详解ASP.NET MVC的整个生命周期
一、介绍
二、MVC生命周期详述
View的初始化和渲染呈现
三、结束
一、介绍我们做开发的,尤其是做微软技术栈的,有一个方向是跳不过去的,那就是MVC开发。我相信大家,做ASP.NET MVC 开发有的有很长时间,当然,也有刚进入这个行业的。无论如何,如果有人问你,你知道ASP.NET MVC的生命周期吗?你知道它的来世今生吗?你知道它和 ASP.NET WEBFORM 有什么区别吗?估计,这些问题,有很多人会答不上来,或者说不清楚。今天,我就把我的理解写出来,也是对我自己学习的一次回顾和总结吧。当然,由于本人能力有限,在写的过程中也可能会有一些错误,希望大家多多包涵,当然,更希望大家能不灵赐教,我们共同进步。
在开始之前,我们先来说说,ASP.NET Web Form 和 Asp.net MVC 有什么区别,这里说的区别,当然是本质区别,不是适用语法那个层次的。其实,说起来,ASP.NET WEB FORM 和 ASP.NET MVC 它们两个没有本质区别,使用的都是ASP.NET WEB FORM 的管道处理模型,ASP.NET MVC 也是通过扩展 IHttpModule 和 IHttpHandler 来实现的,都是基于 ASP.NET 的 HttpApplication 的管道处理模型扩展的,在这个层面来说,它们是一样的。当然,大家不要抬杠,我说的本质区别都是在这个方面,不同意的勿喷。
有人会问,ASP.NET MVC 和 ASP.NET WEBAPI 它们会有什么不同吗?好像 WebAPi 能做的,WebMVC都可以完成,第一眼看上去,好像是这样,但是它们有着本质的不同。WebAPI 的处理管道是重新写过的,不是基于 HTTPApplication 管道扩展的。ASP.NET WEB API 类似专人做专事,它的管道处理模型更高效,并且有了 Restfull 的概念。当然,大家如何向了解更细的内容,就需要看源码了。或再说回来,到了 NET CORE 时代,二者又融合管道了。
二、MVC生命周期详述1、我们既然要说 ASP.NET MVC的生命周期,为了给大家一个整体印象,俗话说,文不如图,我就贴一张图,按着箭头走,相信大家也会不能理解。
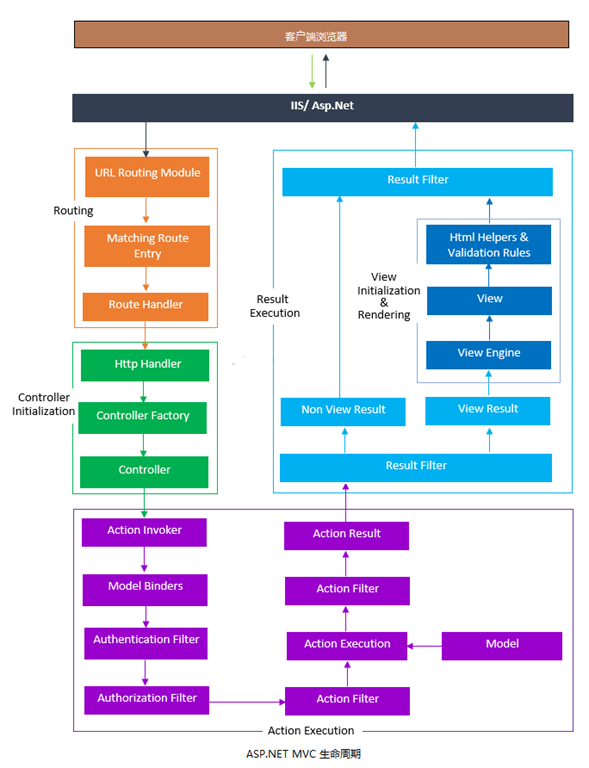
2、上图很简单,大家按着箭头走,也能理解的差不多。以下是按着我的理解,划分了4个模块。
(1)、路由模块
RouteBase 是对路由规则的抽象,也就是说,一个 RouteBase 对象,也就代表了一个条 路由规则。在 ASP.NET MVC 中,有一个唯一的子类实现就是 Route ,它同样也是路由规则的代表。我们有了路由规则,一定会把这个规则存放在一个地方,这个地方保存了很多路由规则,这个地方就是 RouteCollection,中文叫“路由集合”,因为这个集合里面包含的就是 RouteBase 对象。
RouteCollection 就是路由集合,用于保存路由规则对象,它的定义形式:
[TypeForwardedFrom("System.Web.Routing, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=Neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35")]
public class RouteCollection : Collection<RouteBase>
{
private class ReadLockDisposable : IDisposable
{
private ReaderWriterLockSlim _rwLock;
public ReadLockDisposable(ReaderWriterLockSlim rwLock)
{
this._rwLock = rwLock;
}
void IDisposable.Dispose()
{
this._rwLock.ExitReadLock();
}
}
......
RouteTable 就是路由表,其实它和 RouteCollection 是一样的。
public class RouteTable
{
private static RouteCollection _instance = new RouteCollection();
public static RouteCollection Routes
{
get
{
return RouteTable._instance;
}
}
}
在ASP.NET MVC处理管线中的第一站就是路由模块。当请求到达路由模块后,ASP.NET MVC 框架就会根据 RouteTable 中配置的路由模板来匹配当前请求以获得对应的 Controller 和 Action 信息。具体的匹配过程就是有UrlRoutingModule(System.Web.Routing.UrlRoutingModule)来实现的。如果遇到一个匹配的规则,就会立刻跳出下面的配置。也就是说,配置过程是有顺序的,如果有一个匹配,后面就算有匹配的也不会执行的。
namespace System.Web.Routing
{
[TypeForwardedFrom("System.Web.Routing, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=Neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35")]
public class UrlRoutingModule : IHttpModule
{
private static readonly object _contextKey = new object();
private static readonly object _requestDataKey = new object();
private RouteCollection _routeCollection;
public RouteCollection RouteCollection
{
get
{
if (this._routeCollection == null)
{
this._routeCollection = RouteTable.Routes;
}
return this._routeCollection;
}
set
{
this._routeCollection = value;
}
}
protected virtual void Dispose()
{
}
protected virtual void Init(HttpApplication application)
{
if (application.Context.Items[UrlRoutingModule._contextKey] != null)
{
return;
}
application.Context.Items[UrlRoutingModule._contextKey] = UrlRoutingModule._contextKey;
application.PostResolveRequestCache += new EventHandler(this.OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache);
}
private void OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication httpApplication = (HttpApplication)sender;
HttpContextBase context = new HttpContextWrapper(httpApplication.Context);
this.PostResolveRequestCache(context);
}
[Obsolete("This method is obsolete. Override the Init method to use the PostMapRequestHandler event.")]
public virtual void PostMapRequestHandler(HttpContextBase context)
{
}
public virtual void PostResolveRequestCache(HttpContextBase context)
{
RouteData routeData = this.RouteCollection.GetRouteData(context); 第一步匹配路由规则
if (routeData == null)
{
return;
}
IRouteHandler routeHandler = routeData.RouteHandler; 第二步:如有匹配,就找到RouteHandler对象,该类型的实例是:MvcRouteHandler。
if (routeHandler == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, SR.GetString("UrlRoutingModule_NoRouteHandler"), new object[0]));
}
if (routeHandler is StopRoutingHandler)
{
return;
}
RequestContext requestContext = new RequestContext(context, routeData);
context.Request.RequestContext = requestContext;
IHttpHandler httpHandler = routeHandler.GetHttpHandler(requestContext);第三步,根据 RouteHandler 对象,找到最终处理请求的 IHttpHandler 的对象,该类型是 MvcHandler
if (httpHandler == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("UrlRoutingModule_NoHttpHandler"), new object[]
{
routeHandler.GetType()
}));
}
if (!(httpHandler is UrlAuthFailureHandler))
{
context.RemapHandler(httpHandler);第四步,有找到的 IHttpHandler 处理请求。
return;
}
if (FormsAuthenticationModule.FormsAuthRequired)
{
UrlAuthorizationModule.ReportUrlAuthorizationFailure(HttpContext.Current, this);
return;
}
throw new HttpException(401, SR.GetString("Assess_Denied_Description3"));
}
void IHttpModule.Dispose()
{
this.Dispose();
}
void IHttpModule.Init(HttpApplication application)
{
this.Init(application);
}
}
}
(2)、Controller 创建模块
经过了路由模块,生成了 RouteData 路由数据,它包含了根据路由规则匹配的 Controller 和 Action。有了路由数据,需要有处理器来处理请求,这个任务就交给了 RouteData 的 RouteHandler 属性,它的类型是 IRouteHandler,它的值就是MvcRouteHandler,MvcRouteHandler 调用 GetHttpHandler 获取处理请求的 IHttpHandler 对象,在 MVC 框架中就是 MvcHandler,详细代码如下:
namespace System.Web.Mvc
{
/// <summary>Selects the controller that will handle an HTTP request.</summary>
public class MvcHandler : IHttpAsyncHandler, IHttpHandler, IRequiresSessionState
{
private struct ProcessRequestState
{
internal IAsyncController AsyncController;
internal IControllerFactory Factory;
internal RequestContext RequestContext;
internal void ReleaseController()
{
this.Factory.ReleaseController(this.AsyncController);
}
}
[CompilerGenerated]
[Serializable]
private sealed class <>c
{
public static readonly MvcHandler.<>c <>9 = new MvcHandler.<>c();
public static BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> <>9__20_0;
public static EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> <>9__20_1;
public static Func<KeyValuePair<string, object>, bool> <>9__26_0;
internal IAsyncResult <BeginProcessRequest>b__20_0(AsyncCallback asyncCallback, object asyncState, MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState innerState)
{
IAsyncResult result;
try
{
result = innerState.AsyncController.BeginExecute(innerState.RequestContext, asyncCallback, asyncState);
}
catch
{
innerState.ReleaseController();
throw;
}
return result;
}
internal void <BeginProcessRequest>b__20_1(IAsyncResult asyncResult, MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState innerState)
{
try
{
innerState.AsyncController.EndExecute(asyncResult);
}
finally
{
innerState.ReleaseController();
}
}
internal bool <RemoveOptionalRoutingParameters>b__26_0(KeyValuePair<string, object> entry)
{
return entry.Value == UrlParameter.Optional;
}
}
private static readonly object _processRequestTag = new object();
internal static readonly string MvcVersion = MvcHandler.GetMvcVersionString();
/// <summary>Contains the header name of the ASP.NET MVC version.</summary>
public static readonly string MvcVersionHeaderName = "X-AspNetMvc-Version";
private ControllerBuilder _controllerBuilder;
internal ControllerBuilder ControllerBuilder
{
get
{
if (this._controllerBuilder == null)
{
this._controllerBuilder = ControllerBuilder.Current;
}
return this._controllerBuilder;
}
set
{
this._controllerBuilder = value;
}
}
/// <summary>Gets or sets a value that indicates whether the MVC response header is disabled.</summary>
/// <returns>true if the MVC response header is disabled; otherwise, false.</returns>
public static bool DisableMvcResponseHeader
{
get;
set;
}
/// <summary>Gets a value that indicates whether another request can use the <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpHandler" /> instance.</summary>
/// <returns>true if the <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpHandler" /> instance is reusable; otherwise, false.</returns>
protected virtual bool IsReusable
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>Gets the request context.</summary>
/// <returns>The request context.</returns>
public RequestContext RequestContext
{
get;
private set;
}
/// <summary>Gets a value that indicates whether another request can use the <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpHandler" /> instance.</summary>
/// <returns>true if the <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpHandler" /> instance is reusable; otherwise, false.</returns>
bool IHttpHandler.IsReusable
{
get
{
return this.IsReusable;
}
}
/// <summary>Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="T:System.Web.Mvc.MvcHandler" /> class.</summary>
/// <param name="requestContext">The request context.</param>
/// <exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException">The <paramref name="requestContext" /> parameter is null.</exception>
public MvcHandler(RequestContext requestContext)
{
if (requestContext == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("requestContext");
}
this.RequestContext = requestContext;
}
/// <summary>Adds the version header by using the specified HTTP context.</summary>
/// <param name="httpContext">The HTTP context.</param>
protected internal virtual void AddVersionHeader(HttpContextBase httpContext)
{
if (!MvcHandler.DisableMvcResponseHeader)
{
httpContext.Response.AppendHeader(MvcHandler.MvcVersionHeaderName, MvcHandler.MvcVersion);
}
}
/// <summary>Called by ASP.NET to begin asynchronous request processing.</summary>
/// <returns>The status of the asynchronous call.</returns>
/// <param name="httpContext">The HTTP context.</param>
/// <param name="callback">The asynchronous callback method.</param>
/// <param name="state">The state of the asynchronous object.</param>
protected virtual IAsyncResult BeginProcessRequest(HttpContext httpContext, AsyncCallback callback, object state)
{
HttpContextBase httpContext2 = new HttpContextWrapper(httpContext);
return this.BeginProcessRequest(httpContext2, callback, state);
}
/// <summary>Called by ASP.NET to begin asynchronous request processing using the base HTTP context.</summary>
/// <returns>The status of the asynchronous call.</returns>
/// <param name="httpContext">The HTTP context.</param>
/// <param name="callback">The asynchronous callback method.</param>
/// <param name="state">The state of the asynchronous object.</param>
protected internal virtual IAsyncResult BeginProcessRequest(HttpContextBase httpContext, AsyncCallback callback, object state)
{
IController controller;
IControllerFactory factory;
this.ProcessRequestInit(httpContext, out controller, out factory);
IAsyncController asyncController = controller as IAsyncController;
if (asyncController != null)
{
BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> arg_51_0;
if ((arg_51_0 = MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_0) == null)
{
arg_51_0 = (MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_0 = new BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(MvcHandler.<>c.<>9.<BeginProcessRequest>b__20_0));
}
BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> beginDelegate = arg_51_0;
EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> arg_71_0;
if ((arg_71_0 = MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_1) == null)
{
arg_71_0 = (MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_1 = new EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(MvcHandler.<>c.<>9.<BeginProcessRequest>b__20_1));
}
EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> endDelegate = arg_71_0;
MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState invokeState = new MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState
{
AsyncController = asyncController,
Factory = factory,
RequestContext = this.RequestContext
};
SynchronizationContext synchronizationContext = SynchronizationContextUtil.GetSynchronizationContext();
return AsyncResultWrapper.Begin<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(callback, state, beginDelegate, endDelegate, invokeState, MvcHandler._processRequestTag, -1, synchronizationContext);
}
Action action = delegate
{
try
{
controller.Execute(this.RequestContext);
}
finally
{
factory.ReleaseController(controller);
}
};
return AsyncResultWrapper.BeginSynchronous(callback, state, action, MvcHandler._processRequestTag);
}
/// <summary>Called by ASP.NET when asynchronous request processing has ended.</summary>
/// <param name="asyncResult">The asynchronous result.</param>
protected internal virtual void EndProcessRequest(IAsyncResult asyncResult)
{
AsyncResultWrapper.End(asyncResult, MvcHandler._processRequestTag);
}
private static string GetMvcVersionString()
{
return new AssemblyName(typeof(MvcHandler).Assembly.FullName).Version.ToString(2);
}
/// <summary>Processes the request by using the specified HTTP request context.</summary>
/// <param name="httpContext">The HTTP context.</param>
protected virtual void ProcessRequest(HttpContext httpContext)
{
HttpContextBase httpContext2 = new HttpContextWrapper(httpContext);
this.ProcessRequest(httpContext2);
}
/// <summary>Processes the request by using the specified base HTTP request context.</summary>
/// <param name="httpContext">The HTTP context.</param>
protected internal virtual void ProcessRequest(HttpContextBase httpContext)
{
IController controller;
IControllerFactory controllerFactory;
this.ProcessRequestInit(httpContext, out controller, out controllerFactory);
try
{
controller.Execute(this.RequestContext);
}
finally
{
controllerFactory.ReleaseController(controller);
}
}
private void ProcessRequestInit(HttpContextBase httpContext, out IController controller, out IControllerFactory factory)
{
HttpContext current = HttpContext.Current;
if (current != null)
{
bool? flag = ValidationUtility.IsValidationEnabled(current);
bool flag2 = true;
if (flag.GetValueOrDefault() == flag2 & flag.HasValue)
{
ValidationUtility.EnableDynamicValidation(current);
}
}
this.AddVersionHeader(httpContext);
this.RemoveOptionalRoutingParameters();
string requiredString = this.RequestContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("controller");
factory = this.ControllerBuilder.GetControllerFactory();
controller = factory.CreateController(this.RequestContext, requiredString);
if (controller == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, MvcResources.ControllerBuilder_FactoryReturnedNull, new object[]
{
factory.GetType(),
requiredString
}));
}
}
private void RemoveOptionalRoutingParameters()
{
IDictionary<string, object> arg_2F_0 = this.RequestContext.RouteData.Values;
Func<KeyValuePair<string, object>, bool> arg_2F_1;
if ((arg_2F_1 = MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__26_0) == null)
{
arg_2F_1 = (MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__26_0 = new Func<KeyValuePair<string, object>, bool>(MvcHandler.<>c.<>9.<RemoveOptionalRoutingParameters>b__26_0));
}
arg_2F_0.RemoveFromDictionary(arg_2F_1);
}
/// <summary>Enables processing of HTTP Web requests by a custom HTTP handler that implements the <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpHandler" /> interface.</summary>
/// <param name="httpContext">An <see cref="T:System.Web.HttpContext" /> object that provides references to the intrinsic server objects (for example, Request, Response, Session, and Server) that are used to service HTTP requests.</param>
void IHttpHandler.ProcessRequest(HttpContext httpContext)
{
this.ProcessRequest(httpContext);
}
/// <summary>Called by ASP.NET to begin asynchronous request processing using the base HTTP context.</summary>
/// <returns>The status of the asynchronous call.</returns>
/// <param name="context">The HTTP context.</param>
/// <param name="cb">The asynchronous callback method.</param>
/// <param name="extraData">The data.</param>
IAsyncResult IHttpAsyncHandler.BeginProcessRequest(HttpContext context, AsyncCallback cb, object extraData)
{
return this.BeginProcessRequest(context, cb, extraData);
}
/// <summary>Called by ASP.NET when asynchronous request processing has ended.</summary>
/// <param name="result">The asynchronous result.</param>
void IHttpAsyncHandler.EndProcessRequest(IAsyncResult result)
{
this.EndProcessRequest(result);
}
}
}
HttpRuntime 调用 IHttpHandler 类型的调用 ProcessRequest() 方法,用于处理请求。
protected internal virtual void ProcessRequest(HttpContextBase httpContext)
{
IController controller;
IControllerFactory controllerFactory;
this.ProcessRequestInit(httpContext, out controller, out controllerFactory);创建 IControllerFactory,并创建 IController 对象。
try
{
controller.Execute(this.RequestContext);执行Controller,背后就是调用相应的 Action 方法。
}
finally
{
controllerFactory.ReleaseController(controller);
}
}
核心处理请求的方法是ProcessRequestInit(),用于创建 IController 和 IControllerFactory 实例。IControllerFactory 的实际类型是:DefaultControllerFactory,该类型用于创建 IController 类型的实例。
private void ProcessRequestInit(HttpContextBase httpContext, out IController controller, out IControllerFactory factory)
{
HttpContext current = HttpContext.Current;
if (current != null)
{
bool? flag = ValidationUtility.IsValidationEnabled(current);
bool flag2 = true;
if (flag.GetValueOrDefault() == flag2 & flag.HasValue)
{
ValidationUtility.EnableDynamicValidation(current);
}
}
this.AddVersionHeader(httpContext);
this.RemoveOptionalRoutingParameters();
string requiredString = this.RequestContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("controller");
factory = this.ControllerBuilder.GetControllerFactory();
controller = factory.CreateController(this.RequestContext, requiredString);
if (controller == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, MvcResources.ControllerBuilder_FactoryReturnedNull, new object[]
{
factory.GetType(),
requiredString
}));
}
}
以上加红的代码就是创建 IController 的实例的逻辑。IController 实例创建完成后,判断是否实现了 IAsyncController 接口,如果是,就异步执行 Controller 方法的调用,否则就同步执行。
protected internal virtual IAsyncResult BeginProcessRequest(HttpContextBase httpContext, AsyncCallback callback, object state)
{
IController controller;
IControllerFactory factory;
this.ProcessRequestInit(httpContext, out controller, out factory);
IAsyncController asyncController = controller as IAsyncController; 判读是否是需要异步执行
if (asyncController != null)异步执行
{
BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> arg_51_0;
if ((arg_51_0 = MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_0) == null)
{
arg_51_0 = (MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_0 = new BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(MvcHandler.<>c.<>9.<BeginProcessRequest>b__20_0));
}
BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> beginDelegate = arg_51_0;
EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> arg_71_0;
if ((arg_71_0 = MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_1) == null)
{
arg_71_0 = (MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_1 = new EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(MvcHandler.<>c.<>9.<BeginProcessRequest>b__20_1));
}
EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> endDelegate = arg_71_0;
MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState invokeState = new MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState
{
AsyncController = asyncController,
Factory = factory,
RequestContext = this.RequestContext
};
SynchronizationContext synchronizationContext = SynchronizationContextUtil.GetSynchronizationContext();
return AsyncResultWrapper.Begin<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(callback, state, beginDelegate, endDelegate, invokeState, MvcHandler._processRequestTag, -1, synchronizationContext);
}
Action action = delegate//同步执行。
{
try
{
controller.Execute(this.RequestContext);
}
finally
{
factory.ReleaseController(controller);
}
};
return AsyncResultWrapper.BeginSynchronous(callback, state, action, MvcHandler._processRequestTag);
}
(3)、Action 执行模块,通过 ControllerActionInvoker 调用 InvokeAction() 执行其方法。Action 方法的执行也有2个版本,一个是异步版本,一个是同步版本。由于 ActionInvoker 实现了 IAsyncActionInvoker 接口,所以也是以已方式执行。该类型是 AsyncControllerActionInvoker。
A、当Controller对象被创建之后,紧接着就会执行Controler 对象的 Execute(),其实背后就是调用 InvokeAction() 方法:
public virtual bool InvokeAction(ControllerContext controllerContext, string actionName)
{
if (controllerContext == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("controllerContext");
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(actionName) && !controllerContext.RouteData.HasDirectRouteMatch())
{
throw new ArgumentException(MvcResources.Common_NullOrEmpty, "actionName");
}
ControllerDescriptor controllerDescriptor = this.GetControllerDescriptor(controllerContext);
ActionDescriptor actionDescriptor = this.FindAction(controllerContext, controllerDescriptor, actionName);
if (actionDescriptor != null)
{
FilterInfo filters = this.GetFilters(controllerContext, actionDescriptor); 获取所有过滤器,全局的、控制器的和方法的
try
{
AuthenticationContext authenticationContext = this.InvokeAuthenticationFilters(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor);认证过滤器的执行。
if (authenticationContext.Result != null)
{
AuthenticationChallengeContext authenticationChallengeContext = this.InvokeAuthenticationFiltersChallenge(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor, authenticationContext.Result);
this.InvokeActionResult(controllerContext, authenticationChallengeContext.Result ?? authenticationContext.Result);
}
else
{
AuthorizationContext authorizationContext = this.InvokeAuthorizationFilters(controllerContext, filters.AuthorizationFilters, actionDescriptor);授权过滤器的执行。
if (authorizationContext.Result != null)
{
AuthenticationChallengeContext authenticationChallengeContext2 = this.InvokeAuthenticationFiltersChallenge(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor, authorizationContext.Result);
this.InvokeActionResult(controllerContext, authenticationChallengeContext2.Result ?? authorizationContext.Result);
}
else
{
if (controllerContext.Controller.ValidateRequest)
{
ControllerActionInvoker.ValidateRequest(controllerContext);
}
IDictionary<string, object> parameterValues = this.GetParameterValues(controllerContext, actionDescriptor); 获取方法执行参数。
ActionExecutedContext actionExecutedContext = this.InvokeActionMethodWithFilters(controllerContext, filters.ActionFilters, actionDescriptor, parameterValues); 执行action,同时执行执行方法前后的 IAcctionFilter
AuthenticationChallengeContext authenticationChallengeContext3 = this.InvokeAuthenticationFiltersChallenge(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor, actionExecutedContext.Result);
this.InvokeActionResultWithFilters(controllerContext, filters.ResultFilters, authenticationChallengeContext3.Result ?? actionExecutedContext.Result); 执行 ActionResult,同时执行方法前后的 IResultFilter
}
}
}
catch (ThreadAbortException)
{
throw;
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
ExceptionContext exceptionContext = this.InvokeExceptionFilters(controllerContext, filters.ExceptionFilters, exception);
if (!exceptionContext.ExceptionHandled)
{
throw;
}
this.InvokeActionResult(controllerContext, exceptionContext.Result);//异常过滤器的执行。
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
B、当选择完合适的Action后,接着就是 ModelBinder(默认是System.Web.Mvc.DefaultModelBinder),它会从http请求的参数中提取数据并实现类型转换,数据校验(例如是否必填,数据格式等)以及是否自动装配到action方法的参数中System.Web.Mvc.DefaultModelBinder
protected virtual IDictionary<string, object> GetParameterValues(ControllerContext controllerContext, ActionDescriptor actionDescriptor)
{
Dictionary<string, object> dictionary = new Dictionary<string, object>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
ParameterDescriptor[] parameters = actionDescriptor.GetParameters();
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.Length; i++)
{
ParameterDescriptor parameterDescriptor = parameters[i];
dictionary[parameterDescriptor.ParameterName] = this.GetParameterValue(controllerContext, parameterDescriptor);
}
return dictionary;
}
protected virtual object GetParameterValue(ControllerContext controllerContext, ParameterDescriptor parameterDescriptor)
{
Type parameterType = parameterDescriptor.ParameterType;
IModelBinder arg_92_0 = this.GetModelBinder(parameterDescriptor);
IValueProvider valueProvider = controllerContext.Controller.ValueProvider;
string modelName = parameterDescriptor.BindingInfo.Prefix ?? parameterDescriptor.ParameterName;
Predicate<string> propertyFilter = ControllerActionInvoker.GetPropertyFilter(parameterDescriptor);
ModelBindingContext bindingContext = new ModelBindingContext
{
FallbackToEmptyPrefix = parameterDescriptor.BindingInfo.Prefix == null,
ModelMetadata = ModelMetadataProviders.Current.GetMetadataForType(null, parameterType),
ModelName = modelName,
ModelState = controllerContext.Controller.ViewData.ModelState,
PropertyFilter = propertyFilter,
ValueProvider = valueProvider
};
return arg_92_0.BindModel(controllerContext, bindingContext) ?? parameterDescriptor.DefaultValue;
}
C、Authentication Filter是mvc5中新增的一个Filter,它会先于authorization filter执行,目的是对访问用户的认证。在MVC5之前,认证和授权都是通过authorization filter来实现的,但现在这2个操作就分开来了,各自管各自喽。
AuthenticationContext authenticationContext = this.InvokeAuthenticationFilters(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor);
if (authenticationContext.Result != null)
{
AuthenticationChallengeContext authenticationChallengeContext = this.InvokeAuthenticationFiltersChallenge(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor, authenticationContext.Result);
this.InvokeActionResult(controllerContext, authenticationChallengeContext.Result ?? authenticationContext.Result);
}
D、Action filters有2个方法OnActionExecuting和OnActionExecuted分别在action执行前后执行。我们也可以通过实现IActionFilter接口来实现你个性化的过滤机制
protected virtual ActionExecutedContext InvokeActionMethodWithFilters(ControllerContext controllerContext, IList<IActionFilter> filters, ActionDescriptor actionDescriptor, IDictionary<string, object> parameters)
{
ActionExecutingContext preContext = new ActionExecutingContext(controllerContext, actionDescriptor, parameters);
Func<ActionExecutedContext> seed = () => new ActionExecutedContext(controllerContext, actionDescriptor, false, null)
{
Result = this.InvokeActionMethod(controllerContext, actionDescriptor, parameters)
};
return filters.Reverse<IActionFilter>().Aggregate(seed, (Func<ActionExecutedContext> next, IActionFilter filter) => () => ControllerActionInvoker.InvokeActionMethodFilter(filter, preContext, next))();
}
E、接下来就是执行我们平时在Action方法中写的代码了(根据请求相应结果)
protected virtual ActionResult InvokeActionMethod(ControllerContext controllerContext, ActionDescriptor actionDescriptor, IDictionary<string, object> parameters)
{
object actionReturnValue = actionDescriptor.Execute(controllerContext, parameters);
return this.CreateActionResult(controllerContext, actionDescriptor, actionReturnValue);
}
(4)、ActionResult 执行模块。
A、在 ActionResult 执行前后,仍然会有一个filter(IResultFilter),同样的,通过实现 IResultFilter 接口你可以定制自己的过滤逻辑。
namespace System.Web.Mvc
{
/// <summary>Defines the methods that are required for a result filter.</summary>
public interface IResultFilter
{
/// <summary>Called before an action result executes.</summary>
/// <param name="filterContext">The filter context.</param>
void OnResultExecuting(ResultExecutingContext filterContext);
/// <summary>Called after an action result executes.</summary>
/// <param name="filterContext">The filter context.</param>
void OnResultExecuted(ResultExecutedContext filterContext);
}
}
B、ActionResult 就是把处理的用户请求结果返回。因此 ViewResult, PartialViewResult, RedirectToRouteResult, RedirectResult, ContentResult, JsonResult, FileResult and EmptyResult就是具体的返回类型。
C、上面的返回类型可以大致分为2类:ViewResult 和非ViewResult。对于需要生成html页面给客户端的划到ViewResult,而其他的例如返回文本,json数据等则划分到非ViewResult,对于非ViewResult直接返回就可以了。
A、对于 ViewResult 最终是由合适的 View Engine 通过调用 IView 的 Render() 方法来渲染的:
namespace System.Web.Mvc
{
/// <summary>Defines the methods that are required for a view engine.</summary>
public interface IViewEngine
{
/// <summary>Finds the specified partial view by using the specified controller context.</summary>
/// <returns>The partial view.</returns>
/// <param name="controllerContext">The controller context.</param>
/// <param name="partialViewName">The name of the partial view.</param>
/// <param name="useCache">true to specify that the view engine returns the cached view, if a cached view exists; otherwise, false.</param>
ViewEngineResult FindPartialView(ControllerContext controllerContext, string partialViewName, bool useCache);
/// <summary>Finds the specified view by using the specified controller context.</summary>
/// <returns>The page view.</returns>
/// <param name="controllerContext">The controller context.</param>
/// <param name="viewName">The name of the view.</param>
/// <param name="masterName">The name of the master.</param>
/// <param name="useCache">true to specify that the view engine returns the cached view, if a cached view exists; otherwise, false.</param>
ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext controllerContext, string viewName, string masterName, bool useCache);
/// <summary>Releases the specified view by using the specified controller context.</summary>
/// <param name="controllerContext">The controller context.</param>
/// <param name="view">The view.</param>
void ReleaseView(ControllerContext controllerContext, IView view);
}
}
namespace System.Web.Mvc
{
/// <summary>Defines the methods that are required for a view.</summary>
public interface IView
{
/// <summary>Renders the specified view context by using the specified the writer object.</summary>
/// <param name="viewContext">The view context.</param>
/// <param name="writer">The writer object.</param>
void Render(ViewContext viewContext, TextWriter writer);
}
}
B、整个处理过程是由 IViewEngine 来实现的。ASP.NET MVC 默认提供 WebForm(.aspx)和 Razor(.cshtml) 模板引擎,你可以通过实现 IViewEngine 接口来实现自己的 ViewEngine,然后在Application_Start方法中做如下注册:
protected void Application_Start()
{
//移除所有的View引擎包括Webform和Razor
ViewEngines.Engines.Clear();
//注册你自己的View引擎
ViewEngines.Engines.Add(new CustomViewEngine());
}
C、最后,Html Helpers将帮我们生成 input 标签,基于AJAX的 form 等等。
(5)、作为总结,将每个节点主要的代码类贴出来。
这就是整个流程的代码节点,有些是同步执行,有些是异步执行,把握关键点,我这里只是谢了一个大概。
三、结束UrlRoutingModule-----RouteCollection.GetRouteData(context)----->IRouteHandler routeHandler = routeData.RouteHandler------》IHttpHandler httpHandler = routeHandler.GetHttpHandler(requestContext)-----》context.RemapHandler(httpHandler)------->MvcHandler------->ProcessRequest()------>ProcessRequestInit()--------》IController------>controller.Execute(this.RequestContext)-------->ControllerActionInvoker------->InvoleAction()--------->InvoleActionMethod()------->InvoleActionReslt()
今天就到这里了,东西虽然不多,但是也写了2个多小时。今天就算自己有学习了一边,大家一定要好好的把握这个流程,对于解决程序中的问题,扩展框架都有很大的好处。我们作为程序员的,应该要知道其一,也要知道其二。没事,看看源码,我们对框架和我们自己的代码有更深的了解。当然,这样做也是有代价的,需要更多的时间去支持,我相信我们的付出是值得。不忘初心,继续努力。老天不会辜负努力的人。
到此这篇关于详解ASP.NET MVC的整个生命周期的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关ASP.NET MVC 生命周期内容请搜索软件开发网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持软件开发网!