玩转Asp.net MVC 的八个扩展点
MVC模型以低耦合、可重用、可维护性高等众多优点已逐渐代替了WebForm模型。能够灵活使用MVC提供的扩展点可以达到事半功倍的效果,另一方面Asp.net MVC的设计和高质量的代码也值得我们去阅读和学习。 本文将介绍Asp.net MVC中常用的八个扩展点并举例说明。 一、ActionResult ActionResult代表了每个Action的返回结果。asp.net mvc提供了众多内置的ActionResult类型,如:ContentResult,ViewResult,JsonResult等,每一种类型都代表了一种服务端的Response类型。我们什么时候需要使用这个扩展点呢? 假如客户端需要得到XML格式的数据列表: public void GetUser() { var user = new UserViewModel() { Name = "richie", Age = 20, Email = "abc@126.com", Phone = "139********", Address = "my address" }; XmlSerializer serializer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(UserViewModel)); Response.ContentType = "text/xml"; serializer.Serialize(Response.Output, user); } 我们可以在Controller中定义一个这样的方法,但是这个方法定义在Controller中有一点别扭,在MVC中每个Action通常都需要返回ActionResult类型,其次XML序列化这段代码完全可以重用。经过分析我们可以自定义一个XmlResult类型: public class XmlResult : ActionResult { private object _data; public XmlResult(object data) { _data = data; } public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context) { var serializer = new XmlSerializer(_data.GetType()); var response = context.HttpContext.Response; response.ContentType = "text/xml"; serializer.Serialize(response.Output, _data); } } 这时候Action可以返回这种类型了: public XmlResult GetUser() { var user = new UserViewModel() { Name = "richie", Age = 20, Email = "abc@126.com", Phone = "139********", Address = "my address" }; return new XmlResult(user); } 同样的道理,你可以定义出其他的ActionResult类型,例如:CsvResult等。二、Filter MVC中有四种类型的Filter:IAuthorizationFilter,IActionFilter,IResultFilter,IExceptionFilter 这四个接口有点拦截器的意思,例如:当有异常出现时会被IExceptionFilter类型的Filter拦截,当Action在执行前和执行结束会被IActionFilter类型的Filter拦截。

通过实现IExceptionFilter我们可以自定义一个用来记录日志的Log4NetExceptionFilter: public class Log4NetExceptionFilter : IExceptionFilter { private readonly ILog _logger; public Log4NetExceptionFilter() { _logger = LogManager.GetLogger(GetType()); } public void OnException(ExceptionContext context) { _logger.Error("Unhandled exception", context.Exception); } } 后需要将自定义的Filter加入MVC的Filter列表中: public class FilterConfig { public static void RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilterCollection filters) { filters.Add(new Log4NetExceptionFilter()); } } 为了记录Action的执行时间,我们可以在Action执行前计时,Action执行结束后记录log: public class StopwatchAttribute : ActionFilterAttribute { private const string StopwatchKey = "StopwatchFilter.Value"; private readonly ILog _logger= LogManager.GetLogger(typeof(StopwatchAttribute)); public override void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext filterContext) { filterContext.HttpContext.Items[StopwatchKey] = Stopwatch.StartNew(); } public override void OnActionExecuted(ActionExecutedContext filterContext) { var stopwatch = (Stopwatch)filterContext.HttpContext.Items[StopwatchKey]; stopwatch.Stop(); var log=string.Format("controller:{0},action:{1},execution time:{2}ms",filterContext.ActionDescriptor.ControllerDescriptor.ControllerName,filterContext.ActionDescriptor.ActionName,stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds) _logger.Info(log); } } ActionFilterAttribute是一个抽象类,它不但继承了IActionFilter, IResultFilter等Filter,还继承了FilterAttribute类型,这意味着我们可以将这个自定义的类型当作Attribute来标记到某个Action或者Controller上,同时它还是一个Filter,仍然可以加在MVC的Filter中起到全局拦截的作用。 三、HtmlHelper 在Razor页面中,如果需要写一段公用的用来展示html元素的逻辑,你可以选择使用@helper标记,例如: @helper ShowProduct(List products, string style) { @foreach (var product in products) { @product.Name } } 这一段代码有点像一个方法定义,只需要传入一个list类型和字符串会按照定义的逻辑输出html: Product list using helper @ShowProduct(Model.SportProducts, "list-group-item-info") @ShowProduct(Model.BookProducts, "list-group-item-warning") @ShowProduct(Model.FoodProducts, "list-group-item-danger") 这样抽取的逻辑只对当前页面有效,如果我们想在不同的页面公用这一逻辑如何做呢? 在Razor中输入@Html即可得到HtmlHelper实例,例如我们可以这样用:@Html.TextBox(“name”)。由此可见我们可以将公用的逻辑扩展在HtmlHelper上: public static class HtmlHelperExtensions { public static ListGroup ListGroup(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper) { return new ListGroup(); } } public class ListGroup { public MvcHtmlString Info(List data, Func getName) { return Show(data,getName, "list-group-item-info"); } public MvcHtmlString Warning(List data, Func getName) { return Show(data,getName, "list-group-item-warning"); } public MvcHtmlString Danger(List data, Func getName) { return Show(data,getName, "list-group-item-danger"); } public MvcHtmlString Show(List data, Func getName, string style) { var ulBuilder = new TagBuilder("ul"); ulBuilder.AddCssClass("list-group"); foreach (T item in data) { var liBuilder = new TagBuilder("li"); liBuilder.AddCssClass("list-group-item"); liBuilder.AddCssClass(style); liBuilder.SetInnerText(getName(item)); ulBuilder.InnerHtml += liBuilder.ToString(); } return new MvcHtmlString(ulBuilder.ToString()); } } 有了上面的扩展,可以这样使用了: Product list using htmlHelper @Html.ListGroup().Info(Model.SportProducts,x=>x.Name) @Html.ListGroup().Warning(Model.BookProducts,x => x.Name) @Html.ListGroup().Danger(Model.FoodProducts,x => x.Name) 效果:

四、RazorViewEngine 通过自定义RazorViewEngine可以实现同一份后台代码对应不同风格的View。利用这一扩展能够实现不同的Theme风格切换。再比如站点可能需要在不同的语言环境下切换到不同的风格,也可以通过自定义RazorViewEngine来实现。
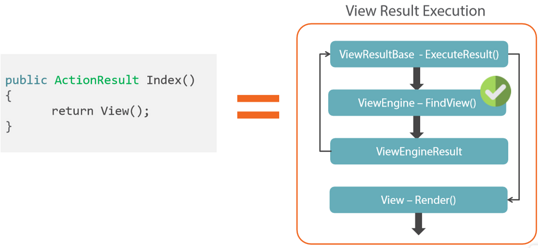
下面让我们来实现一个Theme切换的功能,首先自定义一个ViewEngine: public class ThemeViewEngine: RazorViewEngine { public ThemeViewEngine(string theme) { ViewLocationFormats = new[] { "~/Views/Themes/" + theme + "/{1}/{0}.cshtml", "~/Views/Themes/" + theme + "/Shared/{0}.cshtml" }; PartialViewLocationFormats = new[] { "~/Views/Themes/" + theme + "/{1}/{0}.cshtml", "~/Views/Themes/" + theme + "/Shared/{0}.cshtml" }; AreaViewLocationFormats = new[] { "~Areas/{2}/Views/Themes/" + theme + "/{1}/{0}.cshtml", "~Areas/{2}/Views/Themes/" + theme + "/Shared/{0}.cshtml" }; AreaPartialViewLocationFormats = new[] { "~Areas/{2}/Views/Themes/" + theme + "/{1}/{0}.cshtml", "~Areas/{2}/Views/Themes/" + theme + "/Shared/{0}.cshtml" }; } } 当我们启用这一ViewEngine时,Razor会在/Views/Themes/文件夹下去找View文件。为了启用自定义的ViewEngine,需要将ThemeViewEngine加入到ViewEngines public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication { protected void Application_Start() { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["Theme"])) { var activeTheme = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["Theme"]; ViewEngines.Engines.Insert(0, new ThemeViewEngine(activeTheme)); }; //... } }接下来开始编写不同风格的View了,重点在于编写的View文件夹组织方式要跟ThemeViewEngine中定义的路径要一致,以ServiceController为例,我们编写ocean和sky两种风格的View:

后在web.config制定一种Theme:,ocean文件夹下的View将会被优先采用:

五、Validator 通过在Model属性上加Attribute的验证方式是MVC提倡的数据验证方式,一方面这种方式使用起来比较简单和通用,另一方面这种统一的方式也使得代码很整洁。使用ValidationAttribute需要引入System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations命名空间。 但是有时候现有的ValidationAttribute可能会不能满足我们的业务需求,这需要我们自定义自己的Attribute,例如我们自定义一个AgeValidator: public class AgeValidator: ValidationAttribute { public AgeValidator() { ErrorMessage = "Please enter the age>18"; } public override bool IsValid(object value) { if (value == null) return false; int age; if (int.TryParse(value.ToString(), out age)) { if (age > 18) return true; return false; } return false; } } 自定义的AgeValidator使用起来跟MVC内置的ValiatorAttribute没什么区别: [Required] [AgeValidator] public int? Age { get; set; } 不过我们有时候可能有这种需求:某个验证规则要针对Model中多个属性联合起来判断,所以上面的方案无法满足需求。这时候只需Model实现IValidatableObject接口即可: public class UserViewModel:IValidatableObject { public string Name { get; set; } [Required] [AgeValidator] public int? Age { get; set; } public IEnumerable Validate(ValidationContext validationContext) { if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(Name)) yield return new ValidationResult("the name can not be empty"); if (Name.Equals("lucy")) { if(Age.Value<25) yield return new ValidationResult("lucy's age must greater than 25"); } } } 六、ModelBinder Model的绑定体现在从当前请求提取相应的数据绑定到目标Action方法的参数中。 public ActionResult InputAge(UserViewModel user) { //... return View(); } 对于这样的一个Action,如果是Post请求,MVC会尝试将Form中的值赋值到user参数中,如果是get请求,MVC会尝试将QueryString的值赋值到user参数中。 假如我们跟客户的有一个约定,客户端会POST一个XML格式的数据到服务端,MVC并不能准确认识到这种数据请求,也不能将客户端的请求数据绑定到Action方法的参数中。所以我们可以实现一个XmlModelBinder: public class XmlModelBinder:IModelBinder { public object BindModel(ControllerContext controllerContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext) { try { var modelType = bindingContext.ModelType; var serializer = new XmlSerializer(modelType); var inputStream = controllerContext.HttpContext.Request.InputStream; return serializer.Deserialize(inputStream); } catch { bindingContext.ModelState.AddModelError("", "The item could not be serialized"); return null; } } } 有了这样的自定义ModelBinder,还需要通过在参数上加Attribute的方式启用这一ModelBinder: public ActionResult PostXmlContent([ModelBinder(typeof(XmlModelBinder))]UserViewModel user) { return new XmlResult(user); } 我们使用PostMan发送个请求试试: 刚才我们显示告诉MVC某个Action的参数需要使用XmlModelBinder。我们还可以自定义一个XmlModelBinderProvider,明确告诉MVC什么类型的请求应该使用XmlModelBinder: public class XmlModelBinderProvider: IModelBinderProvider { public IModelBinder GetBinder(Type modelType) { var contentType = HttpContext.Current.Request.ContentType.ToLower(); if (contentType != "text/xml") { return null; } return new XmlModelBinder(); } } 这一Provider明确告知MVC当客户的请求格式为text/xml时,应该使用XmlModelBinder。 public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication { protected void Application_Start() { ModelBinderProviders.BinderProviders.Insert(0, new XmlModelBinderProvider()); //... } 有了XmlModelBinderProvier,我们不再显示标记某个Action中的参数应该使用何种ModelBinder: public ActionResult PostXmlContent(UserViewModel user) { return new XmlResult(user); } 七、自定义ControllerFactory实现依赖注入 MVC默认的DefaultControllerFactory通过反射的方式创建Controller实例,从而调用Action方法。为了实现依赖注入,我们需要自定义ControllerFactory从而通过IOC容器来创建Controller实例。 以Castle为例,需要定义WindsorControllerFactory,另外还要创建ContainerInstaller文件,将组建注册在容器中,后通过ControllerBuilder.Current.SetControllerFactory(new WindsorControllerFactory(container));将MVC的ControllerFactory指定为我们自定义的WindsorControllerFactory。 为了简单起见,这一Nuget包可以帮助我们完成这一系列任务: Install-Package Castle.Windsor.Web.Mvc 上面提到的步骤都会自动完成,新注册一个组件试试: public class ProvidersInstaller:IWindsorInstaller { public void Install(IWindsorContainer container, IConfigurationStore store) { container.Register(Component.For().ImplementedBy().LifestylePerWebRequest()); } } Controller可以进行构造器注入了: private readonly IUserProvider _userProvider; public ServiceController(IUserProvider userProvider) { _userProvider = userProvider; } public ActionResult GetUserByIoc() { var user = _userProvider.GetUser(); return new XmlResult(user); } 八、使用Lambda Expression Tree扩展MVC方法 准确来说这并不是MVC提供的扩展点,是我们利用Lambda Expression Tree写出强类型可重构的代码。以ActionLink一个重载为例: public static MvcHtmlString ActionLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string actionName, object routeValues, object htmlAttributes); 在Razor页面,通过@Html.ActionLink(“Line item 1″, “OrderLineItem”, “Service”, new { id = 1 })可以生成a标签。这一代码的缺点在于Controller和Action都以字符串的方式给出,这样的代码在大型的软件项目中不利于重构,即便Controller和Action字符串编写错误,编译器也能成功编译。 我们可以利用Lambda Expression Tree解析出Controller和Action的名称。理论上所有需要填写Controller和Action字符串的方法都可以通过这一方法来实现。具体实现步骤参考Expression Tree 扩展MVC中的 HtmlHelper 和 UrlHelper。下面给出两种方法的使用对比: <div class="row"> <h2>Mvc way</h2> <ul> <li>@Html.ActionLink("Line item 1", "OrderLineItem", "Service", new { id = 1 }) </li> <li>@Html.ActionLink("Line item 2", "OrderLineItem", "Service", new { id = 2 })</li> <li>@Url.Action("OrderLineItem","Service",new {id=1})</li> <li>@Url.Action("OrderLineItem","Service",new {id=2})</li> </ul> </div> <div class="row"> <h2>Lambda Expression tree</h2> <ul> <li>@Html.ActionLink("Line item 1", (ServiceController c) => c.OrderLineItem(1))</li> <li>@Html.ActionLink("Line item 2", (ServiceController c) => c.OrderLineItem(2))</li> <li>@Url.Action((ServiceController c)=>c.OrderLineItem(1))</li> <li>@Url.Action((ServiceController c)=>c.OrderLineItem(2))</li> </ul> </div>