 任务进来时,通过 threadPoolExecutor 来开启一个新线程执行任务。注意,这里执行的任务是经过 SerialExecutor 包装过的任务,在包装的任务内首先执行的才是FutureTask 中的 WorkerRunnable。
话不多说,直接上图
emmmmmm… 算了算了 画图太浪费时间了,还是简单的做个描述吧。
android.os.AsyncTask#execute(Params…)
android.os.AsyncTask#executeOnExecutor
-> android.os.AsyncTask#onPreExecute
-> exec.execute(mFuture) 调用调度器执行任务
android.os.AsyncTask.SerialExecutor
-> 打包传递进来的Runnable,然后执行入队(offer)操作。
-> 检查当前是否有正在执行的任务,如果没有,则获取任务执行。
从队头取出一个任务,如果不为null,则通过线程池获取一个子线程来执行该任务 (AsyncTask 内包装了一个特有的线程池)。
-> 执行传入进来的runnable 任务,即 可获取返回值的task ,该任务中执行 doInBackground 方法,还有执行结果的消息分发。
-> 继续执行下一个任务,重复 3-4-5,直到任务队列中没有需要执行的任务。
FutureTask -> android.os.AsyncTask.WorkerRunnable
-> android.os.AsyncTask#doInBackground
-> android.os.AsyncTask#postResult 发送消息,通知任务完成。
InternalHandler
-> Message -> android.os.AsyncTask#MESSAGE_POST_RESULT -> android.os.AsyncTask#finish -> android.os.AsyncTask#onPostExecute
-> Message -> android.os.AsyncTask#MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS -> android.os.AsyncTask#onProgressUpdate
作者:A类函数